 |
 |
- Search
| Neurospine > Volume 18(1); 2021 > Article |
|
|
See commentary "Commentary on ŌĆ£Hemodynamic Management of Acute Spinal Cord InjuryŌĆØ" in Volume 18 on page 15.
Abstract
The goal of acute spinal cord injury (SCI) management is to reduce secondary injuries and improve neurological recovery after its occurrence. This review aimed to explore the literature regarding hemodynamic management to reduce ischemic secondary injury and improve neurologic outcome following acute SCI. The PubMed database was searched for studies investigating blood flow, mean arterial pressure (MAP), and spinal cord perfusion pressure after SCI. The 2013 guidelines of the American Association of Neurological Surgeons/Congress of Neurological Surgeons recommended maintaining MAP at 85ŌĆō90 mmHg for 7 days after SCI to potentially improve outcome. However, this recommendation was based on weak evidence for neurologic benefit. The maintenance of MAP will typically require vasopressors, which may have their own set of complications. More recently, studies have suggested the potential importance of considering spinal cord perfusion pressure in addition to the MAP. Further research on the hemodynamic management of acute SCI is required to determine how to optimize neurologic recovery. Evidence-based guidelines for hemodynamic management should acknowledge the gaps in knowledge and the limitations of the current literature.
Spinal cord injury (SCI) causes profound deficits of motor, sensory, and autonomic functions in patients. Two mechanisms are involved in SCI: primary and secondary injury. Secondary injuries are mainly caused by insults occurring at the organism level and exacerbate the SCI, such as hypoxia and hypotension. Preventing or aggressively treating secondary injury is currently the mainstay of care for acute SCI [1,2]. In general, hypotension and hypoxia interfere with neurologic recovery after SCI, resulting in poor outcomes. The American Association of Neurological Surgeons/Congress of Neurological Surgeons (AANS/ CNS) 2013 SCI guideline recommends raising the mean arterial pressure (MAP) between 85 and 90 mmHg for the first 7 days following an acute SCI [3]. This guideline is classified as class III (case series and expert opinion). However, the exact target for optimal MAP is not well established (and may differ between patients). Recently, interest has been raised in maintaining spinal cord perfusion pressure (SCPP) and spinal cord oxygenation, in contrast to or in addition to MAP. This review was carried out to explore the literature regarding post SCI hemodynamic management to describe the current state of the art.
This study was conducted according to the method of Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. We searched PubMed database using MeSH (medical subject headings) terms in various combinations, supplemented with free text. We limited our results to human and animal studies and removed duplications.
After SCI, hemodynamic management can be performed immediately, but optimizing hemodynamic management is still unclear. After SCI, hemodynamic management maintains proper spinal cord perfusion to prevent secondary SCI such as ischemia. Spinal cord perfusion has the same concept as cerebral perfusion [4]. That is, the autoregulation of the cerebral perfusion pressure (MAP-intracranial pressure) is applied to the autoregulation of the spinal perfusion pressure (MAP-spinal pressure). Therefore, the spinal constant blood flow must be kept constant after SCI. However, if the spinal perfusion pressure is reduced to 50 mmHg and increased to 150 mmHg, the blood flow to the spine is not constantly maintained. That is, to keep the spinal perfusion pressure constant, it is important to control the MAP and spinal pressure. We reviewed several papers investigating this issue.
Current clinical practice guidelines recommend maintaining MAP levels between 85 and 90 mmHg for the first 5ŌĆō7 days following an acute cervical SCI and the general avoidance of systemic hypotension, defined as a systolic blood pressure of < 90 mmHg [3].
Various studies have shown that maintaining high MAP levels in an attempt to improve blood flow into an injured spinal cord following an SCI is effective in improving neurological recovery (Table 1). Levi et al. [5] treated 50 cervical SCI patients with fluids and dopamine and/or dobutamine with invasive hemodynamic monitoring to maintain > 90 mmHg and adequate cardiac output. At admission, 31 patients were American Spinal Injury Association grade A, 8 patients were grade B, and 11 patients were grade C/D. Moreover, 82% of the patients used vasopressor. The clinical outcome showed functional improvement in 40% of the patients, no change in 42%, and 18% of the patients died. However, mortality associated with invasive hemodynamic monitoring was minimal. They found that early and prompt hemodynamic management helped reduce potential morbidity and mortality in SCI patients. Vale et al. [6] report early on the importance of MAP in SCI. A total of 77 patients were required to maintain MAP levels above 85 mmHg using intravenous fluids, colloids, and vasopressors. As a result, 33%ŌĆō60% and 88%ŌĆō92% of complete and incomplete cord injury patients, respectively, recovered their neurologic outcome.
Several authors have reported that maintaining MAP levels > 85 mmHg after SCI positively affects the neurological outcome. Hawryluk et al. [7] performed a retrospective analysis of 74 patients with acute SCI between 2005 and 2011 and measured MAP at 1-minute interval. They established a 7-day guideline-maintained MAP value of 85ŌĆō90 mmHg following acute SCI. Vasopressors used dopamine, phenylephrine, and levophed. The American Spinal Injury Association impairment scale (AIS) grades were determined by physical examination on admission and hospital discharge time. The higher average MAP values in the first 2ŌĆō3 days after SCI in this study were strongly associated with neurologic recovery; however, the intensity decreased 5ŌĆō7 days after SCI. The authors argued that a strong correlation exists between MAP values and neurological recovery.
Catapano et al. [8] studied the relationship between MAP level augmentation and neurologic improvement when MAP was maintained above 85 mmHg for 7 days after SCI. A total of 62 patients qualified for neurologic improvement according to their AIS score. Moreover, a total of 33.3%, 76.5%, and 58.3% of patients with AIS A complete cord injury, AIS B/C, and AIS D, respectively, showed improvement of AIS. The correlation between MAP and AIS improvement was positive in patients with AIS A and B/C, but not in patients with AIS D. In this regard, the AIS A patient may acquire greater benefit from MAP augmentation than the AIS D patient. It was confirmed that higher MAP levels were positively correlated with neurologic improvement.
Dakson et al. [9] studied MAP levels in 94 patients with traumatic SCI who were admitted to the intensive care unit for 5 days following SCI. Patients were divided into groups according to their MAP levels: < 85 mmHg (41 patients) and Ōēź 85 mmHg (9 patients) based on the reduction of more than 85 mmHg over 2 hours. Neurologic recovery was measured at 26.7, 115.0, and 252.0 days using the AIS grade. Neurologic improvement was 11 times better in patients with MAP > 85 mmHg than in patients with MAP < 85 mmHg (p = 0.006). This study demonstrated a positive correlation between MAP levels and neurologic recovery improvement.
While these studies demonstrate neurologic benefit to MAP augmentation, it should be realized that there are methodological limitations to concluding a strong relationship between the MAP goals and neurologic recovery. Previously, Saadeh et al. [10] and Sabit et al. [11] conducted a systematic review of blood pressure management after SCI. However, when analyzing previous data, the correlation with the clinical neurologic recovery and hemodynamic management of mean blood pressure is weak. In addition, there is limited high-quality evidence to guide management with MAP > 85ŌĆō90 mmHg.
Many authors have reported the importance of maintaining high MAP levels after SCI. However, maintaining MAP levels above 85 mmHg requires much effort, and when closely examined, it may not be easy to maintain the exact MAP targets. Kong et al. [12] investigated the MAP, intrathecal cerebrospinal fluid pressure (ITP), and SCPP in 21 cervical or thoracic SCI patients. The target MAP level was > 80 mmHg for up to 5 days following SCI. However, all patients had episodes characterized by MAP levels < 80 mmHg, while 81% of MAP levels were < 70 mmHg. In cervical injury, 18.4% of MAP levels were below 80 mmHg and 19.2% of SCPPs were below 60 mmHg, whereas thoracic injury cases presented 35.9% and 28.1% of MAPs were below 80 mmHg and 60 mmHg in thoracic injury, respectively.
In addition, other studies have reported the need for education and effort to maintain MAP during both the prehospital and hospital periods. Tee et al. [13] investigated MAP in patients with acute traumatic SCI during the prehospital and early admission period after injury. A total of 40 acute SCI patients were studied, with their MAP levels maintained above 80 mmHg in early postinjury phases prior to arriving at intensive MAP monitoring sites such as high dependency units, intensive care units, or operating rooms. As a result, the mean calculated MAP was 78.8 mmHg, with 52% of the MAP level < 80 mmHg at the primary receiving hospitals. A total of 51.5% of primary hospitals, 23.2% of transfers, and 39.6% of tertiary units showed MAP maintenance level lower than 80 mmHg. The authors noted the need for education and awareness to optimize hemodynamic management of acute SCI patients during the immediate postinjury period.
MAP maintenance after SCI has potential limitations. In traumatic brain injury, hemodynamic management is important when attempting to control intracerebral pressure to increase both the cerebral perfusion pressure and MAP levels. As a result, controlling SCPP is more important in SCI cases. [14] Accordingly, as the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pressure is controlled by the lumbar intrathecal catheter, the necessity and scope of SCPP monitoring and result-specific neurological recovery are being studied.
Martirosyan et al. [15] studied the importance of spinal cord perfusion in a pig model. The study involved 15 pigs in the control, SCI only, SCI combined with MAP elevation (SCI+MAP), SCI combined with CSF drainage (CSFD) (SCI+CSFD), and SCI combined with both MAP elevation and CSFD (SCI+MAP +CSFD) groups. Spinal cord blood flow (SCBF) was measured for each group. When the SCI+MAP group and the SCI group were compared, the intrathecal pressure increased as the MAP increased. Accordingly, the maintenance of MAP levels alone led only to short-term improvement of SCBF. The combination of MAP level elevation and CSFD significantly and sustainably improved SCBF and SCPP. According to this study, increasing the MAP alone does not effectively improve the SCBF and perfusion. Therefore, the pressure in the spinal cord was more important to increase SCBF and SCPP than to increase MAP alone.
Squair et al. [16] measured MAP and CSF pressure (CSFP) for 1 week following injury in 92 acute SCI patients and measured SCPP. Neurologic impairment was evaluated both at baseline and 6 months following injury. The SCPP in individuals with gradual improvement of neurologic function dropped fewer times below 50 mmHg than that in individuals without improvement (p = 0.012). This effect was not observed for MAP and CSFP. Patients who were exposed to SCPP below 50 mmHg were less likely to improve from their baseline neurologic impairment grade (p = 0.0056). The authors demonstrated that maintaining SCPP above 50 mmHg is a strong predictor for neurologic recovery improvement after SCI. The authors argued that SCPP (differences between MAP and CSFP) could provide a guideline for useful information on hemodynamic management in patients with acute SCI. The authors studied the transition point of SCPP in the same patient [17]. The transition point was determined by examining the linear relationship between the target hemodynamic range and neurologic recovery. Adherence to SCPP and not to MAP targets was the best indicator of improved neurologic recovery occurring with SCPP targets of 60ŌĆō65 mmHg. Failing to maintain the SCPP ( > 50 mmHg) within the target range was an important detrimental factor in neurologic recovery, particularly with a lower target range. This study presented a practical hemodynamic management target-setting guideline, through an empirical data-driven approach.
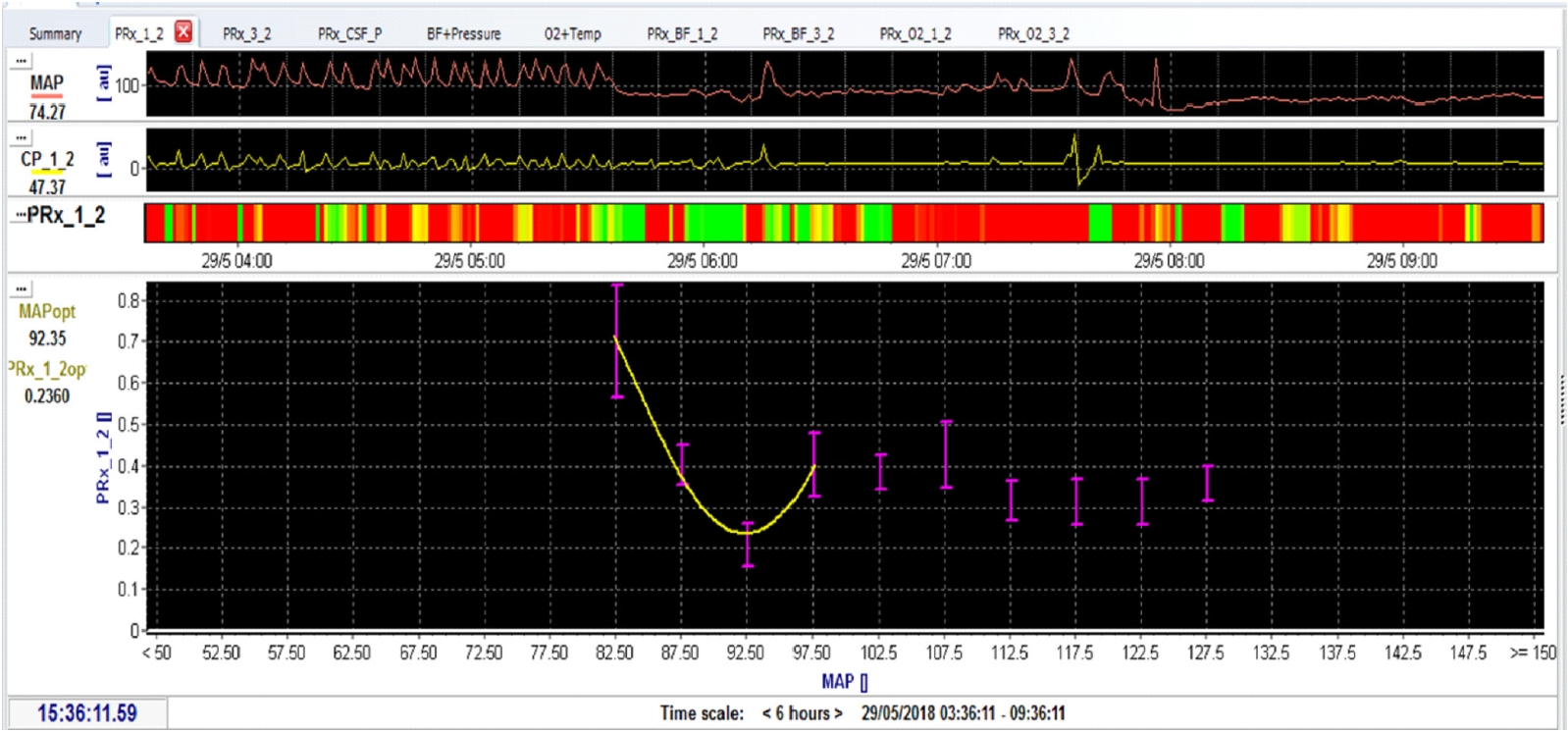
SCI causes edema and swelling, reducing the amount of CSF within the space between the dura mater and neural tissue. This phenomenon is similar to the swollen brain in posttraumatic brain injury. The cerebrovascular pressure reactivity index can be applied to the spinal cord to measure the spinal pressure reactivity index (sPRx), which reflects the response ability of the vascular smooth muscle to change in transmural pressure, and is used as a surrogate index of autoregulation. The sPRx is calculated as a moving correlation coefficient between the slow waves of the intraspinal pressure (ISP) and arterial blood pressure on a 5-minute sliding window. Theoretically, the value of sPRx is negative when spinal autoregulation remains intact because a MAP increase will not change the spinal blood flow, volume, and pressure. When spinal autoregulation is impaired, the sPRx is positive because changes in ISP follow MAP [18]. However, an sPRx equals of ŌĆ£0.3ŌĆØ is a clinically acceptable value. Measuring sPRx in SCI helps establish optimal MAP levels. In other words, when sPRx is < 0.3, autoregulation is performed, and the MAP at this time becomes the optimal MAP (Fig. 1).
Chen et al. [19] measured hemodynamic parameters by placing a pressure probe and a microdialysis catheter on the injured cord site in 14 patients with severe traumatic SCI. The hemodynamic parameters of SCPP were computed as MAP minus ISP, the sPRx was computed as the running ISP/MAP correlation coefficient, and continuous optimum SCPP (cSCPPopt) was computed as the SCPP that minimizes sPRx in a measured, moving 4-hour window. The authors also monitored the injury site metabolism. cSCPPopt varied from patient to patient over time and showed low injury glucose, high pyruvate, and high lactate when the SCPP remained similar. The mean SCPP deviation from cSCPPopt correlated with a worse neurological outcome at 9ŌĆō12 months. The AIS grade improved in 30% of the patients with < 5-mmHg deviation, 10% of the patients with 5- to 15-mmHg deviation, and none in patients with > 15-mmHg deviation. The authors suggest that targeting cSCPPopt after a severe traumatic SCI might improve neurological outcome.
It is also important to improve oxygenation through blood supply to reduce secondary insult in the spinal cord following SCI. However, there are no clinical means to monitor tissue oxygenation. Even when a MAP increase is attempted through the use of vasopressors, there is no known method to assess the effects of MAP increase on regional blood flow and tissue oxygenation. Naturally, real-time measurement instruments that continuously and accurately monitor spinal cord hemodynamics and oxygenation can be directly inserted into the spinal cord. However, direct insertion to the spinal cord could cause additional injury. Recently, a transdural near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) method was introduced, which is noninvasive and does not cause injury to the spinal cord.
NIRS has been used to monitor regional oxygenation in tissues such as brain and skeletal muscles. It can measure oxygenated and deoxygenated hemoglobin, absorbing NIR photons into the tissue by transmitting light photons in the near-infrared (wavelengths, 700ŌĆō1,000 nm). In addition, real-time changes in oxygenated and deoxyhemoglobin concentrations can be monitored using multiple light sources and photodectors [20].
Shadgan et al. [21] compared various direct and invasive methods with NIRS to measure oxygenation in the spinal cord after SCI. Using the T10 contusion-compression injury pig model, the invasive intraparenchymal sensor and the noninvasive transdural NIRS sensor were installed on the injured cord to compare oxygenation. They observed a significant correlation between spinal cord oxygen partial pressure (PO2), NIRS-derived oxygenated hemoglobin, deoxygenated hemoglobin, hemoglobin difference, and tissue oxygenation percentage of invasive intraparenchymal sensors. In particular, during periods of hypoxia and MAP alterations, changes in NIRS-derived spinal cord-oxygenated hemoglobin and tissue oxygenation percentage corresponded well with the changes in spinal cord PO2 that were measured by the intraparenchymal sensor.
A vasopressor is used in patients with SCI to maintain MAP levels at 85ŌĆō90 mmHg for 5ŌĆō7 days following injury. Clinically, phenylephrine, dopamine, and norepinephrine are used among various vasopressors. Although these vasopressors can effectively increase MAP levels, they involve different drug properties depending on the a-adrenergic, b-adrenergic, and dopamine affinity. Thus, knowing which vasopressor is effective to restore perfusion and downstream metabolic needs is necessary. In addition, knowledge of cardiogenic complication-causing drugs will assist with vasopressor utilization (Table 2).
Altaf et al. [22] investigated the effects of norepinephrine and dopamine on ITP and SCPP in 11 patients with acute SCI. These 2 vasopressors were tested in a crossover procedure. Both norepinephrine and dopamine were able to maintain the MAP. However, in contrast to dopamine usage, ITP was significantly lower with the use of norepinephrine (17┬▒ 1 mmHg vs. 20┬▒ 1 mmHg, respectively, p < 0.001). The decrease in ITP with norepinephrine resulted in an increased SCPP during norepinephrine administration when compared with dopamine (67 ┬▒ 1 mmHg vs. 65┬▒ 1 mmHg, respectively, p = 0.0049).
Streijger et al. [23] showed that norepinephrine and phenylephrine are effective in improving SCBF and oxygenation. The pharmacological properties and potentials were compared for the downstream metabolism after SCI. Vasopressors affect intraparenchymal SCBF, PO2, hydrostatic pressure, and metabolism. This experiment indicated that norepinephrine and phenylephrine showed no difference in the increase of MAP levels. After decompression, both norepinephrine and phenylephrine decreased the lactate to pyruvate ratio, but norepinephrine showed a higher SCBF and PO2 increase than phenylephrine. Therefore, compared with phenylephrine, norepinephrine showed superior blood flow restoration and oxygenation in traumatic SCI.
Inoue et al. [24] used various vasopressors to maintain MAP levels at 85ŌĆō90 mmHg in 131 patients with SCI. Vasopressors were used in the order of dopamine (48.0%), phenylephrine (45.0%), norepinephrine (5.0%), epinephrine (1.5%), and vasopressin (0.5%). Complications of ventricle tachycardia, troponin elevation, atrial fibrillation, tachycardia, and bradycardia were compared according to the vasopressors used. Dopamine (p < 0.001), phenylephrine (p = 0.004), age > 60 years (p = 0.013), and complete SCI (p = 0.028) were associated with vasopressor-related complications.
Readdy et al. [25] compared the dopamine- and phenylephrine-induced complications during attempts to regulate MAP levels in 34 patients with acute central cord syndrome. Vasopressor-related cardiogenic complications occurred in 68% of the patients receiving dopamine and 46% of the patients receiving phenylephrine. In patients aged > 55 years, dopamine showed a higher, statistically significant complication rate than phenylephrine (p = 0.044).
The goal of hemodynamic management following SCI is to increase patientsŌĆÖ MAP levels. Certainly, MAP escalation requires intensive treatment and detailed monitoring. In addition, to improve blood flow into the injured spinal cord, it is necessary to measure intrathecal pressure using a lumbar intrathecal catheter. Accordingly, controlling the SCPP prevents hypotension and ischemia of the injured spinal cord, thereby reducing secondary damage following SCI. Further research is required to control SCPP as well as oxygenation and inflammation. In addition, establishing an intensive care unit capable of improved hemodynamic management and proper education of medical staff should be pursued.
According to the 2013 AANS/CNS guideline, Blood pressure management after SCI is the MAP goal of 85ŌĆō90 mmHg for 7 days following SCI (class III recommendation). Unfortunately, there are methodological limitations to concluding a strong relationship between the MAP goals and neurologic recovery [26]. Thus, evidence-based guidelines for hemodynamic management are required to address gaps in knowledge and the limitations of the current body of literature on this topic. Maintaining MAP levels above 85 mmHg improves neurologic recovery; however, to maintain MAP, intensive hemodynamic management is required according to practice guidelines in an intensive care unit as well as outside the hospital setting. In addition, it is also important to maintain SCPP as well as MAP. To maintain MAP, an appropriate vasopressor should be used depending on the patient status. Further research on the hemodynamic management of acute SCI is required to determine how to optimize neurologic recovery.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This study is supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (NRF-2012R1A1A1-014361, NRF-2015R1C1A1A01056299).
Fig.┬Ā1.
Spinal pressure reactivity index (sPRx) is needed to determine the optimal mean arterial pressure (MAP) in spinal cord injury patients and animal models. When sPRx < 0.3, spinal autoregulation is performed, so the MAP at this time becomes the optimal MAP. Accordingly, sPRx can be measured to determine the optimal MAP during spinal cord injury treatment.
Table┬Ā1.
Hemodynamic management of mean arterial pressure (MAP) and spinal cord perfusion pressure (SCPP) in spinal cord injury
| Study | Study type | No. of patients | Goal and duration | Methods to increase MAP | Result | Length of follow-up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vale et al. [6], 1997 | Prospective, case series | Acute cervical and thoracic SCI (n = 77) | MAP > 85 mmHg during 7 days | Crystalloid, colloid, vasopressor | The 33%ŌĆō60% of complete cord injury patients and 88%ŌĆō92% of incomplete cord injury patients recovered their neurologic outcome. | 12 Months |
| Hawryluk et al. [7], 2015 | Retrospective, case series | Acute SCI (n = 74) | MAP > 85ŌĆō90 mmHg during 7 days | Vasopressor (dopamine, phenylephrine and levophed) | The higher average MAP values in the first 2ŌĆō3 days after SCI showed a stronger correlation with neurologic recovery, but the intensity decreased after 5ŌĆō7 days after SCI. | Until discharge |
| Dakson et al. [9], 2017 | Retrospective, comparative | Traumatic SCI (n = 94) | MAP > 85 mmHg | Vasopressor (dopamine, phenylephrine) | Neurologic improvement was 11 times better in patients with MAP > 85 mmHg compared with patients with MAP < 85 mmHg (p = 0.006). | Until discharge |
| Kong et al. [12], 2013 | Prospective observational | Acute cervical and thoracic SCI (n = 21) | MAP > 80 mmHg | Volume resuscitation, vasopressor | Episodes with MAP < 80 mmHg were observed in all patinets, and 81% of MAP < 70 mmHg. | 5-Day postinjury |
| SCPP > 60 mmHg for 3ŌĆō5 days | ||||||
| Catapano et al. [8], 2016 | Retrospective, case series | Acute SCI (n = 33) | MAP > 85ŌĆō90 mmHg during 7 days | AIS improvement was positive in patients with AIS A, and B/C, but not in patients with AIS D. | Until discharge | |
| Tee et al. [13], 2017 | Prospective observational | Acute cervical and thoracic SCI (n = 40) | MAP was 78.8 mmHg, with 52% of MAP measurements < 80 mmHg at primary receiving hospitals, 23.2% of transfers, and 39.6% of tertiary. | |||
| Squair et al., [16] 2017 | Prospective observational | Acute SCI (n = 92) | MAP 80ŌĆō85 mmHg SCPP > 50 mmHg | Volume augmentation, vasopressor (neoepinephrine, phenylephrine, dopamine) | This effect was not observed MAP and CSFP. Those who were exposed to SCPP below 50 mmHg were less likely to improve from their baseline neurologic impairment grade (p = 0.0056). | 6 Months |
| Squair et al. [16], 2017 | Prospective observational | Acute SCI (n = 92) | MAP 80ŌĆō85 mmHg | Volume augmentation, vasopressor (neoepinephrine, phenylephrine, dopamine) | Adherence to SCPP targets, not MAP targets, was the best indicator of improved neurologic recovery, which occurred with SCPP targets of 60ŌĆō65 mmHg. | 6 Months |
Table┬Ā2.
Vasopressor for hemodynamic management after SCI
| Study | Study type | No. of patients | Goal and duration | Methods to increase MAP | Neurological recovery measure | Length of follow-up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Readdy et al. [25], 2015 | Retrospective cohort analysis | Acute traumatic SCI (n = 34) | MAP > 85ŌĆō90 mmHg during 7 days | Vasopressor (dopamine vs. phenylephrine) | In patients older than 55 years, dopamine showed a statistically significant complication rate than phenylephrine (p = 0.044). | Until discharge |
| Mean of 101 hours | ||||||
| Altaf et al. [22], 2017 | Prospective crossover interventional study | Cervical or thoracic SCI (n = 11) | MAP > 90 mmHg | Vasopressor (dopamine, norepinephrine) | The decrease in ITP with norepinephrine resulted in an increased SCPP during the norepinephrine when compared with dopamine (67 ┬▒ 1 mmHg vs. 65 ┬▒ 1 mmHg, respectively, p = 0.0049). | 3ŌĆō5 Days after SCI |
| Inoue et al. [24], 2014 | Retrospective cohort study | SCI (n = 131) | 85ŌĆō90 mmHg during 7 days | Vasopressor (dopamine, phenylephrine, norepinephrine, epinephrine, vasopressin) | Dopamine (p < 0.001), phenylephrine (p = 0.004), age > 60 years old (p = 0.013), and complete SCI (p = 0.028) were associated with vasopressor-related complications. | |
| Streijger et al. [23], 2018 | Animal study | Pig model | Vasopressor | After decompression, both norepinephrine and phenylephrine decreased lactate to pyruvate ratio, but norepinephrine showed higher SCBF and PO2 increase than phenylephrine. |
REFERENCES
1. Hawryluk GWJ, Rowland J, Kwon BK, et al. Protection and repair of the injured spinal cord: a review of completed, ongoing, and planned clinical trials for acute spinal cord injury. Neurosurg Focus 2008 25:E14.

2. Rowland JW, Hawryluk GWJ, Kwon B, et al. Current status of acute spinal cord injury pathophysiology and emerging therapies: promise on the horizon. Neurosurg Focus 2008 25:E2.

3. Walters BC, Hadley MN, Hurlbert RJ, et al. Guidelines for the management of acute cervical spine and spinal cord injuries: 2013 update. Neurosurgery 2013 60:82-91.


4. Powers WJ. Acute hypertension after stroke: the scientific basis for treatment decisions. Neurology 1993 43:461-7.


5. Levi L, Wolf A, Belzberg H. Hemodynamic parameters in patients with acute cervical cord trauma: description, intervention, and prediction of outcome. Neurosurgery 1993 33:1007. -16. discussion 16-7.


6. Vale FL, Burns J, Jackson AB, et al. Combined medical and surgical treatment after acute spinal cord injury: results of a prospective pilot study to assess the merits of aggressive medical resuscitation and blood pressure management. J Neurosurg 1997 87:239-46.


7. Hawryluk G, Whetstone W, Saigal R, et al. Mean arterial blood pressure correlates with neurological recovery after human spinal cord injury: analysis of high frequency physiologic data. J Neurotrauma 2015 32:1958-67.



8. Catapano JS, Hawryluk GWJ, Whetstone W, et al. Higher mean arterial pressure values correlate with neurologic improvement in patients with initially complete spinal cord injuries. World Neurosurg 2016 96:72-9.



9. Dakson A, Brandman D, Thibault-Halman G, et al. Optimization of the mean arterial pressure and timing of surgical decompression in traumatic spinal cord injury: a retrospective study. Spinal Cord 2017 55:1033-8.


10. Saadeh YS, Smith BW, Joseph JR, et al. The impact of blood pressure management after spinal cord injury: a systematic review of the literature. Neurosurg Focus 2017 43:E20.


11. Sabit B, Zeiler FA, Berrington N. The impact of mean arterial pressure on functional outcome post trauma-related acute spinal cord injury: a scoping systematic review of the human literature. J Intensive Care Med 2018 33:3-15.


12. Kong CY, Hosseini AM, Belanger LM, et al. A prospective evaluation of hemodynamic management in acute spinal cord injury patients. Spinal Cord 2013 51:466-71.


13. Tee JW, Altaf F, Belanger L, et al. Mean arterial blood pressure management of acute traumatic spinal cord injured patients during the pre-hospital and early admission period. J Neurotrauma 2017 34:1271-7.


14. Melhem S, Shutter L, Kaynar A. A trial of intracranial pressure monitoring in traumatic brain injury. Crit Care 2014 18:302.



15. Martirosyan NL, Kalani MYS, Bichard WD, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid drainage and induced hypertension improve spinal cord perfusion after acute spinal cord injury in pigs. Neurosurgery 2015 76:461. -8. discussion 468-9.


16. Squair JW, B├®langer LM, Tsang A, et al. Spinal cord perfusion pressure predicts neurologic recovery in acute spinal cord injury. Neurology 2017 89:1660-7.


17. Squair JW, B├®langer LM, Tsang A, et al. Empirical targets for acute hemodynamic management of individuals with spinal cord injury. Neurology 2019 93:e1205-11.


18. Varsos GV, Werndle MC, Czosnyka ZH, et al. Intraspinal pressure and spinal cord perfusion pressure after spinal cord injury: an observational study. J Neurosurg Spine 2015 23:763-71.


19. Chen S, Smielewski P, Czosnyka M, et al. Continuous monitoring and visualization of optimum spinal cord perfusion pressure in patients with acute cord injury. J Neurotrauma 2017 34:2941-9.


20. Nielsen HB. Systematic review of near-infrared spectroscopy determined cerebral oxygenation during non-cardiac surgery. Front Physiol 2014 5:93.



21. Shadgan B, Macnab A, Fong A, et al. Optical assessment of spinal cord tissue oxygenation using a miniaturized near infrared spectroscopy sensor. J Neurotrauma 2019 36:3034-43.


22. Altaf F, Griesdale DE, Belanger L, et al. The differential effects of norepinephrine and dopamine on cerebrospinal fluid pressure and spinal cord perfusion pressure after acute human spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 2017 55:33-8.


23. Streijger F, So K, Manouchehri N, et al. A direct comparison between norepinephrine and phenylephrine for augmenting spinal cord perfusion in a porcine model of spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma 2018 35:1345-57.


24. Inoue T, Manley GT, Patel N, et al. Medical and surgical management after spinal cord injury: vasopressor usage, early surgerys, and complications. J Neurotrauma 2014 31:284-91.



- Related articles in NS
-
Spinal Robotics in Adult Spinal Deformity Surgery: A Systematic Review2024 March;21(1)
The Role and Future of Endoscopic Spine Surgery: A Narrative Review2023 March;20(1)
Multimodal Repair of Spinal Cord Injury With Mesenchymal Stem Cells2022 September;19(3)
Established and Emerging Therapies in Acute Spinal Cord Injury2022 June;19(2)
Commentary on ŌĆ£Hemodynamic Management of Acute Spinal Cord InjuryŌĆØ2021 March;18(1)
-
Journal Impact Factor 3.2