Comparison of the Efficacy of Romosozumab and Teriparatide for the Management of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures
Article information
Abstract
Objective
Romosozumab is increasingly employed to manage osteoporosis. However, no studies have analyzed its effects on recent osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (OVCFs). Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of romosozumab compared with teriparatide in managing OVCFs.
Methods
The electronic medical records of postmenopausal patients with recent OVCFs who were administered romosozumab or teriparatide for one year from March 2018 to August 2022 were retrospectively reviewed. We compared the 2 groups for demographics, radiological outcomes (compression ratio, Cobb angle, and bone mineral density [BMD]), and clinical outcomes (Numerical Rating Scale [NRS] for back pain).
Results
Fifty-five patients with OVCFs, 32 patients treated with romosozumab and 23 with teriparatide, were included in this study. The change of BMD (g/cm2) values was significantly higher (p = 0.016) in the romosozumab (0.04 ± 0.06) than in the teriparatide group (0.00 ± 0.08) in the femur total. Furthermore, in subgroup analysis, the change of BMD (g/cm2) values in the lumbar spine was significantly higher (p = 0.016) in the romosozumab (0.12 ± 0.06) than in the teriparatide group (0.07 ± 0.06) in the lumbar spine. The decrease in NRS was significantly higher (p = 0.013) in the romosozumab (6.6 ± 2.0) than in the teriparatide group (5.5 ± 2.1). However, there was no significant difference in radiologic outcomes between the 2 groups.
Conclusion
Our findings suggest that romosozumab may be more effective than teriparatide in treating OVCFs in postmenopausal females, particularly in improving BMD and reducing back pain as measured by NRS.
INTRODUCTION
Among postmenopausal women, osteoporosis is a major clinical challenge characterized by low bone mass, microarchitectural deterioration of bone tissue, and decreased bone strength [1-3]. Considering that osteoporosis can lead to fragility fractures, it is not only one of the most common causes of disability, but also a major contributor to medical care costs [4-9]. Therefore, evidence-based prevention and management of osteoporosis are essential to reduce these burdens.
As percutaneous vertebroplasty became less competitive in managing osteoporotic fractures [3,10], anabolic osteoporosis agents have emerged with the ability to markedly increase bone density, managing microstructural defects and low bone mass and contributing to reduced fracture risk [11]. For example, teriparatide (Forsteo, Eli Lilly and Co., Indianapolis, IN, USA), a recombinant human parathyroid hormone, is the first approved anabolic agent that stimulates osteoblastic bone formation to improve bone quality and bone mass [12,13]. In addition, romosozumab (Evenity, Amgen, Thousand Oaks, CA, USA) is a monoclonal antibody that inhibits sclerostin, thereby increasing bone formation and reducing bone resorption [14-17]. Romosozumab has been increasingly used as a novel treatment to reduce fracture risk induced by osteoporosis [18].
However, the efficacy of bone-forming agents in patients with osteoporotic fractures remains unclear. Therefore, the present study aimed to compare the efficacy between romosozumab and teriparatide for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (OVCFs) in terms of clinical and radiological outcomes and changes in bone mineral density (BMD).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
1. Participants
The electronic medical records of patients recently diagnosed with OVCFs and administered with romosozumab or teriparatide for one year from March 2018 to August 2022 were retrospectively reviewed. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine (IRB No. 2022-1725), which waived the requirement of obtaining informed consent. Eligible patients included ambulatory postmenopausal females. All patients presented evidence of osteoporosis based on a dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry BMD T score of ≤ -2.5 at the lumbar spine (L-spine), total hip, or femoral neck. The exclusion criteria were as follows: previous fusion surgery or vertebroplasty; severe cardiac, pulmonary, or hepatic disease; recently taken medication affecting bone metabolism, including bisphosphonates, parathyroid hormone analog, antineoplastic drug, or steroids; previously experienced spine or hip fractures; and metabolic or bone disease, neurological deficits, or pathologic fractures.
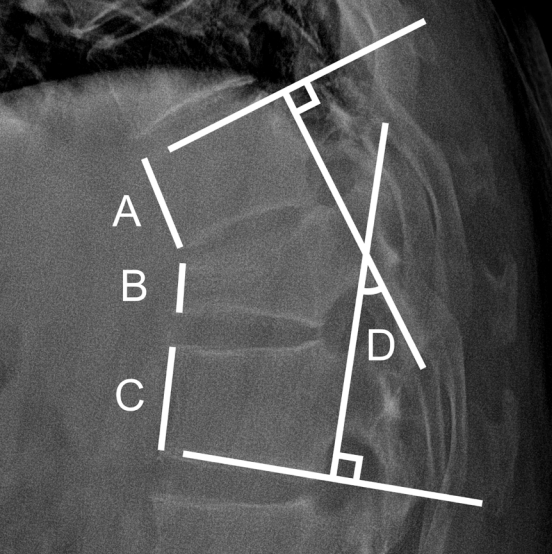
The overall study population was classified into the romosozumab and teriparatide groups. Factors such as age, fracture level, BMD, and T score of BMD at baseline and 12 months were compared between the 2 groups. Spinal radiography had been followed up for at least 1 year with periodic evaluation of plain radiographs. The compression ratio was determined and compared by measuring the ratio of the anterior height of the upper, lower, and fractured vertebral levels. To determine and compare Cobb angles, the angle between the superior endplate of the vertebral body above and the inferior endplate of the vertebral body below the fractured vertebra on lateral view was measured (Fig. 1). Patient-reported outcomes were recorded using the Numerical Rating Scale (NRS) as the pain index at onset and after 3, 6, 9, and 12 months. Finally, to eliminate bias in BMD measurements from multiple institutions, patients whose BMD and BMD T score were measured at a single center were separated from the study population, and subgroup analysis was performed [19,20].
2. Prescription Details
A healthcare professional administered 210 mg (2 doses, 105 mg each) of romosozumab (Evenity, Amgen, Thousand Oaks, CA, USA) subcutaneously during 12 monthly hospital visits. Teriparatide, delivered as a preassembled commercially available pen device (Forsteo, Eli Lilly and Co., Indianapolis, IN, USA), was self-administered subcutaneously at 20 µg daily for 12 months.
3. Statistical Analysis
Demographic data and clinical outcomes are presented as the mean ± standard deviation for continuous variables or as counts with percentages for categorical variables. Delta variables (Δ) were calculated by subtracting the baseline value from the value after 12 months. The Wilcoxon signed-rank test and paired t-test were used to compare the effects of each drug before and after treatment according to the normality test results. Moreover, the Wilcoxon rank-sum test and independent t-test were used to compare the 2 drugs. Statistical significance was considered at p< 0.05. Statistical analyses were performed using R version 4.1.1 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria).
RESULTS
1. Patient Characteristics
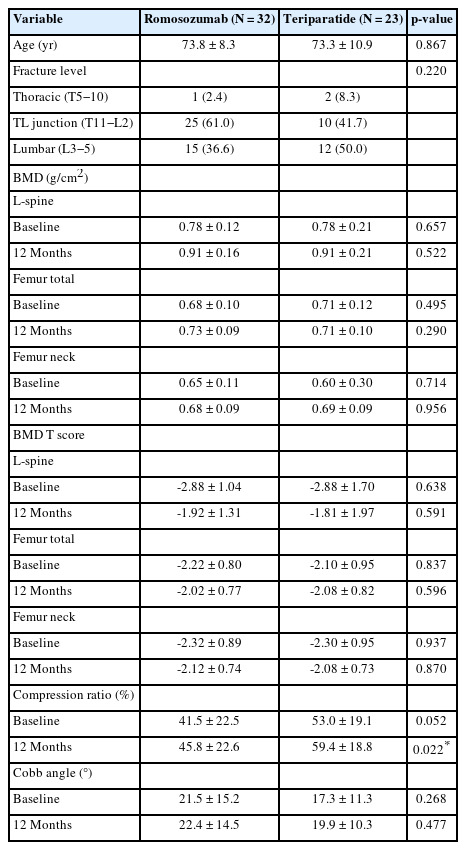
Fifty-five patients were included in the final cohort. The romosozumab group comprised 32 patients, whereas the teriparatide group comprised 23 patients. Demographic data, including age, fracture level, BMD and BMD T score, compression ratio, and Cobb angle, of both groups were compared (Table 1). Patients in the romosozumab group had a mean age of 73.8 ± 8.3 years compared with 73.3 ± 10.9 years in the teriparatide group (p = 0.867). All patients in both groups were females. The mean baseline BMD values of the romosozumab and teriparatide groups were 0.78 ± 0.12 and 0.78 ± 0.21 g/cm2 for the L-spine (p = 0.657), 0.65 ± 0.11 and 0.60 ± 0.30 g/cm2 for the femur neck (p = 0.714), and 0.68 ± 0.10 and 0.71 ± 0.12 g/cm2 for the femur total (p = 0.495), respectively. After 12 months, the mean BMD values of the romosozumab and teriparatide groups were 0.91 ± 0.16 and 0.91 ± 0.21 g/cm2 for the L-spine (p = 0.522), 0.68 ± 0.09 and 0.69 ± 0.09 g/cm2 for the femur neck (p = 0.956), and 0.73 ± 0.09 and 0.71 ± 0.10 g/cm2 for the femur total (p = 0.290), respectively. No significant differences were observed in demographic and BMD data (Table 1).
2. Comparison of Changes in BMD and BMD T Score Between Baseline and 12 Months After Treatment
To analyze the effects of treatment after 12 months, the differences between baseline and 12-month values of BMD and T score were compared. In the romosozumab group, the mean Δ BMD values and mean Δ T scores were 0.13 ± 0.08 g/cm2 and 0.97 ± 0.60 for the L-spine, 0.03 ± 0.07 g/cm2 and 0.20 ± 0.57 for the femur neck, and 0.04 ± 0.06 g/cm2 and 0.20 ± 0.43 for the femur total, respectively. In the teriparatide group, the mean Δ BMD values and mean Δ T scores were 0.13 ± 0.15 g/cm2 and 1.07 ± 1.15 for the L-spine, 0.09 ± 0.29 g/cm2 and 0.21 ± 0.77 for the femur neck, and 0.00 ± 0.08 g/cm2 and 0.02 ± 0.55 for the femur total, respectively. Only the difference in the mean Δ BMD of the femur total between the romosozumab and teriparatide groups was statistically significant (p = 0.016), whereas no significant differences were observed between the romosozumab and teriparatide groups (Table 2).
In addition, subgroup analysis was performed for the heterogeneous clinical findings and changes in BMD and BMD T score. Hence, BMD measurements performed at a single center were considered. Eighteen out of 32 patients from the romosozumab group and 13 out of 23 patients from the teriparatide group were included in this subgroup analysis. In the romosozumab group, the Δ BMD values and Δ T scores were 0.12 ± 0.06 g/cm2 and 0.97 ± 0.47 for the L-spine, 0.02 ± 0.06 g/cm2 and 0.22 ± 0.52 for the femur neck, and 0.02 ± 0.04 g/cm2 and 0.19 ± 0.36 for the femur total, respectively. In the teriparatide group, the mean Δ BMD values and mean Δ T scores were 0.07 ± 0.06 g/cm2 and 0.65 ± 0.44 for the L-spine, 0.00 ± 0.04 g/cm2 and -0.02 ± 0.33 for the femur neck, and 0.00 ± 0.03 g/cm2 and 0.01 ± 0.24 for the femur total, respectively. Only Δ BMD values of the L-spine between the romosozumab and teriparatide groups were significantly different (p = 0.023), whereas other values were not statistically different (Table 3).
3. Comparison of Radiological Outcomes
For the comparison of radiological outcomes, changes in the compression ratios and Cobb angles between baseline and 12 months were used. The mean Δ compression ratios of the romosozumab and teriparatide groups were 4.3 ± 5.8 and 6.4 ± 7.3, and the mean Δ Cobb angles were 1.0 ± 4.6, and 2.7 ± 6.1, respectively (Table 4).
4. Comparison of Clinical Outcomes
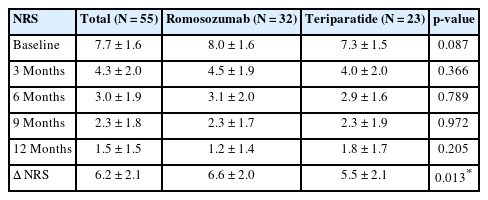
The NRS scores were assessed at 3-month intervals for 12 months from the onset of back pain. The overall NRS scores for the romosozumab and teriparatide groups decreased from 8.0 ± 1.6 to 1.2 ± 1.4 and from 7.3 ± 1.5 to 1.8 ± 1.7, respectively (Fig. 2, Table 5). No significant differences were noted at baseline (p = 0.087), 3 months (p = 0.366), 6 months (p = 0.789), 9 months (p = 0.972), and 12 months (p = 0.205) between the 2 groups. However, the overall change in NRS scores between baseline and 12 months showed a statistically significant reduction in the romosozumab group (p = 0.013) (Table 5).
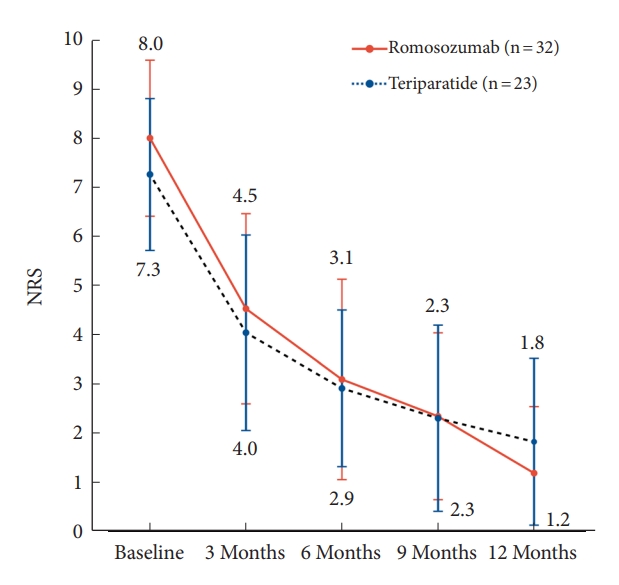
Trends of back pain levels in the Numerical Rating Scale (NRS) over time for patients treated with romosozumab and teriparatide. In terms of pain reduction, the romosozumab and teriparatide groups showed a similar reduction trend from baseline to 6 months of treatment. However, the romosozumab group exhibited a greater rate of pain reduction than the teriparatide group between 6 and 12 months after treatment. The overall pain reduction effect was significantly greater in the romosozumab group than in the teriparatide group (p = 0.013).
DISCUSSION
Previous studies have extensively discussed the efficacy of romosozumab and teriparatide in treating osteoporosis without recent OVCFs [11,21-24]. To the best of our knowledge, the present study is the first to evaluate the effectiveness of romosozumab compared with teriparatide in managing osteoporosis with recent OVCFs. Langdahl et al. [11] conducted the STRUCTURE study, a randomized controlled trial comparing romosozumab with teriparatide in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. The STRUCTURE study reported BMD changed from baseline of 9.8% (95% confidence interval [CI], 9.0%–10.5%) for romosozumab and 5.4% (95% CI, 4.7%–6.1%) for teriparatide in the lumbar spine. In the present study, BMD changed from baseline of 16.9% (95% CI, 13.5%–20.2%) for romosozumab and 18.6% (95% CI, 9.5%–27.7%) for teriparatide in the lumbar spine. These higher BMD changes may be attributed to differences in inclusion criteria, specifically the presence of recent OVCFs. In the context of recent OVCFs, romosozumab and teriparatide, as anabolic agents, may promote the healing process of fractures. Therefore, the presence of recent OVCFs may have influenced the higher BMD changes observed in the present study compared with the STRUCTURE study.
Moreover, the outcomes of the present study suggest that treating osteoporotic fractures with romosozumab had several noticeable features. First, the response to romosozumab, expressed as the increase in BMD, in patients with OVCFs appeared to be greater than that to teriparatide because osteoporotic fractures, a severe form of osteoporosis with a lower BMD, would achieve a more dramatic BMD gain. In the present study, 55 postmenopausal females with OVCFs were examined. The results showed that L-spine and femur neck BMD values were increased in the romosozumab and teriparatide groups, whereas the femur total BMD gain was significantly greater in the romosozumab group after 12 months of treatment. In the subgroup analysis, the mean L-spine BMD change was positive in both groups, wherein the romosozumab group exhibited a significantly greater surge than the teriparatide group. The L-spine BMD gain was significantly greater in the romosozumab group than in the teriparatide group after 12 months of treatment. This finding may explain the more significant decrease in NRS score in the romosozumab group than in the teriparatide group. Despite the romosozumab group having a slightly higher baseline NRS (8.0 ± 1.6) than the teriparatide group (7.3 ± 1.5), the romosozumab group had lower NRS at 12 months (1.2 ± 1.4) compared with the teriparatide group (1.8 ± 1.7). Furthermore, the change in NRS was significantly greater in the romosozumab group (6.6 ± 2.0) than in the teriparatide group (5.5 ± 2.1), with a p-value of 0.013. We speculate that the greater increase in L-spine BMD may be associated with a reduction in NRS back pain. Notably, L-spine BMD increased more in the romosozumab group (0.12 ± 0.06) than in the teriparatide group (0.07 ± 0.06), with a p-value of 0.023. Therefore, romosozumab may effectively alleviate back pain compared with teriparatide.
Considering that drugs for osteoporosis are administered over a 12-month period, patient compliance level may vary depending on the distance from the clinic, dosing interval, and patient’s propensity for the dosing method. Although romosozumab has the advantage of direct administration by a medical practitioner at a clinic at monthly intervals, patients with osteoporosis residing at a considerable distance from the clinic may be lost to follow-up. Moreover, although the distance from the clinic does not impact teriparatide administration, patients tend to experience a feeling of burden regarding daily drug administration or self-administration. Thus, patients should be provided with continuous motivation and detailed explanation regarding the effects and necessity of drugs to increase compliance.
This study had several limitations that need to be addressed. First, the study was conducted retrospectively and was not a randomized controlled trial. Second, only 3 clinical and radiological variables were measured (i.e., pain score, compression ratio, and Cobb angle), without hematological and/or chemical parameters such as bone formation or resorption markers. Third, the ratio of fracture levels was different between the 2 groups because of the small number of enrolled patients although it was considered statistically insignificant in Table 1. Finally, according to Finkelstein et al. [25], the increase in hip BMD was more pronounced between 12 and 24 months of treatment than during the first 12 months. However, the study period only covered the first 12-month dosing period. Thus, further studies spanning up to 24 months of dosing are needed to verify our findings.
CONCLUSION
Romosozumab and teriparatide enhanced spinal BMD in postmenopausal female patients with OVCFs. However, romosozumab exhibited a more significant increase in BMD in the femur total and L-spine compared with teriparatide in the overall population and subgroup analyses, respectively. In addition, patients treated with romosozumab reported a more significant reduction in NRS scores than those treated with teriparatide. Thus, romosozumab may be more effective in managing osteoporotic fractures in postmenopausal female patients with OVCFs compared with teriparatide.
Notes
Conflict of Interest
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Funding/Support
This study received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author Contribution
Conceptualization: JHP; Data curation: DP; Formal analysis: DP, HKS, JS, JKJ, SHL; Methodology: DP, HKS, JS, CK, SHL; Project administration: DP; Visualization: HKS, SHL; Writing - original draft: JKJ; Writing - review & editing: SEK, SHL.
Acknowledgements
Previous presentation: This material was presented as an oral abstract at Neuro Spine Congress held at the Kim Dae Jung Convention Center on September 22, 2023.