- Search
| Neurospine > Volume 21(1); 2024 > Article |
|
|
Abstract
Objective
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) has been performed for spinal tumors. However, the quantitative effect of SRS on postoperative residual cervical dumbbell tumors remains unknown. This study aimed to quantitatively evaluate the efficacy of SRS for treating postoperative residual cervical dumbbell tumors.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed cases of postoperative residual cervical dumbbell tumors from 1995 to 2020 in 2 tertiary institutions. Residual tumors underwent SRS (SRS group) or were observed with clinical and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) follow-up (observation group). Tumor regrowth rates were compared between the SRS and observation groups. Additionally, risk factors for tumor regrowth were analyzed.
Results
A total of 28 cervical dumbbell tumors were incompletely resected. Eight patients were in the SRS group, and 20 in the observation group. The mean regrowth rate was not significantly lower (p = 0.784) in the SRS group (0.18 ± 0.29 mm/mo) than in the observation group (0.33 ± 0.40 mm/mo). In the multivariable Cox regression analysis, SRS was not a significant variable (hazard ratio [HR], 0.57; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.18–1.79; p = 0.336).
Spinal dumbbell tumors are spinal tumors that acquire an hourglass shape when encountering the dura mater or bony elements, or passing through the neural foramen [1]. Spinal dumbbell tumors account for approximately 18% of spinal tumors. Among them, cervical dumbbell tumors account for approximately 44% of all dumbbell tumors [2]. The standard treatment for dumbbell tumors is gross total resection. However, for cervical dumbbell tumors, gross total resection is not always feasible in some circumstances such as: (1) a large extraforaminal portion at the upper cervical level, (2) a high risk of vertebral artery (VA) injury due to encasement of the VA, or (3) multiple cervical nerve root involvement due to extraforaminal growth [3,4]. In addition, when the facet joint has to be preserved to avoid instrumentation (a lateral mass screw or a pedicle screw) due to severe osteoporosis or other comorbidities that require a short operation time, this can lead to incomplete resection of the tumor. This is because the foraminal and extraforaminal portions cannot be sufficiently exposed without total facetectomy. Consequently, an incomplete resection is performed in various situations and may result in residual tumors following surgery.
When tumors remain following incomplete resection, stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) can be an additional treatment option instead of a secondary operation. SRS using the Leksell frame has previously been limited to intracranial lesions. However, with advances in technology, hypofractionated radiotherapy has also been applied to extracranial lesions, including those in the spine.
Currently, SRS is a widely used treatment modality for benign spinal tumors [5-8]. Previous studies suggested SRS as a useful treatment modality for recurrent cervical dumbbell tumors following surgery [9-11]. However, these studies reported qualitative analyses of the effect of SRS. To the best of our knowledge, no studies have specifically evaluated the efficacy of SRS for residual cervical dumbbell tumors following surgery. Moreover, its quantified effect on these tumors has not been established yet. The purpose of this study was to quantitatively evaluate the efficacy of SRS for postoperative residual cervical dumbbell tumors in terms of the regrowth rate and the change in tumor size before and after SRS.
The study was conducted according to the Helsinki Declaration (https://www.wma.net/policies-post/wma-declaration-of-helsinki-ethical-principles-for-medical-research-involving-human-subjects/) and approved by the Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) of 2 tertiary referral hospitals (IRB numbers 2022-1213, 2022-09-092). The requirement of informed consent from the patients was waived by the IRB because of the study’s retrospective nature.
We retrospectively reviewed the patients who underwent an operation for a cervical dumbbell tumor from 1995 to 2020 at the Asan Medical Center and Samsung Medical Center. Cervical dumbbell tumors were defined as tumors that acquired an hourglass shape by passing through the neural foramen at the cervical level and had intraspinal, foraminal, and extraforaminal portions. Tumors that acquired an hourglass shape by encountering the dura mater and did not have foraminal and extraforaminal portions were excluded from this study. In addition, tumors extending only to a vertebral body, not the neural foramen, were also excluded. Cases with missing data were excluded from the analysis.
After reviewing the electronic medical and operative records and radiologic findings from the 2 centers, we integrated the data. In this study, we included the cases with residual tumors following incomplete resection. Residual tumors were identified by the surgeon’s impression that the tumor was not grossly totally removed and postoperative gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Tumor volume (cm3) was calculated using the formula π 6 × A × B × C
Patients were classified into 2 groups: the SRS group, who underwent SRS for postoperative residual tumor, and the observation group, who did not receive postoperative SRS. In the SRS group, SRS was performed to prevent the regrowth of residual cervical dumbbell tumors when they were identified at the first postoperative MRI, which was taken within one week after the operation. Conversely, in the observation group, residual tumors were observed with clinical and MRI follow-up without undergoing SRS. Depending on each surgeon’s discretion, it was decided whether to perform SRS or not.
SRS was conducted using either the CyberKnife image-guided radiosurgery system (Accuray Inc., Sunnyvale, CA, USA) or the Novalis Tx system (Varian Medical Systems, Palo Alto, CA, USA). The CyberKnife system was adopted at the Asan Medical Center, and the Novalis system at the Samsung Medical Center. SRS was performed daily with 1,300–2,561 cGy (mean prescribed dose=2,174.35 cGy), and 1–5 fractionation (mean fractions=3.18).
If the increase in tumor diameter was greater than 2 mm during follow-up, the tumor was classified as regrowth [4,16,17]. Otherwise, it was classified as no regrowth. We assessed the risk factors associated with the regrowth of residual cervical dumbbell tumors following surgery. These factors were evaluated in terms of patient demographics, radiographic findings, and whether SRS had been performed.
Regrowth rate (mm/mo) was defined as the increase in tumor size (mm) divided by the follow-up MRI period (months). Tumor size (mm) was determined by the maximal diameter measured on axial images of gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted MRI [4,18-20]. The follow-up MRI period spanned from the first postoperative MRI to the last follow-up MRI. If the patients underwent an additional procedure (either revision surgery and/or delayed SRS), the follow-up MRI period was defined as the duration from the first postoperative MRI to the last follow-up before that procedure.
We evaluated the changes in the sizes of the residual tumors before and after undergoing SRS. The size prior to SRS was determined using the MRI taken immediately before the SRS. Post-SRS measurements were taken from the MRI conducted at the final follow-up.
Statistical analysis was performed using R ver. 4.1.1 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria). All statistical tests were 2-sided, and p< 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Continuous variables are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD) or median (range). Categorical variables are presented as a number (%). A Wilcoxon rank-sum test was used to compare the regrowth rate between the SRS and observation groups. A Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used to compare the diameters of residual tumors that underwent SRS before and after the SRS procedure. Fisher exact test was used to assess the association between 2 categorical variables. The Kaplan-Meier survival curve method was used to analyze the time-to-event outcome for the regrowth of tumors. Comparisons between the survival curves of the 2 groups were conducted using the log-rank test. Risk factors for the regrowth of residual tumors were assessed using multivariable Cox regression analysis. The occurrence of regrowth was defined as the dependent variable. Independent variables included age, sex, tumor pathology, preoperative and postoperative tumor volume on the MRI, and whether SRS was performed.
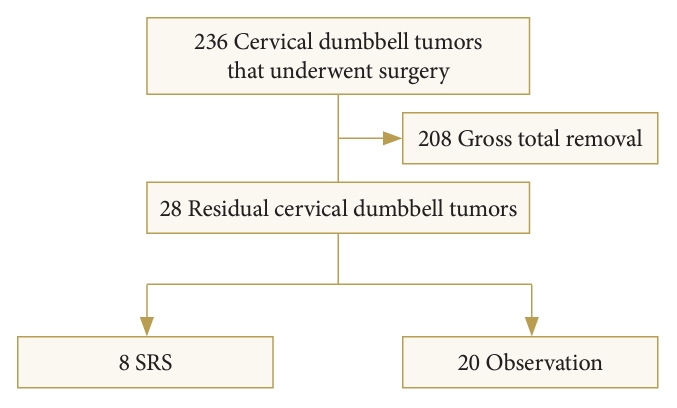
A total of 236 patients underwent surgery for cervical dumbbell tumors in our institutions. Cervical dumbbell tumors were incompletely resected in 28 patients; of these, 17 were treated at the Asan Medical Center, and 11 at Samsung Medical Center. In these patients, the intraspinal portions were completely removed, but the foraminal and/or extraforaminal portions remained. Of the 28 patients, 8 patients underwent SRS and were categorized into the SRS group; 7 of these were treated with the CyberKnife system and 1 with the Novalis system.
The remaining 20 patients were observed with clinical and MRI follow-up and were categorized into the observation group (Fig. 1).
There were no significant differences in age, sex, pathology, tumor volume, tumor diameter, occurrence of regrowth, and follow-up periods between the SRS and observation groups (Table 1). Among the 20 patients in the observation group, 10 underwent delayed SRS due to tumor recurrence. However, their follow-up as the observation group was considered to have ended after delayed SRS was performed. Therefore, in Table 1, all 20 patients in the observation group were included as being in the follow-up without SRS.
Among a total of 28 patients, regrowth occurred in 6 patients (75.0%) in the SRS group and in 13 patients (65.0%) in the observation group (Table 1). Among the 13 patients in the observation group, 10 patients presented with aggravated symptoms. Subsequently, these 10 patients received delayed SRS for therapeutic purposes; 8 were treated with the CyberKnife system and 2 with the Novalis system. For these patients, the follow-up for observation was considered finished once regrowth with aggravated symptoms occurred and delayed SRS was performed. Two patients in the SRS group and 3 in the observation group underwent secondary operations due to aggravated symptoms during follow-up, although SRS was performed.
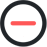
Fig. 2 shows the Kaplan-Meier survival curves of both the SRS and observation groups. Log-rank tests found no significant differences between the 2 groups (p = 0.81). In the multivariable Cox regression analysis, SRS was not a significant variable (hazard ratio [HR], 0.57; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.18–1.79; p = 0.336). Additionally, age, sex, tumor pathology, and tumor volume were not significant variables (p ≥ 0.05) (Table 2).
The mean regrowth rate was lower in the SRS group (0.18 ± 0.29 mm/mo) than in the observation group (0.33 ± 0.40 mm/mo). In contrast, the median (range) regrowth rate was lower in the observation group (0.10 mm/mo[-0.12 to 1.12]) than in the SRS group (0.11 mm/mo [-0.12 to 0.85]). However, there was no significant difference in the regrowth rates between the SRS and observation groups (p = 0.784) (Fig. 3).
A total of 18 patients underwent SRS: SRS in 8 patients from the SRS group and delayed SRS in 10 patients from the observation group, in whom tumor regrowth occurred before SRS. After SRS, 1 patient from the observation group was lost to follow-up. Therefore, 17 patients were included in the analysis comparing tumor size before and after SRS. The mean diameter ± SD of the 17 residual tumors was significantly higher post-SRS (26.3 ± 9.9 mm) than pre-SRS (22.2 ± 7.9 mm) (p = 0.004). In the SRS group (N = 8), the mean diameter ± SD was significantly higher post-SRS (26.4 ± 10.2 mm) than pre-SRS (20.4 ± 6.5 mm) (p = 0.023). In the observation group who underwent delayed SRS (N = 9), the mean diameter ± SD was significantly higher post-SRS (26.3 ± 10.4 mm) than pre-SRS (23.7 ± 9.0 mm) (p = 0.039) (Fig. 4).
A 67-year-old-woman presented with a tingling sensation and numbness in her left arm, hand, and foot for 2 months. Neurologic examination showed hypoesthesia of the upper and lower extremities and decreased motor power (grade 4 of both hands grasping on the Medical Research Council scale). Findings from deep tendon reflex testing were normal. Hoffman signs were positive on both hands. Gadolinium-enhanced MRI demonstrated a homogenously enhanced, dumbbell-shaped tumor of approximately 4 cm at the left C2–3 level (Fig. 5A). Surgery (C2–3 total laminectomy and tumor removal without instrumentation) was performed. The intraspinal portion of the tumor was grossly totally resected. However, residual tumor (the foraminal and extraforaminal portions) was identified on postoperative MRI (Fig. 5B). The biopsy result confirmed the tumor was a schwannoma. Follow-up MRI (1 year after the operation) showed regrowth of the tumor with cord compression (Fig. 5C). SRS was applied to treat the residual regrowing tumor. The prescribed dose was 21 Gy in 3 fractions. On follow-up MRI at 5 years postoperatively, the residual tumor had increased to approximately 4 cm, comparable to that before the operation (Fig. 5D). In addition, the patient complained of aggravated tingling sensations and gait disturbance. Therefore, it was decided to perform revision surgery. The tumor was grossly totally removed with left C2–3 total facetectomy with C2–3 (right)-4 pedicle screw fixation (Fig. 5E). Postoperative MRI showed no residual tumor (Fig. 5F).
In this study, SRS did not decrease the tumor regrowth rate significantly (HR, 0.57; 95% CI, 0.18–1.79; p = 0.336). Moreover, although SRS was performed to prevent or suppress the regrowth of residual tumors, the mean tumor diameter increased significantly after SRS (p = 0.004). In addition, 5 of 17 patients (29.4%) who underwent SRS received a secondary operation due to increased residual tumor size and aggravated symptoms. These findings are in contrast to those of previous studies that reported the efficacy of SRS for benign spinal tumors (Table 3) [6,7,10,11,17,21,22]. Although tumor sizes increased, as observed on MRI, this could be attributed to secondary degeneration, such as cystic changes following SRS, rather than to tumor regrowth. In intracranial schwannoma, tumor enlargement with cystic changes following SRS has been reported [18-20,23]. In addition, some hypotheses could be adopted from vestibular schwannoma because of its histological similarity to dumbbell tumor. In vestibular schwannoma, regrowth following SRS has been reported [24,25]. Several hypotheses for regrowth following SRS have been proposed for vestibular schwannoma: (1) radiation-induced tumor swelling, (2) delayed radiation injury, which causes chronic intratumoral bleeding, and (3) a biological response to radiation [26-29]. However, we could not find an article that reported an increased size of a spinal cord tumor following SRS, except for the study of Dodd et al. [21] Dodd et al. [21] briefly mentioned a transient increase of intradural extramedullary spinal tumor size due to radiation-induced tumor swelling after Cyberknife radiosurgery. Further studies are needed to elucidate whether these hypotheses could also apply to cervical dumbbell tumors.
We also evaluated the preoperative and postoperative tumor size as risk factors for residual tumor regrowth. In multivariable Cox regression analysis, the preoperative and postoperative tumor volume were not significant risk factors for residual tumor regrowth. This result aligns with those of previous studies [4,30].
The concept of SRS was first introduced by Lars Leksell in 1951. Initially, the SRS target was limited to intracranial lesions, using a stereotactic head frame. However, with advancements of technology, radiosurgery has been applied to extracranial lesions, including those in the spine. SRS, which involves hypofractionated, high-dose irradiation of an extracranial lesion [31], has been used as the primary treatment for tumors in patients deemed poor surgical candidates due to old age, poor general condition, or comorbidities. In 2006, Dodd et al. [21] treated 51 patients with 55 benign spinal tumors using Cyberknife radiosurgery as a primary treatment modality because of medical comorbidities, multiple lesions, or strong patient preferences. They followed up 28 of 51 patients during a mean follow-up of 36 months and found that the tumor volume was stable in 61% and it decreased in 39% [21]. In addition, residual tumors following incomplete resection were another indication for SRS [10,11].
Previous studies suggested that postoperative SRS would be an effective treatment modality for residual spinal tumors following surgery [9-11]. However, these studies were qualitative in nature. No previous studies analyzed the efficacy of SRS for residual cervical dumbbell tumors quantitatively in terms of the tumor regrowth rate and tumor size changes before and after SRS. To the best of our knowledge, our study is the first to quantitatively analyze the efficacy of SRS.
In our institutions, osteolysis of the facet joint was one of the important factors in determining the surgical strategy for cervical dumbbell tumors. If osteolysis of the facet was present at the index level, tumors were grossly totally removed, and screw fixation and fusion were performed. On the contrary, if the facet joint was intact without osteolysis, we grossly totally removed the intraspinal portion, but when the foraminal portion remained, postoperative SRS was performed. As spine surgeons, we wanted to preserve the facet joint without instrumentation if possible. However, we now believe it would be better to resect the tumor maximally, including the foraminal portion at the initial operation, then observe the outcome. Postoperative SRS for residual cervical dumbbell tumors did not show significant efficacy in preventing the regrowth of the tumors. In light of this result, we believe that achieving gross total resection of a cervical dumbbell tumor during the initial operation is more important than performing postoperative adjuvant SRS.
Nakamura et al. [3] reported that 57 cases of cervical dumbbell tumor were grossly totally resected, and no tumor recurred. In contrast, 2 of 13 subtotal resections underwent re-operation due to aggravation of neurological symptoms by the regrowth of residual tumors. Ryu et al. [30] reported that 1 of 59 cases of cervical dumbbell tumor following gross total resection regrew, and 9 of 31 cases of cervical dumbbell tumor following subtotal resection regrew. Statistical analysis showed a significant difference in the proportion (p = 0.002) [30]. These results show the importance of gross total resection of cervical dumbbell tumors.
Kitamura et al. [32] previously reported that residual tumors with a surgical margin distal from the entrance of the neural foramen were less likely to regrow. They categorized the surgical margin as follows: zone 1, in the spinal canal; zone 2, at the entrance of the neural foramen, touching the posterolateral corner of the intervertebral disc or vertebral body; and zone 3, in the neural foramen distal from its entrance. When the surgical margin was classified as zone 3, the regrowth incidence of the tumor was significantly lower than that for zones 1 and 2 (p = 0.007). In other words, the risk of regrowth of residual cervical dumbbell tumor is lower after maximal resection, even if it is a subtotal resection. Therefore, although subtotal resection is inevitable in various situations such as a large extraforaminal portion, a high risk of VA injury, or multiple cervical nerve root involvement, it is important to resect the tumor as much as possible while preserving the neurovascular structure.
Therefore, our results indicate that SRS will not prevent regrowth of residual cervical dumbbell tumors or the need for a secondary operation due to tumor regrowth.
There are some limitations to concluding that SRS is ineffective. First, the nature of this retrospective study could lead to biased results because SRS was performed at the discretion of each surgeon. However, there were no significant differences in demographics between the SRS and observation groups (Table 1). Second, only 28 patients were included, which is a relatively small sample size and may not be sufficient to statistically verify the efficacy of SRS. The statistical analysis did not show any significant difference between the SRS and observation groups. However, the mean regrowth rate of the SRS group (0.18 ± 0.29 mm/mo) was lower than that of the observation group (0.33 ± 0.40 mm/mo). Therefore, if more patients were included in the study, the results may have reached statistical significance. This is because, even though SRS was effective in practice, statistical significance may not be obtained if the number of patients is too small.
Third, when measuring the size of residual tumors on the first postoperative MRI, it may be difficult to distinguish the residual tumor from hematoma and postoperative changes. Therefore, there could be a discrepancy between the actual and the measured size of the residual tumor. Furthermore, the criterion for regrowth, defined as a ‘2-mm increase in diameter’, may carry different clinical implications depending on the tumor size, particularly in terms of proportional increase. In addition, the tumor diameter on an axial MRI image does not reflect the tumor size in the sagittal plane. This can lead to a difference between the tumor diameter on the axial image and the actual 3-dimensional tumor volume. Although the tumor volume was calculated using the ellipsoid formula, this method assumes an ellipsoidal shape. Therefore, calculated tumor volume may differ from true tumor volume because of its dumbbell shape.
Lastly, Ki-67 was not evaluated in the study. Sohn et al. [4] reported a higher Ki-67 index in spinal schwannoma with regrowth. However, we could not include Ki-67 in the study due to the unavailability of Ki-67 for the majority of patients. Further studies are warranted to investigate the association between Ki-67 and the regrowth of residual cervical dumbbell tumors.
In our study, SRS did not significantly reduce the regrowth rate of residual cervical dumbbell tumors compared to the observation group. Moreover, tumor diameters increased significantly despite undergoing SRS. Hence, we believe that achieving gross total resection during the initial operation is more important than postoperative adjuvant SRS. Even if complete resection is not achievable, maximal tumor removal in the initial surgery is essential to prevent tumor recurrence rather than relying on subsequent SRS.
NOTES
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Previous Presentation: This material was presented as an oral abstract at the 15th Korean Cervical Research Society Regular Academic Conference held at the Sejong Convention Center on June 18, 2022 and the 2nd KOREAN SPINE ONCOLOGY RESEARCH SOCIETY (NS) – KOREAN SOCIETY OF SPINE TUMOR (OS) joint conference on August 27, 2022.
Fig. 2.
Kaplan-Meier survival curves of each group. No significant difference was observed between the 2 groups (p=0.81). SRS, stereotactic radiosurgery.
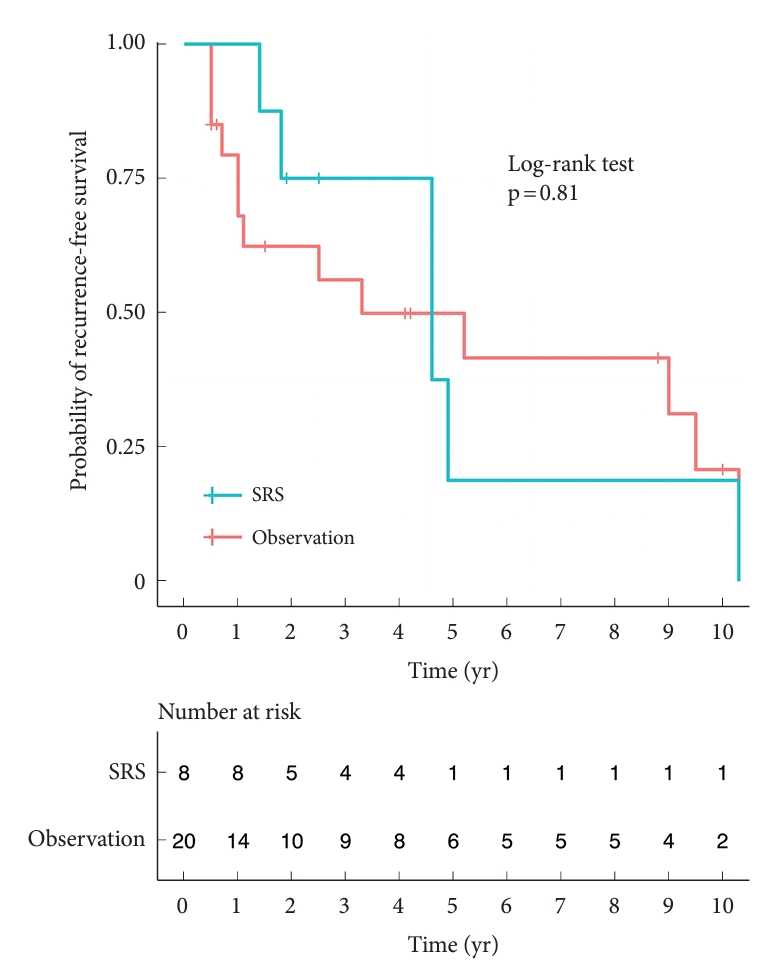
Fig. 3.
The mean regrowth rate was higher in the observation group than in the stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) group. However, there was no significant (p=0.784) between-group difference. The mean regrowth rate ± standard deviation of each group is shown in the graph. SRS, stereotactic radiosurgery.

Fig. 4.
Mean tumor sizes were increased despite performing stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS). When comparing tumor diameters before and after SRS, the mean diameter was significantly higher post-SRS than pre-SRS in the total (p=0.004), SRS in SRS group (p=0.023), and delayed SRS in observation group (p=0.039). The mean tumor diameter ± standard deviation of each group is shown in the graph. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, statistically significant difference.
Fig. 5.
A 67-year-old-woman presented with a tingling sensation and numbness in her left arm. (A) Gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) demonstrating a homogenously enhanced, dumbbell-shaped tumor of approximately 4 cm at the left C2–3 level. (B) Residual tumor (foraminal and extraforaminal portions) on postoperative MRI. (C) Regrowth of the tumor with cord compression on follow-up MRI (1 year after the operation). (D) Despite stereotactic radiosurgery, an increase in residual tumor size, comparable to that before operation, was observed on follow-up MRI at 5 years after the operation. (E) Revision surgery was performed, gross total resection of the tumor with left C2–3 total facetectomy with C2–3 (right)-4 pedicle screw fixation. (F) No residual tumor is visible on postoperative MRI.

Table 1.
Demographics and characteristics of cervical dumbbell tumors
Table 2.
Cox regression analysis for regrowth of residual cervical dumbbell tumor following surgery
Table 3.
Summary of previous studies on SRS for benign spinal tumors
| Study | No. of lesions | Pathologic findings | Modality | Radiation dose (cGy) | Recurrence rate† |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dodd et al. [21] (2006) | 55 | 16 Meningiomas | CyberKnife | 2,031 (1,600–3,000) | 3/55 (5.5%) |
| 30 Schwannomas | 1,264 (500–2,100) | ||||
| 9 Neurofibromas | 1,061 (700–2,000) | ||||
| Gerszten et al. [7] (2008) | 73 | 13 Meningiomas | CyberKnife | 2,125 (1,750–2,500) | 0/13 (0%) |
| 35 Schwannomas | 2,203 (1,750–2,500) | 3/35 (8.6%) | |||
| 25 Neurofibromas | 2,130 (1,500–2,500) | 0/25 (0%) | |||
| Selch et al. [17] (2009) | 25 | 8 Schwannomas | Novalis | 1,212 (1,200–1,500) | 0/25 (0%) |
| 8 Neurofibromas | |||||
| 9 No pathologic confirmation | |||||
| Sachdev et al. [6] (2011) | 103 | 32 Meningiomas | CyberKnife | 2,057 (1,600–3,000) | 1/103 (1.0%) |
| 47 Schwannomas | 1,874 (1,400–2,400) | ||||
| 24 Neurofibromas | 1,913 (1,600–2,100) | ||||
| Shin et al. [22] (2015) | 92 | 69 Schwannomas | Novalis | Median 1,300 | 3/92 (3.3%) |
| 23 Neurofibromas | Median 2,500 for large tumors |
REFERENCES
1. Asazuma T, Toyama Y, Maruiwa H, et al. Surgical strategy for cervical dumbbell tumors based on a three-dimensional classification. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2004;29:E10-4.


2. Ozawa H, Kokubun S, Aizawa T, et al. Spinal dumbbell tumors: an analysis of a series of 118 cases. J Neurosurg Spine 2007;7:587-93.


3. Nakamura M, Iwanami A, Tsuji O, et al. Long-term surgical outcomes of cervical dumbbell neurinomas. J Orthop Sci 2013;18:8-13.


4. Sohn S, Chung CK, Park SH, et al. The fate of spinal schwannomas following subtotal resection: a retrospective multicenter study by the Korea spinal oncology research group. J Neurooncol 2013;114:345-51.



5. Chin AL, Fujimoto D, Kumar KA, et al. Long-term update of stereotactic radiosurgery for benign spinal tumors. Neurosurgery 2019;85:708-16.



6. Sachdev S, Dodd RL, Chang SD, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery yields long-term control for benign intradural, extramedullary spinal tumors. Neurosurgery 2011;69:533-9.



7. Gerszten PC, Burton SA, Ozhasoglu C, et al. Radiosurgery for benign intradural spinal tumors. Neurosurgery 2008;62:887-96.



8. Chang UK, Rhee CH, Youn SM, et al. Radiosurgery using the Cyberknife for benign spinal tumors: Korea Cancer Center Hospital experience. J Neurooncol 2011;101:91-9.



9. Murovic JA, Charles Cho S, Park J. Surgical strategies for managing foraminal nerve sheath tumors: the emerging role of CyberKnife ablation. Eur Spine J 2010;19:242-56.




10. Gerszten PC, Burton SA. Clinical assessment of stereotactic IGRT: spinal radiosurgery. Med Dosim 2008;33:107-16.


11. Hwang L, Okoye CC, Patel RB, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for benign spinal tumors: meningiomas, schwannomas, and neurofibromas. J Radiosurg SBRT 2019;6:167-77.


12. Feldman JP, Goldwasser R, Mark S, et al. A mathematical model for tumor volume evaluation using two-dimensions. J Appl Quant Methods 2009;4:455-62.
13. Murovic JA, Gibbs IC, Chang SD, et al. Foraminal nerve sheath tumors: intermediate follow-up after Cyberknife radiosurgery. Neurosurgery 2009;64(2 Suppl):A33-43.

14. Kim HJ, Kim W. Method of tumor volume evaluation using magnetic resonance imaging for outcome prediction in cervical cancer treated with concurrent chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Radiat Oncol J 2012;30:70-7.



15. Le Fèvre C, Sun R, Cebula H, et al. Ellipsoid calculations versus manual tumor delineations for glioblastoma tumor volume evaluation. Sci Rep 2022;12:10502.


16. Bozorg Grayeli A, Kalamarides M, Ferrary E, et al. Conservative management versus surgery for small vestibular schwannomas. Acta Otolaryngol 2005;125:1063-8.


17. Selch MT, Lin K, Agazaryan N, et al. Initial clinical experience with image-guided linear accelerator-based spinal radiosurgery for treatment of benign nerve sheath tumors. Surg Neurol 2009;72:668-74.


18. Hasegawa T, Kida Y, Yoshimoto M, et al. Evaluation of tumor expansion after stereotactic radiosurgery in patients harboring vestibular schwannomas. Neurosurgery 2006;58:1119-28.



19. Murakami K, Jokura H, Kawagishi J, et al. Development of intratumoral cyst or extratumoral arachnoid cyst in intracranial schwannomas following gamma knife radiosurgery. Acta Neurochirurgica 2011;153:1201-9.



20. Nishioka K, Abo D, Aoyama H, et al. Stereotactic radiotherapy for intracranial nonacoustic schwannomas including facial nerve schwannoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2009;75:1415-9.


21. Dodd RL, Ryu MR, Kamnerdsupaphon P, et al. CyberKnife radiosurgery for benign intradural extramedullary spinal tumors. Neurosurgery 2006;58:674-85.



22. Shin DW, Sohn MJ, Kim HS, et al. Clinical analysis of spinal stereotactic radiosurgery in the treatment of neurogenic tumors. J Neurosurg Spine 2015;23:429-37.


23. Shirato H, Sakamoto T, Takeichi N, et al. Fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for vestibular schwannoma (VS): comparison between cystic-type and solid-type VS. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2000;48:1395-401.


24. Whitmeyer M, Brahimaj BC, Beer-Furlan A, et al. Resection of vestibular schwannomas after stereotactic radiosurgery: a systematic review. J Neurosurg 2021;135:881-9.

25. Wise SC, Carlson ML, Tveiten ØV, et al. Surgical salvage of recurrent vestibular schwannoma following prior stereotactic radiosurgery. Laryngoscope 2016;126:2580-6.



26. Iwai Y, Yamanaka K, Yamagata K, et al. Surgery after radiosurgery for acoustic neuromas: surgical strategy and histological findings. Neurosurgery 2007;60(2 Suppl 1):ONS75-82. discussion ONS82.

27. Nagano O, Higuchi Y, Serizawa T, et al. Transient expansion of vestibular schwannoma following stereotactic radiosurgery: clinical article. J Neurosurg 2008;109:811-6.

28. Nakamura H, Jokura H, Takahashi K, et al. Serial follow-up MR imaging after gamma knife radiosurgery for vestibular schwannoma. Am J Neuroradiol 2000;21:1540-6.


29. Prasad D, Steiner M, Steiner L. Gamma surgery for vestibular schwannoma. J Neurosurg 2000;92:745-59.


30. Ryu SM, Lee SH, Lee KM, et al. Subtotal resection of cervical schwannomas and growth rate of residual tumors. J Neurosurg Spine 2019;30:794-800.


- TOOLS
-
METRICS

-
- 1 Crossref
- Scopus
- 1,619 View
- 62 Download
-
Journal Impact Factor 3.8
SURGERY: Q1
CLINICAL NEUROLOGY: Q1