- Search
| Neurospine > Volume 17(1); 2020 > Article |
|
|
Abstract
Instrumented spine procedures have been performed for decades to treat a wide variety of spinal disorders. New technologies have been employed to obtain a high degree of precision, to minimize risks of damage to neurovascular structures and to diminish harmful exposure of patients and the operative team to ionizing radiations. Robotic spine surgery comprehends 3 major categories: telesurgical robotic systems, robotic-assisted navigation (RAN) and virtual augmented reality (AR) systems, including AR and virtual reality. Telesurgical systems encompass devices that can be operated from a remote command station, allowing to perform surgery via instruments being manipulated by the robot. On the other hand, RAN technologies are characterized by the robotic guidance of surgeon-operated instruments based on real-time imaging. Virtual AR systems are able to show images directly on special visors and screens allowing the surgeon to visualize information about the patient and the procedure (i.e., anatomical landmarks, screw direction and inclination, distance from neurological and vascular structures etc.). The aim of this review is to focus on the current state of the art of robotics and AR in spine surgery and perspectives of these emerging technologies that hold promises for future applications.
Instrumented spine procedures have been performed for many decades to treat a variety of spinal disorders. In the last decade, the volume of elective instrumented lumbar spinal fusion procedures has steeply increased among patients aged over 65 [1,2]. Such increment is mainly motivated by the higher demand of instrumented spine surgery for lumbar stenosis and spondylolisthesis, due to both the aging population and a lower threshold to operate on older patients [3-6].
For this reason, a great consensus to find new technologies to perform lumbar spinal fusion emerged over the last decades [7,8].
Indeed, spine surgery has been revolutionized by technology in the past 20 years. Innovation has been mainly focused on minimally invasive spine surgery (MISS) [9,10]. MISS was principally conceived for the need to perform invasive procedures with a high degree of precision while minimizing the risk of damaging contiguous neurovascular structures. In addition, further implementations have facilitated the surgical access to deep structures, favoring operating room dynamics and logistics and diminishing harmful exposure to ionizing radiations [11].
Robotic spine surgery comprehends 3 different categories [12]: telesurgical robotic systems, robotic-assisted navigation (RAN) and virtual augmented reality (AR) systems.
Telesurgical robotic systems include devices that can be operated from a remote command station utilizing a hand-held control, allowing to perform surgery via instruments directly manipulated by the robot. The main advantage of these systems is to perform surgery on the patient being far from the operating table, even remotely. The first telesurgical robotic system introduced on the market was the da Vinci (Intuitive Surgical Inc., Sunnyvale, CA, USA) [13].
RAN technologies employ the robotic guidance of surgeonoperated instruments utilizing pre- and/or intraoperative imaging in real time. However, no robotic control over instrumentation is needed. RAN has been originally used in spine surgery for the placement of lumbar pedicle screws in spinal fusion [14]. Still, pedicle screw insertion is not the only field of application. Indeed, RAN has been proved to be a safe technique for spinal decompression, oncologic spine surgery, and MISS including cage positioning [9,15-18].
AR is a new promising technology consisting in dedicated software and hardware capable of showing images directly onto special lenses or monitors, hence allowing the surgeon to visualize key information about the patient and the procedure in real time.
This review aims to describe the current state of the art of robotics and AR systems in spine surgery. The main systems already available and under development are summarized in the context of clinical applications and published results.
Initially approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for laparoscopic surgery, the da Vinci (Fig. 1) has been subsequently utilized in different fields such as cardiac surgery, thoracic surgery, and urology. The da Vinci system allows the surgeon to operate from a control station, far from the operatory table. The system allows the surgeon to have a 3-dimensional vision of the operatory field and can also give a magnification of up to 10x. Other advantages are tremor filtering, limitless wrist range of motion and improved surgeon ergonomics. With a stable internet connection, it is even possible to perform an operation remotely without the physical presence of the surgeon in the operating room [19]. In spine surgery, the da Vinci has been used for laparoscopic anterior lumbar interbody fusion in 2 small reports with good results [20,21]. Using the robot, the visualization of the disc space and surrounding structures was considered superior compared to the traditional laparoscopic approach [21]. The main limitations of the da Vinci include the high costs of the surgical setup and the steep learning curve leading to an increase of operative time. Moreover, the da Vinci system is not cleared by the FDA for spinal surgery and therefore only a few cases and evidences are available.
SpineAssist (Mazor Robotics Inc., Caesarea, Israel) was developed and tested in 2004 [22] and became the first FDA-approved robot for spine surgery. The system needed to be fixed to the spinous processes of the patient or attached to a frame triangulated by percutaneously placed guidewires for MISS. The system setup relied on a preoperative computer tomography (CT) scan to perform the operative planning. Subsequently, the robot evaluated the position of the pedicles and indicated the right trajectories of the instruments, such as wires or pedicle screws. The procedure was possible since the SpineAssist merged the preoperative CT scan with intraoperative fluoroscopy. The precision of the SpineAssist was very high: with its 6 degrees of freedom, it ensured less than 1-mm deviation of the implant from the preoperative template, resulting in 98% of correct screw placement [23]. Additionally, the time of exposure to ionizing radiations was decreased up to 50% compared to free-hand (FH) procedures [24]. However, the main limitation of this system included the necessity to employ pins and needles fixed to specific anatomical landmarks. Skidding and other dislocation of the cannula was also reported [25].
Renaissance was the second-generation robotic system for spine surgery developed by Mazor Robotics Inc. (Caesarea, Israel) and released in 2011 to replace SpineAssist. Apart from being smaller and lighter, the Renaissance system was improved with better ergonomics, enhanced sensitivity and a 10 times faster software processing with upgraded image recognition algorithms [26]. After loading the preoperative CT scan of the patient onto the platform, the system built up a 3-dimensional (3D) reconstruction of the spine with the possibility to select the desired vertebral segments, type of intervention, and characteristics of the instrumentation. Following the choice between percutaneous or open surgical access, fluoroscopic images were required in order to be matched with preoperative CT. Subsequently, based on acquired data, the computer determined the correct access point and the robot proceeded with its localization. Besides transpedicular screw placement, the Renaissance system was utilized for spine tumor biopsies and vertebro-kyphoplasties. Overall, the robot demonstrated to be reliable and accurate with a 98.9% rate of successful screw placement [27]. In a small randomized controlled trial, Hyun et al. [28] compared MISS transpedicular screw placement performed with the classical fluoroscopy-guided technique versus the placement performed through Renaissance. The use of robotic guidance resulted in a 100% accurate screw placement, while 2 pedicle breaches and one facet violation occurred in the fluoroscopy-guided group. Furthermore, radiation exposure and length of hospital stay were significantly reduced in the robotic group. However, some authors reported the risk of screw misplacement due to “skiving” of the drill tip or trocar along the side of the facet [29], an issue already noticed with the SpineAssist.
Mazor X was introduced in 2016 and it is the latest robotic system for spine surgery from Mazor Robotics Inc. (Caesarea, Israel). This new model is an upgrade of the previous versions, assembled after the experience acquired by more than 1,000 procedures performed with the SpineAssist and Renaissance. The Mazor X (Fig. 2) utilizes a fully automatic robotic arm which obviates the need for the patient-mounted track utilized by previous models [30]. Mazor X allows for preoperative or intraoperative planning and robotic execution of multiple trajectories. The robot is anchored to the operating bed and connected to the patient’s skeletal anatomy with a rigidly affix that is less invasive than the previous ones. There is no rail where the robot can move, but an external workstation functioning as a robotic arm. With an innovative imaging cross-modality registration process, each vertebral body is registered independently. The robotic guidance system analyses and pairs images from different modalities, such as matching a preoperative CT with intraoperative fluoroscopy or 3D surgical imaging, including images captured at different times and on different anatomical planes. A new feature introduced in this system is a 3D real-time camera able to perform a volumetric assessment of the surgical field so as to self-detect its location and avoid collisions with other components of the system. Moreover, the robot is able to process images acquired through preoperative CT or other imaging modalities in order to segment out individual vertebral bodies, providing 3D axial, coronal, and sagittal slice data to assist the surgical planning [31]. Recent reports have confirmed the accuracy of the system, with a 98.7% rate of grade I (i.e., no breach or deviation) screw placement and a mean time of screw insertion of 3.6 minutes, which reduced both operative time and radiation exposure. In addition, authors reported a favorable learning curve compared to older versions of the system [32].
Recently, Mazor Robotics Inc. has been acquired by Medtronic (Minneapolis, MN, USA) and the Mazor X system has been implemented with Medtronic StealthStation technology. The upgraded Mazor X Stealth Edition comes with a surgical navigation system capable of interfacing with multiple imaging modalities, including CT, magnetic resonance imaging, C-arms, and O-arms. This allows a 3D reconstruction of the patient’s spinal anatomy, which can be explored live and on different layers on a touch screen. Based on preoperative and intraoperative imaging, together with optical and electromagnetic sensors, surgical instruments are tracked in real time in respect of anatomical landmarks. Furthermore, surgical trajectories can be simulated and stored prior or during surgery [33]. As the Mazor X Stealth Edition was released only at the beginning of 2019, no study is currently available regarding its application.
ExcelsiusGPS (Globus Medical, Inc., Audubon, PA, USA) is a robotic system approved by FDA and CE-marked for spine surgery (Fig. 3). Instruments are positioned and screws are placed under navigation through the guidance of a rigid robotic arm that precisely aligns to the pedicles and the preplanned direction. ExcelsiusGPS relies on the use of intraoperative CT or the combination of preoperative CT images and intraoperative 2-dimensional (2D) or 3D images, which are obtained with stereotactic arrays placed bilaterally at the posterior superior iliac spines. The real core of the system is the software that provides a real-time visualization of instrument positioning and screw placement in respect to patient’s anatomy. Moreover, the system is equipped with sensors able to detect drill skiving or sliding of the reference frame, as well as to automatically compensate for patient movements [34]. ExcelsiusGPS was validated in a cadaveric study demonstrating a 100% accuracy of screw placement with no breach > 2 mm, with reduced screw insertion time and radiation exposure compared to the conventional approaches [35]. Huntsman et al. [36] used the robot to place pedicle screws in 100 cases and found that successful screw placement occurred with a rate of 99% and a 0% chance of reintervention. Similarly, Godzik et al. [37] showed in their study an accuracy of 96.6% in the placement of 116 screws on 28 patients. Another recent investigation conducted by Benech et al. [38] reported the results on 53 patients undergoing spine surgery with pedicle and cortical screws placement using the ExcelsiusGPS. According Gertzbein and Robbins classification system based on CT imaging, they found that 98.3% were graded A (screw completely in the pedicle) or B (breach< 2 mm), 1.0% screws were graded C (breach< 4 mm), and only 0.7% screws were graded D (breach< 6 mm). In a similar study from Vardiman et al [39], 348 screws placed with navigated robotic assistance resulted in a high level of accuracy (97.7% grades A and B).
ROSA Spine (Medtech, Montpellier, France) is a freestanding robotic assistant composed of an arm and a navigation camera with a floor-flexible base which does not need to be attached to the patient. Similar to Mazor X, it is equipped with a stereoscopic camera to track patient movements and readjust robot position in real time, providing an accurate and safe pedicle screw placement and avoiding the risk of neurological injuries [40]. A preoperative CT is needed for the robot setup. Subsequently, after positioning a reference pin in the iliac wing and a fiducial box held by the robotic arm, images are acquired by a 3D or a 2D intraoperative imaging systems thus allowing the ROSA to build up a 3D reconstruction of patient’s anatomy. It is then possible to merge preoperative and intraoperative scans in order to plan the surgical trajectory, along which the robot automatically aligns. A guide-tube needle is placed at the posterior aspect of the vertebral body, serving as a reference for the insertion of a wire which guides the placement of transpedicular screws [41]. Reported results are still limited but very promising. Indeed, in a perspective case-matched study, ROSA reached an accuracy of 97% in screw placement compared with an accuracy of 92% in the FH control group [42].
Differently from other robotic systems, TianJi (Beijing Tinavi Medical Technology Co., Beijing, China) does not need bone fixation. It is built with an image-navigated robotic positioning platform including a robotic arm, an optical tracking system, and a robotic workstation. During the procedure, images obtained intraoperatively by a C‐arm are uploaded into the robotic workstation and a 3D reconstruction is created. Subsequently, the planning of the screw orientation is directly performed on the workstation by the surgeon and the robotic arm with a guidance cannula automatically moves to the planned position. In order to check for optimal pin trajectories, a fluoroscopic rescan by C‐arm is acquired and followed by definitive screw placement. TianJi was used in both oblique lumbar interbody fusion (OLIF) and transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion surgeries. Wu et al. [43] performed OLIF using this system on 10 patients with good results, with 71% of the screws being graded A and 25% graded B according to Gertzbein and Robbins classification, concluding that the robot granted a high level of accuracy for screw insertions and a high level of safety. Moreover, the TianJi system was successfully utilized for transpedicular screw placement at the thoracolumbar region in a prospective randomized controlled trial, which showed that 95.3% of the screws were perfectly positioned (grade A), 3.4% were graded B and the remaining few cases C and D according to Gertzbein and Robbins classification. In addition, the use of the robot resulted in reduced blood loss and surgeon exposure to ionizing radiations when compared to the conventional FH techniques [44]. Furthermore, the TianJi was used to perform screw internal fixation in the upper cervical spine (C1 and C2) with excellent results [45,46]. In a randomized controlled study, 98.3% of the screws were graded A with minimal deviation in respect to the preplanned trajectory [47].
Brainlab (Munich, Germany) has recently released a passive robotic arm provided with 7 degrees of freedom that can be implemented with a specific module for spine surgery (Fig. 4). The system works together with the manufacturer’s major navigation systems and it is provided with a rigid affix that is safely anchored to the bone in order to allow passive precise positioning and alignment along a preplanned drilling trajectory. Moreover, an automatic robotic alignment module with a trackable trocar for drilling preparation will implement the system later this year. The use of Cirq has been successfully reported in a case of L3–4 instrumentation with percutaneous pedicle screws [48].
In the last decade, numerous AR systems have been described in the literature regarding the treatment of degenerative cervical, thoracic and lumbar spine diseases, vertebroplasty, kyphoplasty, spine deformities, and biopsies [49]. AR is based on computer-generated data that becomes superimposed on the real world through the projection of digital images on special screens or wearable devices, thus being able to “augment” the quantity of information that can be inferred by the sole surgeon’s eyes. For example, AR may assist surgeons in transpedicular screw placement by visualizing the patient anatomy and preplanned drilling trajectories on a visor in real time [49,50]. In 2 cadaveric studies, Elmi-Terander et al. [51] utilized a hybrid system involving both navigation and AR and thus called augmented reality surgical navigation (ARSN). After acquiring a 3D CT scan, a 3D reconstruction of the spine with automatic detection the pedicles allowed the planning of screw insertion. Subsequently, the surgical field recorded by 4 cameras with different angulations was shown on a high-definition monitor with the superimposition of 2D and 3D images of the vertebral segments together with the drilling trajectory [52]. The studies showed that ARSN resulted in a higher accuracy of thoracic pedicle screw placement compared to the FH technique without the need for intraoperative fluoroscopy or prior surgeon training [51]. Moreover, the system proved to be efficacious even when adopting a minimally invasive approach with the percutaneous placement of Jamshidi needles to determine screw entry point and orientation [52]. The use of ARSN was further utilized to automatically track instrument position in order to provide the surgeon with a real-time feedback of the instrument location. Such implementation led to an improved identification of the bone screw entry point and angulation, with a 97.4%–100% accuracy of the virtual screw placement as extrapolated from positional data [53]. Given the promising results, the same authors recently published the outcomes of a small prospective cohort study on 20 patients undergoing pedicle screw positioning with ARSN. In this study, 94.1% of the screws were perfectly placed in the pedicles, with a mean screw insertion time of 5.2±4.1 minutes [54]. Furthermore, the mean radiation exposure of the surgical staff was significantly lower due to the absence of intraoperative fluoroscopic imaging [55].
The same system was recently utilized in a pilot randomized clinical trial to test AR during percutaneous vertebroplasty. In this study, the virtual trajectory for the injection was superimposed to live images to guide vertebroplasty trocar placement. Such approach demonstrated to be technically feasible and accurate. Time for trocar deployment was longer compared to the traditional fluoroscopic approach but the radiation exposure was significantly lower in the experimental group [56].
Ma et al. [57] presented a unique AR navigation system equipped with ultrasound-assisted registration for transpedicular screw placement. The system was tested on both an agar phantom and sheep lumbosacral specimen: although using Kirschner wires, the system allowed to provide an acceptable accuracy with the advantage of a reduced radiation exposure.
Also Google (Mountain View, CA, USA) invested in AR with Google Glass: a miniaturized computer, projector, and prism screen, combined in a pair of glasses. The eyeglasses can project any image, such as navigation or neuromonitoring, directly in front of the surgeon’s eyes. Yoon et al. [58] used Google Glass during pedicle screw placement in a clinical study on 10 patients. Neuronavigation images were directly visualized on the headup display and resulted in slightly reduced screw placement times. Google Glass was also successfully used for 3D visualization of anatomical landmarks in sacroiliac joint screw placement in a cadaveric study [59].
HoloLens (Microsoft Corp., Redmond, WA, USA) is a headset able to project realistic virtual experiences onto the surrounding environment in association to enhanced information on real objects: such technology is referred as mixed reality. Indeed, the visor can show high-quality 3D images generated by a holographic computer in the visual field of the surgeon [60]. Agten et al. [61] tested the HoloLens on a sawbone spine phantom embedded in hardened opaque agar for lumbar facet joint injections. After acquiring a CT scan of the phantom, a 3D reconstruction was generated and loaded onto the headset. The model was then projected as a hologram in the surgeon’s visual field, who proceeded with needle insertion. Results showed that 97.5% of needle placements were successful and the procedure itself demonstrated to be significantly faster if compared to CT-guided injections. A similar experimental setup was utilized for lumbar pedicle screw placement simulated by Kirschner wires insertion. Visualization of the spine hologram through the HoloLens resulted in > 90% correct screw placement with faster insertion times [62-64] and no significant difference in accuracy between AR-navigated screw placement and conventional navigation [65]. Comparable outcomes were reported in a cadaveric study conducted by Urakov et al. [66] comparing the accuracy of screw placement with either AR or traditional fluoroscopic guidance. While no major breaches occurred under radiological assistance, the use of HoloLens was accompanied by 3 major medial breaches and 3 major inferior breaches out of 19 screws, suggesting that the system is promising but still needs considerable improvements [66]. Furthermore, HoloLens has also been tested for assisting rod bending during spinal instrumentation. After transpedicular screw placement in a sawbone spine model, a custom-made pointing device has been sequentially positioned on the head of each screw. After all screws were captured, each point was connected by a line, defining a rod template of the appropriate length and curvature in form of a 3D hologram that could be freely moved in the surrounding space. The use of AR resulted in significantly shorter rod bending time and accuracy of rod length compared to the conventional technique without AR [67].
The first and only AR headset that has received an FDA clearance for spine surgery is xvision (Augmedics, Arlington Heights, IL, USA). This wireless system is equipped with near-eye displays showing 3D navigation data including patient’s anatomy and instrument position directly onto the surgeon’s retina (Fig. 5). In a proof-of-concept cadaveric study, the use of xvision resulted in 98.9% percutaneous screw placement accuracy and reduced the need of continuous shift from the operating field to separate screens to visualize procedure-related key information [68].
The employment of AR has also found a possible application in microscope-based MISS. In fact, by using the heads-up displays of the operating microscope, a 3D representation of vertebrae and implants from preoperative imaging was superimposed to the microscope video and implemented with navigation in 2 recent studies on spinal tumors [69] and degenerative spine disease [70]. This approach greatly facilitated surgery due to intuitive understanding of the 3D anatomy and additionally yielded to a 70% reduction of effective dose radiation [69]. In addition, Umebayashi et al. [71] recently reported the use of AR in microscopic transvertebral anterior cervical foraminotomy and posterior cervical laminoforaminotomy: 2 minimally invasive although complex techniques requesting accurate planning and great surgical skills. During navigated surgery, O-arm imaging was used to build a 3D model of the patient’s vertebrae and the keyhole tunnel was marked and subsequently transferred to the microscope and merged with the live view, thus greatly facilitating the procedure. A similar system was also employed in a case of congenital vertebral deformity to accurately define resection volumes and osteotomy planes, in order to acquire a higher degree of precision and surgical safety [72].
Another device used in spine surgery is MicroOptical (MicroOptical Corp., Westwood, MA, USA): a head-up display used for visualizing intraoperative fluoroscopy during open reduction and internal fracture fixations and spinal pedicle screw placement in a study of 50 cases. The study demonstrated a reduction of surgical time since the surgeon had not to turn away from the patient to view the imaging monitor. Moreover, reduction of unprotected turn of the body minimized the risk of unwanted fluoroscopy radiation [73].
Due to its peculiar features, AR is also being discussed as a training tool. ImmersiveTouch (ImmersiveTouch Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) is a platform composed of a haptic instrument with trigger points and a high-resolution stereoscopic display that establish an AR environment in which the virtual patient, the virtual instruments and surgeon’s hands are represented. Such system has been tested to train fellows and residents in thoracic pedicle screw placement. After a practice session with fluoroscopic guidance, participants attended a test session without the aid of fluoroscopy during which AR-assisted transpedicular screw placement was assessed. Results showed a minor failure rate and a 15% rate of improvement between the 2 sessions, thus demonstrating the efficacy of the simulator [74]. In a similar training session on percutaneous spinal needle placement with the use of ImmersiveTouch, participants showed improvements in accuracy and reduction of fluoroscopy exposure after the first attempt using the simulator [75].
In the last decade, several robotic and AR systems for spine surgery have been released on the market and tested in numerous clinical studies. Although representing a promising technology with evident benefits for both patient care and surgical performance, such devices still raise several questions regarding handling, feasibility, and cost/benefit ratio. Major features, advantages and disadvantages, and field of application of aforementioned systems are summarized in Table 1.
Probably, the most important advantage of robotic surgery is lower radiation exposure, especially for the surgeon. It has been demonstrated that spine surgeons present a 40–50 times higher radiation exposure compared to other orthopaedic surgeons. Fomekong et al. [76] proved that the cumulative radiation exposure remained below measurable levels with the use of robotic systems. Similarly, Fan et al. [77] reported that the average fluoroscopy time for screw placement in RAN was 4.02±1.6 minutes vs. 8.89±3.1 using the FH technique. Roser et al. [78] found a trend toward decreased radiation time with robotic assistance, whereas Ringel et al. [25] reported similar intraoperative radiation times between the robotic-assisted and the FH methods. However, several variables, including the type of system, the surgeon’s learning curve and the difficulty of the case must be taken into account [79].
Moreover, robotic spine surgery gives the possibility to operate with a lower risk of neurovascular damage if compared to FH approaches, thanks to the use of motors and stabilizers [80].
As far as the reoperation rate is concerned, Kantelhardt et al. [81] demonstrated that only 1% of robotic procedures (including both percutaneous and open approaches) needed revision surgery, compared to the 12.2% reoperation rate showed for conventional procedures. Moreover, the study reported postoperative infections in 2.7% of the patients undergoing robot-guided procedures compared to 10.7% in open nonrobotic ones. Fan et al. [77] showed that under robotic guidance blood loss was also reduced (362±120 mL using RAN vs. 557±261 in FH procedures).
Kim et al. [82] documented a decrease in time to ambulation after robotic surgery, with an average of 39.7 hours for FH technique versus a mean of 36.2 hours using the Renaissance system. This was also reflected on the length of stay of patients operated with the use of robotic surgery: in fact, Hyun et al. [28] showed an average length of stay of 9.4 days for FH procedures vs. 6.8 days for robotic surgical procedures. Likewise, Fan et al. [80] demonstrated a decrease of number in postoperative days from 6.3±1.2 in the RAN group vs. 8.9±1.8 in the FH group.
The accuracy of screw placement has been widely investigated. In a recent meta-analysis, Yu et al. [14] compared 2,062 thoracic and lumbar pedicle screws implanted in 750 patients using RAN or FH technique. They found that only 4.6% of RAN screws breached > 2 mm from the predicted trajectory compared to 16% of screws placed by FH techniques. Therefore, significant superiority of robotic surgery in accuracy of screw placement compared with FH has been extensively demonstrated [83].
Despite many studies show the evidence of advantages of robotic surgery in timing, rates of infections and complications, there are evidences of the contrary. Indeed, some limitations of robotic spine surgery have been described. Regarding operative time, there is no uniform consensus. Wagner et al. [84] found that the mean operatory time was incremented in robotic surgery and associated with an increase in clinical complications. Contrariwise, in a study by Fan et al. [85] no significant differences in timing between RAN and FH were reported.
Other complications include hardware or software failure, cannula misplacement or skidding of the drilling tip on the pedicle surface due to peculiar bone anatomical configurations, a notorious defect encountered with SpineAssist and Renaissance [25,29,86]. The possibility of clinical complications such as hemothorax [87] and pulmonary embolism [88] was also reported.
Moreover, another issue with this technology is the demanding learning curve. In fact, this surgery needs a moderate quantity of time to be completely experienced. Schatlo et al. [89] reported that robotic spine surgery required almost 25 cases per surgeon to acquire a high degree of accuracy. In the first 10–20 cases there was the necessity of a skilled supervision to avoid mismatch during the screw placement, due to the risk of inaccuracy in inexperienced surgeons.
However, the biggest limitation of robots is the high cost of the instruments, which importantly reduces the possibility of a wider development of this surgery and consequently the average knowledge level for the single surgeon.
Thus, upcoming systems should be more competitive on the market while easier to approach and set up. Curexo Inc. (Seoul, Korea) is releasing CUVIS-spine, a robotic system for transpedicular screw placement able to reconstruct patient’s spinal anatomy upon either fluoroscopic 2D images or 3D images acquired with an O-arm and to guide screw insertion along preplanned trajectories within 1 mm of error range. In addition, real-time patient position monitoring can be used to correct the surgery plan in real time and can help reduce the radiation exposure for both the patient and the medical staff because only 2 or 3 X-ray images are needed for operation [90,91].
In a recent study, we described a novel robotic drilling system equipped with force and position sensors that are able to identify the specific vertebral bone layers by relying on tissue average impedance [92,93]. In this pilot study, we demonstrated that average impedance along the drilled tunnel closely correlated with bone mineral density calculated in Hounsfield units at the postprocedural CT scan of the tunnel, thus being predictive of the drill tip location without the need of additional radiation exposure (data not published yet).
Robotic systems and AR represent promising technologies. They have shown evident advantages in spine surgery as far as accuracy, radiation exposure, blood loss, hospital stay, and decreasing rate of complications are concerned. However, costs and learning curve are still too high to be routinely performed in all spinal procedures. For this reason, further cost-benefit analyses and larger clinical studies are necessary.
Fig. 1.
The da Vinci telesurgical system (Intuitive Surgical, Sunnyvale, CA, USA). Image courtesy of Intuitive Surgical Inc.
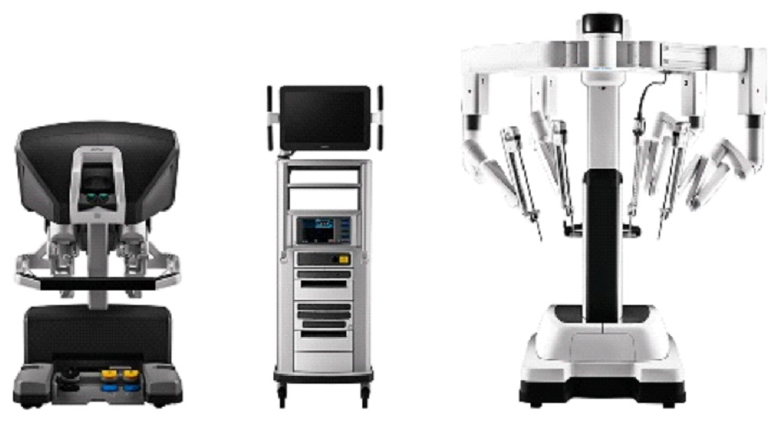

Fig. 2.
Transpedicular screw drilling using the Mazor X (Mazor Robotics Inc., Caesarea, Israel) robotic system.
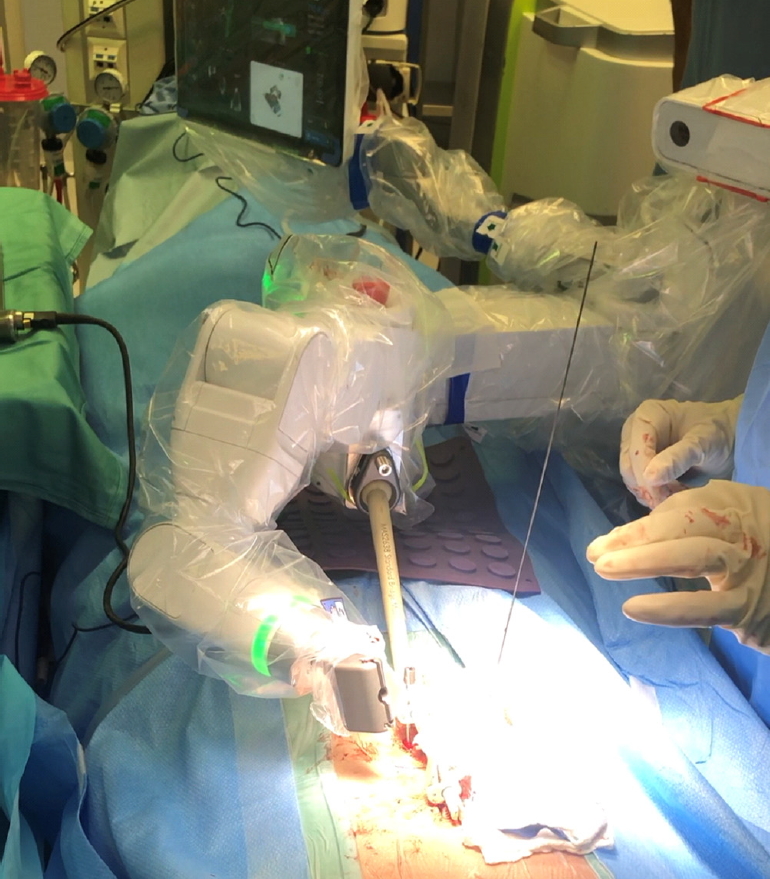
Fig. 3.
The ExcelsiusGPS (Globus Medical, Inc., Audubon, PA, USA) surgical system allows to guide pedicle screw insertion utilizing a patient-mounted reference array.
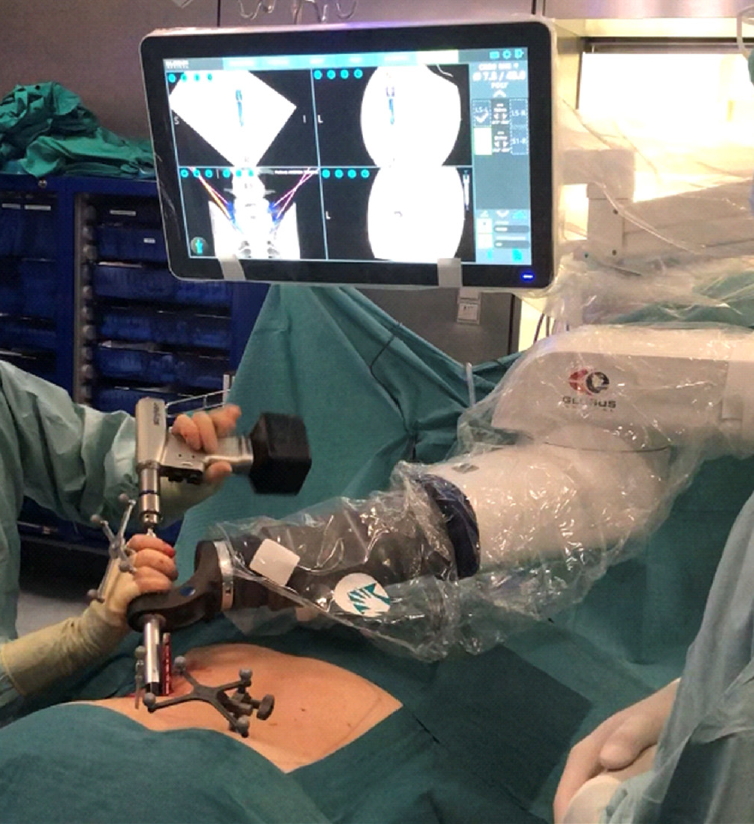
Fig. 4.
Cirq (Brainlab, Munich, Germany) robotic arm used for pedicle screw drilling in a case of L5–S1 grade II isthmic spondylolisthesis.
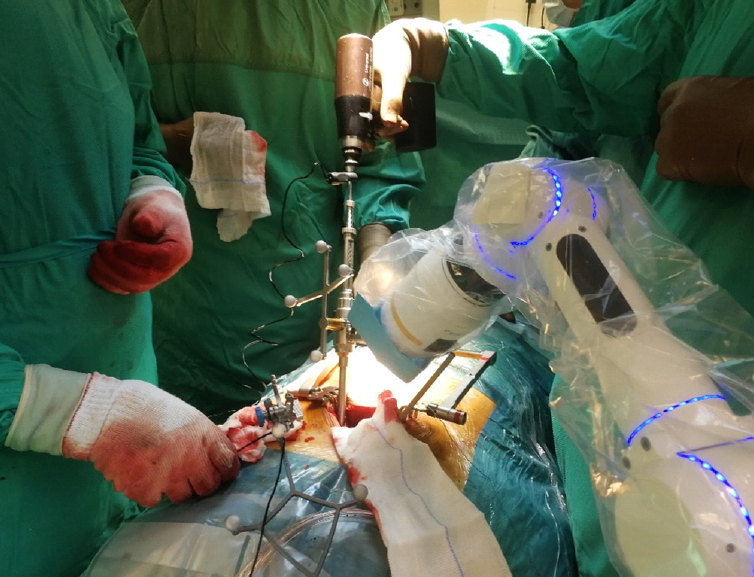
Fig. 5.
The xvision headset (Augmedics, Arlington Heights, IL, USA) utilized to assist percutaneous screw placement in a cadaveric human torso. Written consent has been regularly obtained for publication.
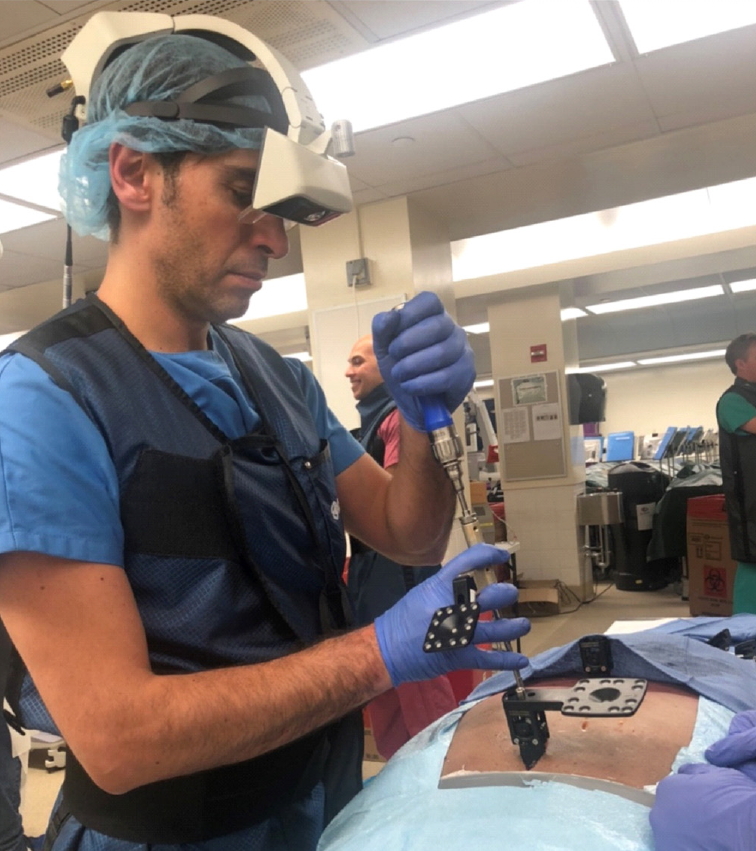
Table 1.
Summary of main robotic systems for spine surgery including relevant information
| System | Main features | Clinical applications | Accuracy | Limitations | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| da Vinci | Telesurgical robotic system remotely operated from a command station | ALIF | - | High cost, steep learning curve, not cleared by FDA for spine surgery | [19-21] |
| Spine-Assist | First navigated robotic system approved for spine surgery | Transpedicular screw placement | 98% | Need for rigid bone fixation, skidding and dislocation of the cannula | [22-25] |
| Renaissance | Second version of the SpineAssist | Transpedicular screw placement | 98.9%–100% | Skiving of the trocar or the drill tip | [26-29] |
| Tumor biopsies | |||||
| Vertebro-kyphoplasties | |||||
| Mazor X | Third upgrade of previous systems. Enhanced imaging elaboration, fully automated robotic arm and 3D volumetric assay of the surgical field | Transpedicular screw placement | 98.7% | Still limited clinical evidence available | [30-33] |
| TLIF | |||||
| Excelsius-GPS | Able to track instruments in real time, sense cannula dislocations and compensate for patient’s movements | Transpedicular screw placement | 96.6%–99% | Need for rigid bone fixation | [34-39] |
| ROSA Spine | Robotic arm with a floor-flexible base capable of readjust its position in real time and track patient’s movements | Transpedicular screw placement | 96% | Need for rigid bone fixation | [40-42] |
| Tianji | Built with a robotic arm and an optical tracking system, the robot moves to preplanned position without the need for bone fixation | Transpedicular screw placement | 96%–98.3% | Still limited clinical evidence available | [43-47] |
| OLIF | |||||
| TLIF | |||||
| Atlantoaxial fixation | |||||
| Cirq | Robotic arm with 7 degrees of freedom developed to work together the manufacturer’s navigation system | Transpedicular screw placement | - | Still limited clinical evidence available | [48] |
REFERENCES
1. O’Lynnger TM, Zuckerman SL, Morone PJ, et al. Trends for spine surgery for the elderly: implications for access to healthcare in North America. Neurosurgery 2015 77 Suppl 4:S136-41.



2. Vadalà G, Di Martino A, Russo F, et al. Autologous bone marrow concentrate combined with platelet-rich plasma enhance bone allograft potential to induce spinal fusion. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 2016 30(4 Suppl 1):165-72.
3. Friedly J, Standaert C, Chan L. Epidemiology of spine care: the back pain dilemma. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am 2010 21:659-77.



4. Di Martino A, Russo F, Denaro V. Spontaneous fusion of L5 spondyloptosis: should we learn from nature? Spine J 2012 12:529.


5. Di Martino A, Russo F, Denaro L, et al. How to treat lumbar disc herniation in pregnancy? A systematic review on current standards. Eur Spine J 2017 26(Suppl 4):496-504.



6. Vadalà G, Russo F, Battisti S, et al. Early intervertebral disc degeneration changes in asymptomatic weightlifters assessed by t1ρ-magnetic resonance imaging. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2014 39:1881-6.



7. Vadalà G, Russo F, Musumeci M, et al. Clinically relevant hydrogel-based on hyaluronic acid and platelet rich plasma as a carrier for mesenchymal stem cells: rheological and biological characterization. J Orthop Res 2017 35:2109-16.


8. Vadalà G, Russo F, Ambrosio L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells for intervertebral disc regeneration. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 2016 30(4 Suppl 1):173-9.
9. Russo F, Hartman RA, Bell KM, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of transpedicular nucleotomy with intact annulus fibrosus. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2017 42:E193-201.


10. Vadala’ G, Russo F, Ambrosio L, et al. Biotechnologies and biomaterials in spine surgery. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 2015 29(4 Suppl):137-47.
11. Banczerowski P, Czigléczki G, Papp Z, et al. Minimally invasive spine surgery: systematic review. Neurosurg Rev 2015 38:11-26.



12. Overley SC, Cho SK, Mehta AI, et al. Navigation and robotics in spinal surgery: where are we now? Neurosurgery 2017 80(3S):S86-99.



13. Shweikeh F, Amadio JP, Arnell M, et al. Robotics and the spine: a review of current and ongoing applications. Neurosurg Focus 2014 36:E10.

14. Yu L, Chen X, Margalit A, et al. Robot-assisted vs freehand pedicle screw fixation in spine surgery - a systematic review and a meta-analysis of comparative studies. Int J Med Robot 2018 14:e1892.


15. Hernandez D, Garimella R, Eltorai AEM, et al. Computer-assisted orthopaedic surgery. Orthop Surg 2017 9:152-8.



16. Nooh A, Aoude A, Fortin M, et al. Use of computer assistance in lumbar fusion surgery: analysis of 15222 patients in the ACS-NSQIP Database. Global Spine J 2017 7:617-23.



17. Vadalà G, Russo F, Pattappa G, et al. A nucleotomy model with intact annulus fibrosus to test intervertebral disc regeneration strategies. Tissue Eng Part C Methods 2015 21:1117-24.


18. Vadalà G, De Strobel F, Bernardini M, et al. The transpedicular approach for the study of intervertebral disc regeneration strategies: in vivo characterization. Eur Spine J 2013 22 Suppl 6:S972-8.



19. The da Vinci Surgical System [Internet] Sunnyvale (CA), Intuitive Surgical Inc.. 2019 [2020 Jan 20]. Available from; https://www.davincisurgerycommunity.com/web/guest/systems_i_a.
20. Lee JY, Bhowmick DA, Eun DD, et al. Minimally invasive, robot-assisted, anterior lumbar interbody fusion: a technical note. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg 2013 74:258-61.



21. Beutler WJ, Peppelman WC Jr, DiMarco LA. The da Vinci robotic surgical assisted anterior lumbar interbody fusion: technical development and case report. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2013 38:356-63.


22. Dreval’ ON, Rynkov IP, Kasparova KA, et al. Results of using Spine Assist Mazor in surgical treatment of spine disorders. Zh Vopr Neirokhir Im N N Burdenko 2014 78:14-20.
23. van Dijk JD, van den Ende RP, Stramigioli S, et al. Clinical pedicle screw accuracy and deviation from planning in robot-guided spine surgery: robot-guided pedicle screw accuracy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2015 40:E986-91.


24. Devito DP, Kaplan L, Dietl R, et al. Clinical acceptance and accuracy assessment of spinal implants guided with Spine-Assist surgical robot: retrospective study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2010 35:2109-15.


25. Ringel F, Stüer C, Reinke A, et al. Accuracy of robot-assisted placement of lumbar and sacral pedicle screws: a prospective randomized comparison to conventional freehand screw implantation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2012 37:E496-501.


27. Onen MR, Simsek M, Naderi S. Robotic spine surgery: a preliminary report. Turk Neurosurg 2014 24:512-8.


28. Hyun SJ, Kim KJ, Jahng TA, et al. Minimally invasive robotic versus open fluoroscopic-guided spinal instrumented fusions: a randomized controlled trial. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2017 42:353-8.


29. Hu X, Ohnmeiss DD, Lieberman IH. Robotic-assisted pedicle screw placement: lessons learned from the first 102 patients. Eur Spine J 2013 22:661-6.



30. Kochanski RB, Lombardi JM, Laratta JL, et al. Image-guided navigation and robotics in spine surgery. Neurosurgery 2019 84:1179-89.



31. D’Souza M, Gendreau J, Feng A, et al. Robotic-assisted spine surgery: history, efficacy, cost, and future trends. Robot Surg 2019 6:9-23.



32. Khan A, Meyers JE, Siasios I, et al. Next-generation robotic spine surgery: first report on feasibility, safety, and learning curve. Oper Neurosurg (Hagerstown) 2019 17:61-9.



33. StealthStation S8 Surgical Navigation System [Internet] Dublin (Ireland), Medtronic. 2019 [2020 Jan 23]. Available from: https://www.medtronic.com/us-en/healthcare-professionals/products/neurological/surgical-navigation-systems/stealthstation.html.
34. Zygourakis CC, Ahmed AK, Kalb S, et al. Technique: open lumbar decompression and fusion with the Excelsius GPS robot. Neurosurg Focus 2018 45(VideoSuppl1):V6.

35. Vaccaro AR, Harris JA, Wadhwa R, et al. ExcelsiusGPS® Robotic Navigation Platform improves screw accuracy and reduces radiation exposure compared to conventional fluoroscopic techniques in a simulated surgical model. White paper (GMWP51). Audubon (PA): Globus Medical, Inc; 2018.
36. Huntsman KT, Ahrendtsen LA, Riggleman JR, et al. Robotic-assisted navigated minimally invasive pedicle screw placement in the first 100 cases at a single institution. J Robot Surg 2020 14:199-203.



37. Godzik J, Walker CT, Hartman C, et al. A quantitative assessment of the accuracy and reliability of robotically guided percutaneous pedicle screw placement: technique and application accuracy. Oper Neurosurg (Hagerstown) 2019 17:389-95.



38. Benech CA, Perez R, Benech F, et al. Navigated robotic assistance results in improved screw accuracy and positive clinical outcomes: an evaluation of the first 54 cases. J Robot Surg 2019 Aug 8 [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11701-019-01007-z.


39. Vardiman AB, Wallace DJ, Crawford NR, et al. Pedicle screw accuracy in clinical utilization of minimally invasive navigated robot-assisted spine surgery. J Robot Surg 2019 Jul 19 [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11701-019-00994-3.


40. Lefranc M, Peltier J. Evaluation of the ROSATM Spine robot for minimally invasive surgical procedures. Expert Rev Med Devices 2016 13:899-906.


41. Chenin L, Peltier J, Lefranc M. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with the ROSA(TM) Spine robot and intraoperative flat-panel CT guidance. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2016 158:1125-8.



42. Lonjon N, Chan-Seng E, Costalat V, et al. Robot-assisted spine surgery: feasibility study through a prospective case-matched analysis. Eur Spine J 2016 25:947-55.



43. Wu JY, Yuan Q, Liu YJ, et al. Robot-assisted percutaneous transfacet screw fixation supplementing oblique lateral interbody fusion procedure: accuracy and safety evaluation of this novel minimally invasive technique. Orthop Surg 2019 11:25-33.



44. Han X, Tian W, Liu Y, et al. Safety and accuracy of robot-assisted versus fluoroscopy-assisted pedicle screw insertion in thoracolumbar spinal surgery: a prospective randomized controlled trial. J Neurosurg Spine 2019 Feb 8 1. -8. [Epub] https://doi.org/10.3171/2018.10.SPINE18487.

45. Tian W. Robot-assisted posterior C1-2 transarticular screw fixation for atlantoaxial instability: a case report. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2016 41 Suppl 19:B2-5.


46. Tian W, Liu YJ, Liu B, et al. Guideline for posterior atlantoaxial internal fixation assisted by orthopaedic surgical robot. Orthop Surg 2019 11:160-6.



47. Fan M, Lui Y, Tian W. Internal fixation in upper cervical spinal surgery: a randomized controlled study. In: The 18th Annual Meeting of the International Society for Computer Assisted Orthopaedic Surgery; 2018 Jun 6-9; Beijing, China. 2018 2:pp 51-5.

48. Krieg SM, Meyer B. First experience with the jump-starting robotic assistance device Cirq. Neurosurg Focus 2018 45(VideoSuppl1):V3.

49. Yoo JS, Patel DS, Hrynewycz NM, et al. The utility of virtual reality and augmented reality in spine surgery. Ann Transl Med 2019 7(Suppl 5):S171.



50. Edström E, Burström G, Nachabe R, et al. A novel augmented-reality-based surgical navigation system for spine surgery in a hybrid operating room: design, workflow, and clinical applications. Oper Neurosurg (Hagerstown) 2019 Aug 27 [Epub]. pii: opz236. https://doi.org/10.1093/ons/opz236.


51. Elmi-Terander A, Skulason H, Söderman M, et al. Surgical navigation technology based on augmented reality and integrated 3D intraoperative imaging: a spine cadaveric feasibility and accuracy study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2016 41:E1303-11.



52. Elmi-Terander A, Nachabe R, Skulason H, et al. Feasibility and accuracy of thoracolumbar minimally invasive pedicle screw placement with augmented reality navigation technology. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2018 43:1018-23.



53. Burström G, Nachabe R, Persson O, et al. Augmented and virtual reality instrument tracking for minimally invasive spine surgery: a feasibility and accuracy study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2019 44:1097-104.


54. Elmi-Terander A, Burström G, Nachabe R, et al. Pedicle screw placement using augmented reality surgical navigation with intraoperative 3D imaging: a first in-human prospective cohort study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2019 44:517-25.


55. Edström E, Burström G, Omar A, et al. Augmented reality surgical navigation in spine surgery to minimize staff radiation exposure. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2020 45:E45-53.


56. Auloge P, Cazzato RL, Ramamurthy N, et al. Augmented reality and artificial intelligence-based navigation during percutaneous vertebroplasty: a pilot randomised clinical trial. Eur Spine J 2019 Jul 2 [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-019-06054-6.


57. Ma L, Zhao Z, Chen F, et al. Augmented reality surgical navigation with ultrasound-assisted registration for pedicle screw placement: a pilot study. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 2017 12:2205-15.



58. Yoon JW, Chen RE, Han PK, et al. Technical feasibility and safety of an intraoperative head-up display device during spine instrumentation. Int J Med Robot 2017 Sep;13(3):https://doi.org/10.1002/rcs.1770. Epub 2016 Aug 29.

59. Wang H, Wang F, Leong AP, et al. Precision insertion of percutaneous sacroiliac screws using a novel augmented reality-based navigation system: a pilot study. Int Orthop 2016 40:1941-7.



60. Microsoft. HoloLens 2 [Internet] Redmond (WA), Microsoft. 2019 [2020 Jan 30]. Available from; https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/hololens.
61. Agten CA, Dennler C, Rosskopf AB, et al. Augmented reality-guided lumbar facet joint injections. Invest Radiol 2018 53:495-8.


62. Liu H, Wu J, Tang Y, et al. Percutaneous placement of lumbar pedicle screws via intraoperative CT image-based augmented reality-guided technology. J Neurosurg Spine 2019 Dec 20 1. -6. [Epub] https://doi.org/10.3171/2019.10.SPINE19969
.

63. Gibby JT, Swenson SA, Cvetko S, et al. Head-mounted display augmented reality to guide pedicle screw placement utilizing computed tomography. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 2019 14:525-35.



64. Liebmann F, Roner S, von Atzigen M, et al. Pedicle screw navigation using surface digitization on the Microsoft HoloLens. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 2019 14:1157-65.



65. Müller F, Roner S, Liebmann F, et al. Augmented reality navigation for spinal pedicle screw instrumentation using intraoperative 3D imaging. Spine J 2019 Oct 25 [Epub]. pii: S1529-9430(19)31058-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spinee.2019.10.012.

66. Urakov TM, Wang MY, Levi AD. Workflow caveats in augmented reality-assisted pedicle instrumentation: cadaver lab. World Neurosurg 2019 126:e1449-55.


67. Wanivenhaus F, Neuhaus C, Liebmann F, et al. Augmented reality-assisted rod bending in spinal surgery. Spine J 2019 19:1687-9.


68. Molina CA, Theodore N, Ahmed AK, et al. Augmented reality-assisted pedicle screw insertion: a cadaveric proof-of-concept study. J Neurosurg Spine 2019 Mar 29 1. -8. [Epub] https://doi.org/10.3171/2018.12.SPINE181142
.

69. Carl B, Bopp M, Saß B, et al. Implementation of augmented reality support in spine surgery. Eur Spine J 2019 28:1697-711.



70. Carl B, Bopp M, Saß B, et al. Microscope-based augmented reality in degenerative spine surgery: initial experience. World Neurosurg 2019 128:e541-51.


71. Umebayashi D, Yamamoto Y, Nakajima Y, et al. Augmented reality visualization-guided microscopic spine surgery: transvertebral anterior cervical foraminotomy and posterior foraminotomy. J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev 2018 2:e008.

72. Kosterhon M, Gutenberg A, Kantelhardt SR, et al. Navigation and image injection for control of bone removal and osteotomy planes in spine surgery. Oper Neurosurg (Hagerstown) 2017 13:297-304.



73. Ortega G, Wolff A, Baumgaertner M, et al. Usefulness of a head mounted monitor device for viewing intraoperative fluoroscopy during orthopaedic procedures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2008 128:1123-6.



74. Luciano CJ, Banerjee PP, Bellotte B, et al. Learning retention of thoracic pedicle screw placement using a high-resolution augmented reality simulator with haptic feedback. Neurosurgery 2011 69(1 Suppl Operative):ons14-9.




75. Luciano CJ, Banerjee PP, Sorenson JM, et al. Percutaneous spinal fixation simulation with virtual reality and haptics. Neurosurgery 2013 72 Suppl 1:89-96.



76. Fomekong E, Safi SE, Raftopoulos C. Spine navigation based on 3-dimensional robotic fluoroscopy for accurate percutaneous pedicle screw placement: a prospective study of 66 consecutive cases. World Neurosurg 2017 108:76-83.


77. Fan Y, Du J, Zhang J, et al. Comparison of accuracy of pedicle screw insertion among 4 guided technologies in spine surgery. Med Sci Monit 2017 23:5960-8.



78. Roser F, Tatagiba M, Maier G. Spinal robotics: current applications and future perspectives. Neurosurgery 2013 72 Suppl 1:12-8.



79. Divi S, Pollster S, Ramos E, et al. The current role of robotic technology in spine surgery. Oper Tech Orthop 2017 27:275-82.

80. Fan Y, Du JP, Liu JJ, et al. Accuracy of pedicle screw placement comparing robot-assisted technology and the free-hand with fluoroscopy-guided method in spine surgery: An updated meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 2018 97:e10970.



81. Kantelhardt SR, Martinez R, Baerwinkel S, et al. Perioperative course and accuracy of screw positioning in conventional, open robotic-guided and percutaneous robotic-guided, pedicle screw placement. Eur Spine J 2011 20:860-8.



82. Kim HJ, Jung WI, Chang BS, et al. A prospective, randomized, controlled trial of robot-assisted vs freehand pedicle screw fixation in spine surgery. Int J Med Robot 2017 Sep;13(3):https://doi.org/10.1002/rcs.1779. Epub 2016 Sep 27.

83. Croissant Y, Zangos S, Albrecht MH, et al. Robot-assisted percutaneous placement of K-wires during minimally invasive interventions of the spine. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol 2019 28:373-80.


84. Wagner SC, Morrissey PB, Kaye ID, et al. Intraoperative pedicle screw navigation does not significantly affect complication rates after spine surgery. J Clin Neurosci 2018 47:198-201.


85. Fan Y, Peng Du J, Liu JJ, et al. Radiological and clinical differences among three assisted technologies in pedicle screw fixation of adult degenerative scoliosis. Sci Rep 2018 8:890.




86. Ghasem A, Sharma A, Greif DN, et al. The arrival of robotics in spine surgery: a review of the literature. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2018 43:1670-7.


87. Barzilay Y, Schroeder JE, Hiller N, et al. Robot-assisted vertebral body augmentation: a radiation reduction tool. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2014 39:153-7.


88. Urakov TM, Chang KH, Burks SS, et al. Initial academic experience and learning curve with robotic spine instrumentation. Neurosurg Focus 2017 42:E4.

89. Schatlo B, Martinez R, Alaid A, et al. Unskilled unawareness and the learning curve in robotic spine surgery. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2015 157:1819-23.



90. Curexo launches 1st locally developed spine surgery robot [Internet] Seoul (Korea), Korea Biomedical Review. 2019 [2020 Feb 1]. Available from: http://www.koreabiomed.com/news/articleView.html?idxno=6990.
91. CUVIS-spine, a surgical robot system [Internet] Seoul (Korea), Curexo. 2019 [2020 Feb 4]. Available from: https://\www.youtube.com/watch?v=EUWwEMpn4K4.