- Search
| Neurospine > Volume 19(1); 2022 > Article |
|
|
Abstract
Objective
Spinal cord tumors constitute a small part of spinal surgery owing to their rarity. This retrospective study describes their current management.
Methods
Forty-eight patients were treated for an intramedullary tumor between 2014 and 2020 at a single institution. Patients’ files were retrospectively studied. We detailed clinical status according to neurological deficit and ambulatory ability using the modified McCormick Scale, radiological features like number of levels, associated syringomyelia, surgical technique with or without intraoperative electrophysiological monitoring, pathological findings, and postoperative outcome.
Results
The median age of this population was 43 years, including 5 patients under 18 years. The median delay before first neurosurgical contact was 3 months after the first clinical complaint. Treatment was gross total resection in 43.8%, subtotal resection in 50.0%, and biopsy in 6.2%. A laminectomy was performed for all the patients except 2 operated using the laminoplasty technique. Pathological findings were ependymoma in 43.8%, hemangioblastoma in 20.8%, and pilocytic astrocytoma in 10.4%. Six patients were reoperated for a tumor recurrence less than 2 years after the first surgical resection. One patient was reoperated for a postoperative cervical kyphosis.
Conclusion
Intramedullary tumors are still a challenging disease and they are treated by various surgical techniques. They must be managed in a specialized center including a trained surgical, radiological, electrophysiological, and pathological team. Arthrodesis must be discussed before performing extensive laminectomy to avoid postoperative kyphosis.
Primary spinal cord tumors are a small part of spinal surgery, accounting for around 4% of all central nervous system (CNS) tumors with an incidence of less than 1/100,000 person-years [1-3]. They arise mainly in neuroepithelial tissue (astrocytoma and other glial tumors, ependymomas) or in mesenchymal cells such as hemangioblastomas [2,4]. Given this variety and low incidence, their incidence, clinical presentation, radiological features, and management vary considerably [5-8].
Fewer than half of patients have a neurological improvement at postoperative follow-up [5]. Due to the challenging surgery, the high rate of neurological deterioration after surgery, and pathological outcome, their optimal management remains a matter of debate. A literature search has been performed (2014–2020) to identify the key issues in primary spinal cord tumor management in terms of epidemiology, surgical technique, intraoperative monitoring, imaging characteristics, relevant pathological findings, and functional outcome after surgery.
All patients operated for an intramedullary spinal cord lesion between 2014 and 2020 and registered in the database of our Neurosurgery Department of the University Hospital of Bordeaux, France, were reviewed by PR and LM. We excluded all patients treated for intradural extramedullary lesions. Medical history, clinical status, pathological findings, the World Health Organization (WHO) grade, and radiological results were analyzed. This study has been approved by the Institutional Review Board of Collège de Neurochirurgie (N° IRB00011687).
The patients were first described according to age, sex, delay before first contact with neurosurgical team, and clinical features such as spinal pain or neurological deficit. Autonomy was assessed with the modified McCormick Scale (mMCS). Radiological presentation was detailed according to number of levels involved, tumor location, and association with syringomyelia or not. Surgical management was classified into 3 types: gross total resection (GTR), subtotal resection (STR), and biopsy. Intraoperative management was reported as with or without electrophysiological neuromonitoring, and laminectomy or laminoplasty. Adjunctive treatments were recorded during the first 2 postoperative years.
Patients’ data are summarized in Table 1. Forty-eight patients were operated for an intramedullary lesion between 2014 and 2020 (27 males, 21 females). The median age was 43 years, including 5 patients < 18 years. The median delay between first clinical complaint and first neurosurgical contact was 3 months. Twenty-three patients (47.9%) complained of spinal pain. Preoperative evaluation revealed a motor deficit in 52.0% of patients (25 of 48), a sensory deficit or dysesthesia in 70.8% (34 of 48), and bowel or bladder dysfunction in 31.2% (15 of 48). The median mMCS score was 2. Twelve patients (25.0%) were treated with corticosteroids before the intervention. Pathological findings were 3 cavernomas, 25 ependymomas (1 tumor was WHO grade 1, 21 were WHO grade 2, 3 were WHO grade 3) with a mean proliferation index (Mib-1) 4.3%±2.7%, 10 hemangioblastomas, 5 pilocytic astrocytomas, 2 metastases, 1 glioblastoma, 1 rosette-forming glioneuronal tumor, and 1 unknown. (28 of 48) Twenty-eight patients (58.3%) experienced immediate postoperative worsening. The median mMCS at 6 months was 2±1.1.
The median number of levels involved was 2. Tumors involved the cervical spine in 37.5% (18 of 48), the thoracic spine in 56.2% (27 of 48), and the conus medullaris in 10.4% (5 of 48). Syringomyelia was reported in 41.7% (21 of 48). Patients treated for tumors involving the cervical spine had a preoperative mean mMCS of 2.33±1.23, and mean mMCS at 6 months of 2.59±0.7. When the thoracic spine was involved, the preoperative mean mMCS was 2.37±1.18, and the mean mMCS at 6 months was 2.52 ±1.0. The cona medullaris had the best outcome with a mean preoperative mMCS of 1.83±0.75, and a mMCS at 6 months of 1.83±0.9. When syringomyelia was associated, the mean mMCS at 6 months was 2.6±1.0. Without syringomyelia, the mean mMCS at 6 months was 2.4±1.22.
The 25 patients treated for an ependymoma had a preoperative mMCS of 2.3±1.0. Of these, 44% (11 of 25) presented an immediate postoperative degradation with a postoperative (6 months) mMCS of 2.4±1.1, without any significant difference according to preoperative status (p=0.78). The 5 patients treated for a pilocytic astrocytoma had a preoperative mMCS of 2.4±1.7. Three of these 5 patients presented an immediate postoperative degradation with a similar mean postoperative (6 months) MCS of 2.4±1.1. The 10 patients treated for a hemangioblastoma had a preoperative MCS of 2.3±1.2. Nine of them presented an immediate postoperative degradation with a similar mean postoperative (6 months) MCS of 2.7±1.0. The difference was nonsignificant (p=0.20).
All the patients underwent a laminectomy except for 2 laminoplasties. Of the 48 patients, 25 (52.0%) were monitored using intraoperative evoked potentials. Of these, 19 (76.0%) experienced an immediate postoperative clinical deterioration, including (12 of 25) 12 (48.0%) with intraoperative electrophysiological deterioration and 13 (52.0%) without intraoperative monitoring. These monitored patients had a mean preoperative mMCS of 2.2±1.1 and a mean mMCS at 6 months of 2.8±1.0, without significant difference (p=0.14). Among the patients operated without intraoperative electrophysiological monitoring, 39.1% (9 of 23) suffered an immediate postoperative neurological deterioration with a mean mMCS at 6 months of 2.35±1.0. These results are presented in Table 2.
Twenty-one patients (43.7%) underwent GTR, 24 (50.0%) STR, and 3 (6.2%) biopsies. Among the 25 patients treated for ependymoma, 9 (36.0%) underwent a GTR, and 16 (64.0%) a STR. Among the 10 patients treated for hemangioblastoma, 7 underwent a GTR, 2 a STR, and 1 biopsy. Among the 5 patients treated for pilocytic astrocytomas, 1 underwent a GTR, 3 a STR, and 1 biopsy. Among the 8 other patients, 4 underwent a GTR, 3 a STR, and 1 a biopsy.
Among the patients treated with adjunctive radiotherapy, pathological findings included 11 ependymoma, 2 metastases, and 1 pilocytic astrocytoma. Six patients were reoperated less than 2 years after the first surgical resection, all for an ependymoma except one hemangioblastoma for a second location. Among patients reoperated for an ependymoma, one was treated for a posterior cervical arthrodesis due to a postoperative kyphosis. This patient had been treated for an extended ependymoma from C1 to C7 with a laminectomy.
No patient experienced any postoperative cerebrospinal fluid leak or required reoperation for hematoma or infection. The median postoperative follow-up was 24±5.5 months.
Our single-center experience included 48 patients operated for an intramedullary spinal cord tumor. Owing to progress in surgical techniques, imaging, and molecular analysis, we focused only on the 6 past years. Our population was predominantly male (56% vs. 44%), as elsewhere [5]. Median age was 43 years and 5 patients were under 18 years. Patients’ age varies considerably in the literature [2,5,9].
Spinal tumors include intradural extramedullary tumors, extradural tumors, and intradural intramedullary tumors. We selected patients treated for an intramedullary tumors including 66.7% (32 of 48) of gliomas, which represent 80% of all intramedullary tumors [10]. Of these gliomas, 52.1% (25 of 48) were ependymomas and 10.4% (5 of 48) were pilocytic astrocytomas. There was one glioblastoma and one rosette-forming glioneuronal tumor. Regarding intramedullary tumors, our population seems similar to those in the recent literature, with a predominance of ependymomas followed by hemangioblastomas [11,12].
We included 3 patients with spinal cavernomas, even though they are considered by some as tumors or as malformations by others [13,14]. Results are probably not significantly modified by these 3 patients.
The University of Bordeaux is the regional reference center for von Hippel-Lindau disease, thus explaining the large number of hemangioblastomas, which is higher than in the literature (20.8% compared to 2.1% in the SEER database [15]). Indeed, only one of our patients treated for spinal hemangioblastoma was not followed for von Hippel-Lindau disease.
Ependymomas were more likely located in the thoracic spine (56%, i.e., 14 of 25 of all ependymomas). Hemangioblastomas more often involved the cervical spine (60%, i.e., 6 of 10 of all hemangioblastomas). Pilocytic astrocytomas involved the cervical spine in 2 cases and the thoracic spine in 3 cases. These localizations are similar to those reported by others [5,15].
Associated syringomyelia is reported to be a favorable prognostic factor [2], and a syrinx was observed at diagnosis in 43.7% of patients.
Even if the real relationship between a delayed diagnosis and the overall final functional outcome has not been analyzed in the literature, it seems plausible to affirm that a delayed neurosurgical contact might decrease the overall final outcome. In our retrospective experience, the mean delay appears to be quite high, and it might probably be improved by the training of the general physicians. A spinal cord tumor must be suspected in presence of motor or sensory deficit reported in 70%, and spinal pain in half of our patients (47.9%), showing the interest of inform general physicians, and all spine surgeons.
The mean mMCS of patients with syringomyelia 6 months after surgical resection was 2.6±1.0 and was 2.4±1.22 in those without syringomyelia, with a nonsignificant difference. This lack of difference may be because the mMCS lacks sensitivity. In addition, our population included a high percentage of hemangioblastomas. Hemangioblastomas have a high rate of associated syringomyelia and a poor functional outcome due to the context of a genetic disease involving several possible tumor sites. As in the literature, our patients had a mean preoperative modified McCormick score of 2.3±1.1, and a mean postoperative mMCS at 6 months of 2.5±1.0 [16,17].
Intramedullary spinal cord tumors may present a scoliosis without neurological signs. Those treating spinal deformities should suggest a spine magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) at the beginning of the follow-up [18].
MRI is the modality of choice to evaluate spinal cord tumors. Conventional sequences include T1- and T2-weighted imaging in the sagittal and axial planes, followed by contrast-enhanced T1-weighted imaging. Screening of the entire spine is necessary so as not to miss lesions or metastases. Diffusion-tensor imaging may be performed in the preoperative plane to detect white matter fiber tract alterations at the cord tumor interface. Infiltration of fiber tracts may indicate an absent cleavage plane between the tumor and normal adjacent cord, whereas displacement of fiber tracts suggests the safe resection of the tumor.
After confirming the intramedullary topography, the location within the spinal cord, the signal intensity, the enhancement, and the margins must be analyzed [19]. Intramedullary masses usually expand the spinal cord parenchyma whereas extramedullary lesions displace it. Different neoplastic entities arise from different compartments of the spinal cord. Eccentric masses such as astrocytic tumors arise from the peripheral white matter, and centered masses like ependymal tumors arise from the central canal. Moreover, some tumors have a particular spinal location. For example, hemangioblastomas typically develop on the pial surface, while myxopapillary ependymomas arise from the conus medullaris or the filum terminale.
Enhancement analysis differentiates subependymomas from diffuse astrocytomas (WHO grade 2), which do not present significant enhancement, unlike other tumors which usually enhance. Ependymomas are characterized by a centered location, well-defined margins, a heterogeneous signal with cystic or hemorrhagic components, including polar cysts or a hemosiderin cap sign at the superior or inferior margins. They may be surrounded by edema or syringohydromyelia. Astrocytomas present as an eccentric spinal mass. Cystic changes are possible, while hemorrhage is less common than in ependymomas. Pilocytic astrocytomas are well-circumscribed gliomas, while astrocytomas have ill-defined margins and tend to be of higher grade. The presence of syringohydromyelia, which is more commonly seen in spinal cord ependymoma, is perhaps the most significant factor distinguishing ependymomas from astrocytomas [20]. (Fig. 1). Hemangioblastomas usually appear as a hypervascular enhancing nodule located on the pial surface especially in patients with von Hippel-Lindau syndrome, but they may also appear as a larger intramedullary mass (Fig. 2). Tumoral fluid secretion from leaky vessels causes syringomyelia or a “cyst with nodule” appearance in more than 50% of cases [21]. Flow voids due to enlarged vessels may be visible at the periphery of the cyst [22]. Not all expansile intramedullary lesions are neoplastic. The main differential diagnosis is inflammatory myelitis, cavernoma, and spinal dural arteriovenous fistula (flow voids on spin-echo MRI).
Following general anesthesia, the patient is placed in the prone position. The level is identified by a lateral x-ray film. Surgery is performed via a posterior approach with a midline skin incision and subperiosteal muscle dissection, followed by laminectomy or laminoplasty to expose the thecal sac. Laminoplasty was performed in 2 cases involving 3 levels, while laminectomy was used in the remaining 46 cases. When the laminoplasty was planned, the spinous processes and interspinous ligaments were left intact and the involved laminae were cut bilaterally in a caudal-to-rostral direction and removed as a single unit without disrupting the facet joints. The dura was opened at the midline and retracted by tenting sutures. Myelotomy was then performed with a microscope after locating the median posterior sulcus (sometimes paramedian posterior sulcus, depending on vascularization positioning) and was extended to expose the superior and inferior limits of the tumor in order to minimize manipulating the spinal cord. Central debulking of the tumor was performed with an ultrasound aspirator followed by dissection of the tumor periphery from the normal cord at the cleavage plane, with total removal being the aim in all cases if such a plane existed. In infiltrative tumors lacking a good cleavage plane, maximum resection was attempted with special attention to any changes in the action potentials. Fluorescence guidance for complete tumor resection is showing promise [23]. The dura was then closed with a water-tight suture. In the event of laminoplasty, the laminae were reattached using titanium microplates followed by standard closure.
One patient was reoperated with a posterior cervical arthrodesis for postoperative cervical kyphosis. He was first treated for an extended cervical ependymoma involving the entire cervical cord. The current literature recommends a spinal arthrodesis after resection of an intramedullary lesion involving more than 3 levels and with a laminectomy encompassing a spinal junction [24,25]. The arthrodesis should probably have been performed during the first surgery. This raises the issue of the type of radiological modalities to be performed after histological findings.
Detailing our surgical resections, the rate of GTR seems to be quite lower than the current literature, particularly in ependymomas’ resections (36.0% of GTR). Our retrospective cohort included only one ependymoma WHO grade 1, 21 ependymomas grade 2, and 3 grade 3. This specificity might explain this low GTR rate.
Even if this study did not detail enough the intraoperative neuromonitoring (IONM) to draw conclusions, the current literature confirms the interest of this important tool in spinal cord surgery [26]. In 2012, the American Academy of Neurology recommended that IONM with somatosensory evoked potentials (SSEPs) and transcranial motor evoked potential (Tc-MEP) should be performed to predict an increased risk of adverse outcomes such as paraparesis, paraplegia, and quadriplegia. By identifying the structures involved, it is possible to predict postoperative motor deficits in lesions of the central and peripheral nervous system by using the multimodal system according to the tumor location. These modalities include MEPs, SSEPs, electroencephalography (EEG), and electromyography.
Anesthesia protocols are adapted to IONM, with a combination of propofol, fentanyl, and ketamine. Halogenated agents are contraindicated since they can abolish the responses of motor evoked potentials, while muscle relaxants like curare are limited to the induction phase.
Evoked potentials are performed before the end of surgery, before and after opening the dura mater, during tumor resection, and before and after closure of the dura mater. We analyzed 25 patients with multimodal IONM (MEPs, SSEPs, electroneuromyography, and EEG), all of them with electrodes positioned according to the lesion area. We analyzed the activity of 5 muscles in the upper and lower limbs, i.e., one supralesional, and performed SSEPs on the posterior tibial nerve. A decrease in amplitude of 50% in MEP response triggers an alarm and a decrease of 70% or more indicates that surgery must be stopped. SSEPs are less specific but flattening of responses can also observed. In the 3 patients (12%) where we lost an MEP signal, we used the D-wave. Combining muscle MEPs with D-wave recording is the most comprehensive way to assess the functional integrity of the spinal cord tracts during surgery for intramedullary spinal cord tumors [27].
Finally, caution is required with IONM. Resection should be temporality halted if the MEP signal starts to decrease, and it should be stopped definitively if the patient’s functional prognosis is compromised. This decision also depends on preoperative discussions with the patient.
Ependymomas are the most frequent primary intramedullary spinal tumors [28]. The 2021 WHO classification of CNS tumors distinguishes different subtypes of ependymoma according to their initial anatomical location (supratentorial, posterior fossa, and spinal) and associated molecular alterations [29]. As for other localizations, ependymomas with a spinal origin are classified as grade 2 or grade 3 (anaplastic) according to the histoprognostic WHO criteria. There is not yet sufficient molecular evidence to call this grading system into question (Fig. 3). Nevertheless, a high level of MYCN amplification evidenced by fluorescence in situ hybridization is associated with a more aggressive subclass of spinal cord ependymoma that is characterized by early dissemination and mostly anaplastic morphology [30,31].
The spinal ependymomas include myxopapillary tumors. These constitute a particular entity and are commonly located in the conus-cauda equina region of the spine, mostly in young adults. Initially described as a benign grade 1 tumor, it is now considered CNS WHO grade 2 on the basis of a risk of recurrence similar to classical ependymoma [32].
Primary spinal pilocytic astrocytoma is rare, representing only about 2%–5% of all PAs and about 10% of spinal tumors [33]. These tumors are characterized by a high frequency of alterations in the mitogen-activating protein kinase pathway, which mainly affect the BRAF gene either by a mutation (V600E) or by a tandem duplication resulting in a fusion gene between KIAA1549 and BRAF [34]. These alterations are rarer than in cerebellar or encephalic tumors but can serve as diagnostic as well as therapeutic evidence thanks to the development of targeted therapies [35] (combined BRAF and MEK inhibitors). Other primary spinal glial tumors are exceptional, and concomitant encephalic (glioblastoma, oligodendroglioma, astrocytoma, glioneuronal tumors) or brainstem tumors (altered H3K27M Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Glioma) should be investigated. Spinal cavernoma and spinal hemangioblastoma are also less frequent than encephalic and cerebellar presentations and necessitate research of family history or genetic testing.
Our median postoperative follow-up was 24 months, which seems short. However, our patients were often followed up in another oncological center for geographical reasons. Based on current recommendations, 15 patients underwent postoperative radiotherapy, including 11 ependymomas, 2 metastases, 1 glioblastoma, and 1 recurrent pilocytic astrocytoma. Among these patients, 4 were treated with chemotherapy, including both patients treated for a medullar metastasis, 1 patient treated for a pilocytic astrocytoma, and the patient treated for a glioblastoma. Among the 7 patients reoperated within 2 years after the first surgery, 6 had an ependymoma and one a hemangioblastoma. The latter was reoperated for another occurrence of hemangioblastoma due to von Hippel-Lindau disease.
Radiation therapy (RT) is not only an adjuvant treatment for medullar tumors, even though it is mostly used for the postoperative bed and/or nonoperable lesions. Stereotactic RT is opening new possibilities and is commonly used for reirradiation or relapse [36]. Protontherapy is preferable in pediatric patients, when available. Adjuvant medullar RT is recommended for high-grade tumors such as gliomas and ependymomas following STR [9,37]. In rare cases of leptomeningeal spread of lymphoma or ependymomatosis, craniospinal irradiation may be discussed. In some cases of hemangioblastoma or metastasis from another neoplasm, stereotactic RT may replace normofractionated RT [38,39]. The risk of medullar toxicity is feared by radiation oncologists and limits the RT dose escalation: 45 Gy is the usual limit, while a 50-Gy dose carries a 0.2% risk of myelopathy, 60 Gy 6%, and 69 Gy 50% [40].
The natural history of spinal cord tumors is associated with poor functional outcome, and depending on the type, with poor oncologic outcome. These highly challenging conditions need specific management, but the first diagnostic suspicion might concern every general physician. Due to the lack of improvement of the long-term outcome during the last decades, we described the clinical complaints in order to remind every involved physician.
Complete surgical removal significantly improves the outcome but can lead to high morbidity and a disabling course. Thus, these patients require specific management including specialized imaging, a trained surgical team, highly specific pathological analyses, and an oncological follow-up. Intraoperative electrophysiological monitoring may guide the intraoperative surgical resection, so it has a clear prognostic value for assessing the risk/benefit ratio of GTR. Ependymoma and pilocytic astrocytoma are the most frequent intramedullary tumors besides genetic mutations like von Hippel-Lindau disease. In our opinion, specific imaging is mandatory to avoid making preoperative diagnostic mistakes and erroneous surgical decisions.
These rare pathologies are incompletely understood, and further prospective studies and epidemiological studies would be useful to understand their risk factors and to improve their management as an early diagnosis and treatment play a key role in the management of these conditions.
NOTES
Fig. 1.
Ependymoma (World Health Organization grade II) in a 57-year-old woman. (A, C) Sagittal and axial T2-weighted images reveal a heterogeneous expansile intramedullary mass in the cervical spine, with intratumoral cysts (white arrow) and hemosiderin cap sign (white arrowhead) at the inferior margins of the mass. Surrounding edema is present associated with syringohydromyelia (black arrowhead). (C) Axial T2-weighted image confirms the central location in the spinal cord. (B, D) Sagittal and axial contrast-enhanced T1-weighted images show intratumoral enhancement (black arrow) at C5–6 levels.

Fig. 2.
Not all expansile intramedullary lesions are neoplastic. Case 1: Perimedullary arteriovenous fistula. (A, C) Sagittal and axial T2-weighted images reveal an extensive centromedullary T2-hyperintense spinal cord edema from T7 to the conus medullaris responsible for enlargement of spinal cord. (B) Sagittal contrast-enhanced T1-weighted image shows intramedullary heterogeneous enhancement of conus medullaris (white arrows). Case 2: Central nervous system cavernomatosis with multiple spinal cavernomas. Sagittal and axial T2-weighted gradient-recalled echo sequences (B, D) are more sensitive than T2-weighted spin-echo (SE) sequences (A, C) to detect hemosiderin, showing prominent blooming at C4 and T7 levels (white arrow). Cavernomas are usually nonenhancing intramedullary lesions (not shown). Axial T2-weighted SE sequence (C) reveals typical hypointense rim (white arrowhead). Case 3: Inflammatory neuromyelitis optica. Sagittal T2-weighted images (A) reveal expansile T2-hyperintense myelitis from C2 to C7 with heterogeneous enhancement on sagittal contrast-enhanced T1-weighted image (B).
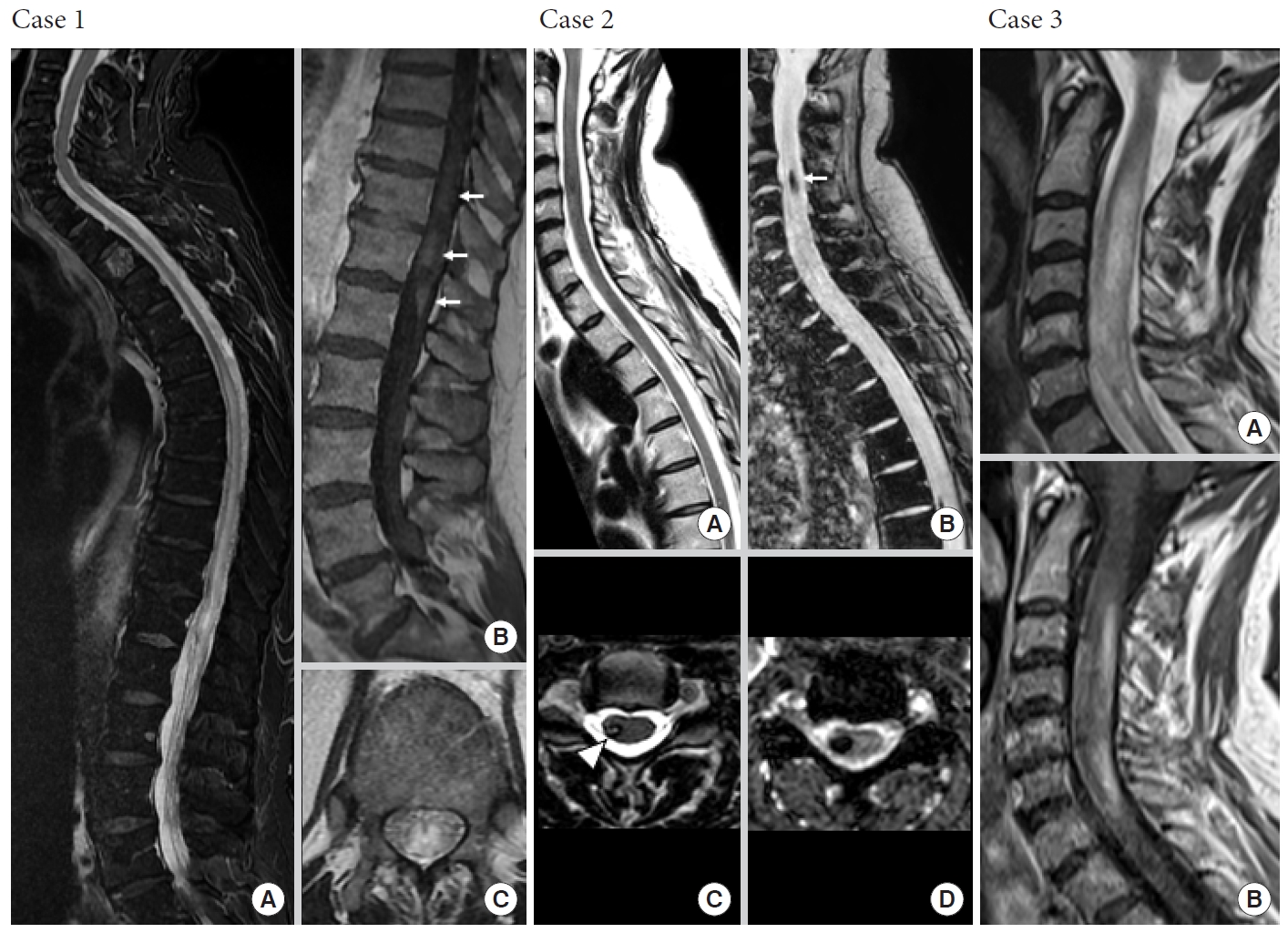
Fig. 3.
(A) Anaplastic ependymoma grade 3 MYCN amplified – (HES, × 20): highly cellular tumor with perivascular pseudorosettes, nuclear atypia, and brisk mitotic activity (arrows). (B) Extensive tumor necrosis (HES, × 10). (C) High ki-67 labeling (× 2.5).
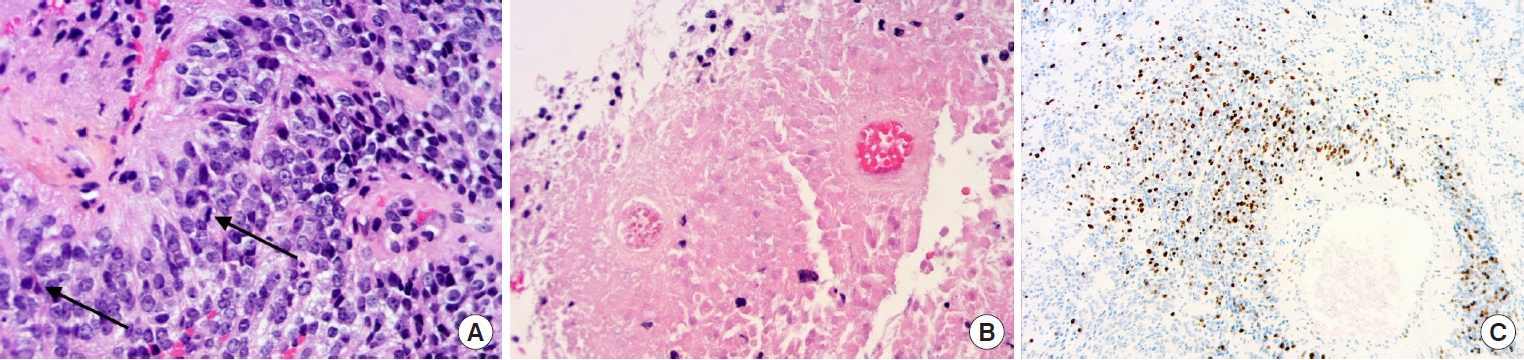
Table 1.
Population data
Table 2.
Electrophysiological monitoring
REFERENCES
1. Schellinger KA, Propp JM, Villano JL, et al. Descriptive epidemiology of primary spinal cord tumors. J Neurooncol 2008;87:173-9.


2. Samartzis D, Gillis CC, Shih P, et al. Intramedullary spinal cord tumors: part I-epidemiology, pathophysiology, and diagnosis. Global Spine J 2015;5:425-35.



3. Hoshimaru M, Koyama T, Hashimoto N, et al. Results of microsurgical treatment for intramedullary spinal cord ependymomas: analysis of 36 cases. Neurosurgery 1999;44:264-9.


4. Helgager J, Driver J, Hoffman S, et al. Molecular advances in central nervous system mesenchymal tumors. Surg Pathol Clin 2020;13:291-303.


5. Hamilton KR, Lee SS, Urquhart JC, et al. A systematic review of outcome in intramedullary ependymoma and astrocytoma. J Clin Neurosci 2019;63:168-75.


6. Babu R, Karikari IO, Owens TR, et al. Spinal cord astrocytomas: a modern 20-year experience at a single institution. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2014;39:533-40.

7. Guss ZD, Moningi S, Jallo GI, et al. Management of pediatric spinal cord astrocytomas: outcomes with adjuvant radiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2013;85:1307-11.



8. Ahmed R, Menezes AH, Awe OO, et al. Long-term disease and neurological outcomes in patients with pediatric intramedullary spinal cord tumors. J Neurosurg Pediatr 2014;13:600-12.


9. Boström A, Kanther NC, Grote A, et al. Management and outcome in adult intramedullary spinal cord tumours: a 20-year single institution experience. BMC Res Notes 2014;7:908.



10. Yang S, Yang X, Hong G. Surgical treatment of one hundred seventy-four intramedullary spinal cord tumors. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2009;34:2705-10.


11. Karikari IO, Nimjee SM, Hodges TR, et al. Impact of tumor histology on resectability and neurological outcome in primary intramedullary spinal cord tumors: a single-center experience with 102 patients. Neurosurgery 2015;76 Suppl 1:S4-13. discussion S13.


12. Helseth A, Mørk SJ. Primary intraspinal neoplasms in Norway, 1955 to 1986. A population-based survey of 467 patients. J Neurosurg 1989;71:842-5.

13. Giammattei L, Messerer M, Prada F, et al. Intramedullary cavernoma: a surgical resection technique. Neurochirurgie 2017;63:426-9.


14. Reitz M, Burkhardt T, Vettorazzi E, et al. Intramedullary spinal cavernoma: clinical presentation, microsurgical approach, and long-term outcome in a cohort of 48 patients. Neurosurg Focus 2015;39:E19.


15. Westwick HJ, Giguère JF, Shamji MF. Incidence and prognosis of spinal hemangioblastoma: a surveillance epidemiology and end results study. Neuroepidemiology 2016;46:14-23.


16. Matsuyama Y, Sakai Y, Katayama Y, et al. Surgical results of intramedullary spinal cord tumor with spinal cord monitoring to guide extent of resection. J Neurosurg Spine 2009;10:404-13.


17. Katsigiannis S, Carolus AE, Schmieder K, et al. Posterolateral myelotomy for intramedullary spinal cord tumors: the other way to do it? Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2020;162:101-7.


18. Yang C, Li G, Fang J, et al. Intramedullary gangliogliomas: clinical features, surgical outcomes, and neuropathic scoliosis. J Neurooncol 2014;116:135-43.


19. Shih RY, Koeller KK. Intramedullary masses of the spinal cord: radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics 2020;40:1125-45.


20. Kim DH, Kim JH, Choi SH, et al. Differentiation between intramedullary spinal ependymoma and astrocytoma: comparative MRI analysis. Clin Radiol 2014;69:29-35.


21. Xu D, Feng M, Suresh V, et al. Clinical analysis of syringomyelia resulting from spinal hemangioblastoma in a single series of 38 consecutive patients. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 2019;181:58-63.


22. Baker KB, Moran CJ, Wippold FJ, et al. MR imaging of spinal hemangioblastoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2000;174:377-82.


23. Millesi M, Kiesel B, Mazanec V, et al. 5-ALA fluorescence for intraoperative visualization of spinal ependymal tumors and identification of unexpected residual tumor tissue: experience in 31 patients. J Neurosurg Spine 2020 Dec 4:1-9. http://doi.org/10.3171/2020.6.SPINE20506. [Epub].


24. Hersh DS, Iyer RR, Garzon-Muvdi T, et al. Instrumented fusion for spinal deformity after laminectomy or laminoplasty for resection of intramedullary spinal cord tumors in pediatric patients. Neurosurg Focus 2017;43:E12.

25. Avila MJ, Walter CM, Skoch J, et al. Fusion after intradural spine tumor resection in adults: a review of evidence and practices. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 2015;138:169-73.


26. Hsu W, Bettegowda C, Jallo GI. Intramedullary spinal cord tumor surgery: can we do it without intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring? Childs Nerv Syst 2010;26:241-5.


27. Deletis V, Sala F. Intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring of the spinal cord during spinal cord and spine surgery: a review focus on the corticospinal tracts. Clin Neurophysiol 2008;119:248-64.


28. Chamberlain MC, Tredway TL. Adult primary intradural spinal cord tumors: a review. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 2011;11:320-8.


29. Ellison DW, Aldape KD, Capper D, et al. cIMPACT-NOW update 7: advancing the molecular classification of ependymal tumors. Brain Pathol 2020;30:863-6.



30. Swanson AA, Raghunathan A, Jenkins RB, et al. Spinal cord ependymomas with MYCN amplification show aggressive clinical behavior. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2019;78:791-7.


31. Ghasemi DR, Sill M, Okonechnikov K, et al. MYCN amplification drives an aggressive form of spinal ependymoma. Acta Neuropathol 2019;138:1075-89.



32. Vera-Bolanos E, Aldape K, Yuan Y, et al. Clinical course and progression-free survival of adult intracranial and spinal ependymoma patients. Neuro Oncol 2015;17:440-7.


33. Burkhard C, Di Patre PL, Schüler D, et al. A population-based study of the incidence and survival rates in patients with pilocytic astrocytoma. J Neurosurg 2003;98:1170-4.


34. Collins VP, Jones DT, Giannini C. Pilocytic astrocytoma: pathology, molecular mechanisms and markers. Acta Neuropathol 2015;129:775-88.



35. Balasubramanian A, Gunjur A, Gan HK, et al. Response to combined BRAF/MEK inhibition in adult BRAF V600E mutant spinal pilocytic astrocytoma. J Clin Neurosci 2020;79:269-71.


36. Napieralska A, Brąclik I, Radwan M, et al. Radiosurgery or hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy after craniospinal irradiation in children and adults with medulloblastoma and ependymoma. Childs Nerv Syst 2019;35:267-75.


37. Oh MC, Ivan ME, Sun MZ, et al. Adjuvant radiotherapy delays recurrence following subtotal resection of spinal cord ependymomas. Neuro Oncol 2013;15:208-15.


38. Bridges KJ, Jaboin JJ, Kubicky CD, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery versus surgical resection for spinal hemangioblastoma: a systematic review. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 2017;154:59-66.



- TOOLS