 |
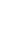 |
- Search
|
|
||
Abstract
NOTES
Conflict of Interest
Dr. Pham reports consultant fees with Medtronic and Thompson Surgical. The other authors have nothing to disclose.
Funding/Support
This study received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author Contribution
Conceptualization: NAP, NJB, ZAP, NBH, CK; Data curation: NAP, SO’B, CDR; Formal analysis: NAP, SO’B, CDR, JG; Methodology: NAP, SO’B, CDR, JG, NBH; Project administration: NAP, ZAP, LDDA, MHP; Visualization: NAP, JG, NJB, ZAP, NBH; Writing - original draft: NAP, SO’B, CDR, NBH, CKB, JG; Writing - review & editing: NAP, SO’B, CDR, CKB, MHP, SC.
Table 1.
| Study | Year | Country | Model | Study design | Experimental (3D-pTi brand) | Comparison | n (3D-pTi) | Outcome measure(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adl Amini et al. [18] | 2021 | USA | Human | Retrospective cohort | Novel | PEEK | 113 (38) | Subsidence |
| Corso et al. [19] | 2022 | USA | Human | Retrospective cohort | CONDUIT | PEEK | 186 (96) | Device-related revision, on-device related reoperation |
| Laratta et al. [14] | 2021 | USA | Ovine | Prospective, randomized cohort | JULIET Ti LL | PEEK | 14 (14)* | Micro-CT osseointegration, quantitative histomorphometry of BIC and ROI bone/cartilage |
| McGilvray et al. [20] | 2018 | USA | Ovine | Prospective, randomized cohort | Tritanium PL | PEEK | 27 (18) | Biomechanical testing of ROM and stiffness, micro-CT BV/ TV and MDBV/MDTV, qualitative histological analysis of osseointegration |
| Van Horn et al. [21] | 2021 | USA | Ovine | Prospective, randomized cohort | HEDRON | PEEK | 18 (6) | Micro-CT BV quantification, histomorphometric BAR quantification |
| Carpenter et al. [16] | 2018 | USA | - | FEA | Tesera Trabecular Technology | Porous PEEK | - | Energy effective strain in adjacent bony layer under compression, tension, and shear forces |
| Papaefstathiou et al. [22] | 2021 | France | - | In vitro | Ti-LIFE technology | PEEK | - | hMSC morphology, proliferation, differentiation via SEM, DNA fluorescent assay and RT-qPCR respectively. Biochemical assays of ALP and calcium content |
3D-pTi, 3-dimensional printed titanium; PEEK, polyetheretherketone; CT, computed tomography; BIC, bone-implant contact; ROI, region of interest; ROM, range of motion; BV/TV, bone volume/total volume; MDBV/MDTV, mean density of bone volume/mean density of total volume; BAR, bone apposition ratio; FEA, finite element analysis; hMSC, human mesenchymal stem cell; SEM, scanning electron microscope; RT-qPCR; reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction; ALP, alkaline phosphatase.
Table 2.
| Study | Outcome measure(s) | Outcome favors |
|---|---|---|
| Adl Amini et al. [18] | Subsidence | 3D-pTi |
| Corso et al. [19] | Device-related reoperation | Equivalent |
| Laratta et al. [14] | Micro-CT osseointegration | 3D-pTi |
| Quantitative histomorphometry of BIC and ROI bone/cartilage | 3D-pTi | |
| McGilvray et al. [20] | Biomechanical testing of ROM and stiffness | 3D-pTi |
| Micro-CT BV/TV and MDBV/MDTV at all time points | 3D-pTi | |
| Qualitative histological analysis of osseointegration | 3D-pTi | |
| Van Horn et al. [21] | Micro-CT BV quantification at 6 weeks | 3D-pTi |
| Mirco-CT BV quantification at 12 weeks | Equivalent | |
| Histomorphometric BAR quantification at 6 weeks and 12 weeks | 3D-pTi | |
| Carpenter et al. [16] | Energy effective strain in adjacent bony layer under compression, tension, and shear forces at 4 and 24 weeks | 3D-pTi |
| Papaefstathiou et al. [22] | hMSC morphology | 3D-pTi |
| Proliferation, measured by cell count | 3D-pTi | |
| Differentiation measured by biochemical assays of ALP and calcium content | Equivalent |
3D-pTi, three-dimensional printed titanium; PEEK, polyetheretherketone; CT, computed tomography; BIC, bone-implant contact; ROI, region of interest; ROM, range of motion; BV/TV, bone volume/total volume; MDBV/MDTV, mean density of bone volume/mean density of total volume; BAR, bone apposition ratio; hMSC, human mesenchymal stem cell; ALP, alkaline phosphatase.
Table 3.
| Study | Age (yr) | % Male | F/U | n (3D-pTi) | 3D-pTi modulus of elasticity | Levels implanted (3D-pTi) | Surgical indications (%) | Surgical approach (%) | Outcome measure(s) | Summary of findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adl Amini et al. [18] 2021 | Median: 60 (IQR, 51.0–70.0) | 54.9 | 29.5 (24–57) Weeks | 113 (38) | 2,500 mPa | 186 (67) | Spondylolisthesis (76.1), spinal stenosis (73.5), foraminal stenosis (61.9) DDD (50.4)* | LLIF (100.0) | Cage subsidence | Statistically significant lower rates of grade 0 subsidence for 3D-pTi and higher rates of severe subsidence for PEEK. Use of printed Ti cages decreased the risk of severe subsidence and the presence of DDD increased the risk |
| Corso et al. [19] 2022 | Mean: 59.2 ± 12.5 | 50.5 | 6 Months | 186 (96) | Not Available | 186 (96) | Multiple 78.5), spondylolisthesis (6.5), DDD (5.9), spinal stenosis (3.8), spondylosis (3.8) | PLIF/TLIF (71.0), ALIF/LLIF (29.0) | Device-related reoperation | Propensity-score matched patients had 0 occurrences of device-related revision in either group. There was 1 non-device-related reoperation in the 3D-printed Ti group and 0 in the PEEK. No statistically significant differences were found |
F/U, follow-up; 3D-pTi, 3-dimensional printed titanium; IQR, interquartile range; LLIF, lateral lumbar interbody fusion; PEEK, polyetheretherketone; DDD, degenerative disk disease; PLIF, posterior lumbar interbody fusion; TLIF, transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion; ALIF, anterior lumbar interbody fusion.
Table 4.
| Study | Age | Sex | F/U | n (3D-pTi) | 3D-pTi modulus of elasticity | Levels implanted (3D-pTi) | Surgical approach | Outcome measure(s) | Summary of findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laratta et al. [14] 2021 | 4–5 years of age | All female | 4 and 8 weeks | 14 (14)* | 2 GPa | 28 (14) | Retroperitoneal anterior fusion at L2–3 and L4–5 | Micro-CT osseointegration, quantitative histomorphometry of BIC and ROI bone/cartilage | Lack of osseointegration about the implant-bone interface for PEEK, with fibrotic tissue present instead. Osseointegration present at the 3D-pTi interface, including de novo osseous formation at the center of the cage. Significantly higher mean bone and cartilage in the ROI for the 3D- pTi implants versus the PEEK implants (p = 0.008 and 0.015 for bone and cartilage, respectively). Significantly higher BIC in the 3D-pTi implants as well. |
| McGilvray et al. [20] 2018 | - | - | 8 and 16weeks† | 27 (18) | Not available | 54 (18) | LLIF at L2–3 and L4–5 | Biomechanical testing of ROM and stiffness, micro-CT BV/TV and MDBV/MDTV, qualitative histological analysis of osseointegration | Statistically significantly lower ROM and higher stiffness in all directions at all time points for 3D-pTi. Statistically significantly higher BV/TV and MDBV/MDTV for the 3D-pTi group at all time points. Qualitatively higher osteoblast/clast activity, fibrous neovascularization, bony filling of implant pores in the 3D-pTi group. |
| Van Horn et al. [21] 2021 | - | All female | 6 and 12 weeks‡ | 18 (6) | Not available | 36 (12) | LIF at L2–3 and L4–5 | Micro-CT BV quantification, histomorphometric BAR quantification | Statistically significantly higher BV at 6 weeks for 3D-pTi but no difference at 12 weeks. Statistically significantly higher BAR for 3D-pTi at both time points. |
F/U, follow-up; 3D-pTi, 3-dimensional printed titanium; CT, computed tomography; BIC, bone-implant contact; ROI, region of interest; PEEK, polyetheretherketone; LLIF, lateral lumbar interbody fusion; ROM, range of motion; BV/TV, bone volume/total volume; MDBV/MDTV, mean density of bone volume/mean density of total volume; LIF, lumbar interbody fusion; BAR, bone apposition ratio.
Table 5.
| Study | Study design | 3D-pTi modulus of elasticity | Porosity | Comparison | Observations collected at: | Summary of findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carpenter et al. [16] 2018 | FEA | NA | 71.15% | 3D-pTI vs. PEEK | 4 and 28 weeks | Significantly higher energy effective strain in the adjacent bony layer under compression, tension, and shear at 4 and 24 weeks for the porous PEEK |
| Papaefstathiou et al. [22] 2021 | In vitro | NA | 70%–75% | 3D-pTi vs. PEEK | 7, 14, 21, 28, and 42 days | For morphology, 3D-pTi formed a dense layer of intermixed hMSC and ECM by day 28. For PEEK, cells were sparse on day 7 but multilayers were formed at day 42. For proliferation, 3D-pTi showed significantly higher cell number at all time points. For differentiation, ALP activity and calcium content per cell, no significant differences were observed. |
REFERENCES

- TOOLS
- Related articles in NS
-
Journal Impact Factor 3.2