- Search
| Neurospine > Volume 17(1); 2020 > Article |
|
|
This article has been corrected. See "Polyetheretherketone Versus Titanium Cages for Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Meta-Analysis and Review of the Literature" in Volume 17 on page 473.
Abstract
Objective
Lumbar fusion with implantation of interbody cage is a common procedure for treatment of lumbar degenerative disease. This study aims to compare the fusion and subsidence rates of titanium (Ti) versus polyetheretherketone (PEEK) interbody cages after posterior lumbar interbody fusion and investigate the effect of clinical and radiological outcomes following fusion on patient-reported outcomes.
Methods
A systematic search strategy of 4 electronic databases (MEDLINE, Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane) was conducted using different MeSH (medical subject headings) terms until January 2020. Pooled odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated using fixed and random-effect models based upon the heterogeneity (I2) to estimate the association between interbody cages and the measured outcomes.
Results
A total of 1,094 patients from 11 studies were reviewed. The final analysis included 421 patients (38.5%) who had lumbar surgery using a Ti and/or a Ti-coated interbody cage and 673 patient (61.5%) who had lumbar surgery using a PEEK cage. Overall, PEEK interbody devices were associated with a significantly lower fusion rate compared with Ti interbody devices (OR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.41–0.93; p = 0.02). There was no difference in subsidence rates between Ti and PEEK groups (OR, 0.91; 95% CI, 0.54–1.52; p = 0.71). Also, there were no statistically significant differences in visual analogue scale (VAS)-low back pain (p = 0.14) and Japanese Orthopedic Association scale (p = 0.86) between the 2 groups. However, the PEEK group had lower odds of leg pain after surgery compared to the Ti group (OR [VAS-leg], 0.61; 95% CI, 0.28–0.94; p = 0.003).
Conclusion
Ti and Ti-coated PEEK cages used for posterior lumbar interbody fusion are associated with similar rates of subsidence, but a higher rate of fusion compared to PEEK interbody cages. Randomized controlled trials are needed to better assess the effect of cage materials and potential factors that could influence the outcomes of interbody lumbar fusion.
Symptoms arising from lumbar degenerative disease are common and can be debilitating, leading to surgical intervention to alleviate pain and restore function. The prevalence of low back pain (LBP) due to lumbar spondylosis is estimated at 3.6% worldwide, and 4.5% in North America [1]. When indicated, the application of interbody techniques to posterior lumbar fusion surgery is performed in a way to promote circumferential fusion across the instrumented levels. The use of interbody fusion techniques has increased and is a technique often utilized in the treatment of spondylolisthesis and spinal deformity [2,3]. However, as rates of both disease and surgical treatment rise, the number of patients undergoing unsuccessful fusion operations has increased as well [4,5]. Hence, understanding factors and surgical techniques influencing achievement of bony fusion is becoming increasingly crucial for improving outcomes in treatment of lumbar spondylosis.
One of the most commonly employed instrumentation techniques for achieving fusion is implantation of an interbody cage. A study from the Nationwide Inpatient Sample database showed as many as 83% of surgeries for degenerative spondylolisthesis involve the use of an interbody cage [6]. The BAK titanium (Ti) cage (Spine-Tech, Minneapolis, MI, USA) was the first cage to be introduced and to be successfully implanted in humans using a posterior approach in 1992 [7]. Ti was used in interbody cages because it enhances cell adhesion and osseointegration favoring bone fusion, but at the same time, may have a higher rate of subsidence compared to polyetheretherketone (PEEK) due to differences in the modulus of elasticity [8,9]. Despite that, PEEK is chemically inert with limited cell adhesion and fixation to bone [10].
The characteristics and clinical outcomes of Ti and PEEK cages for lumbar spinal fusion were explored in several studies [11-20], but the findings were largely inconsistent regarding fusion and subsidence rates. Hence, this study presents a systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the clinical outcomes of interbody cages in posterior lumbar fusion surgery. In this study, we determined the effect of interbody cage materials (Ti vs. PEEK) on fusion rates, cage subsidence rates, and patient-reported outcomes (PROs) following posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF).
We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis in line with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-analysis (PRISMA) guidelines [21]. MEDLINE, Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane were searched for peer-reviewed articles written in English and published from database inception to January 2020, that included retrospective and prospective assessments of outcomes following lumbar spinal fusion using Ti vs. PEEK interbody cages. We used the following search terms: polyetheretherketone, PEEK, Ti, cage, interbody, interbody fusion, and lumbar fusion.
Two of the authors (EM and NF) independently identified articles eligible for review with input by the senior author (JHS). Studies were selected for inclusion in the meta-analysis if they evaluated PEEK and Ti interbody cages in spinal lumbar fusion procedures for degenerative spinal disease, intervertebral disc herniation, spondylolisthesis, and spinal stenosis. Studies were included in the meta-analysis if they reported at least one of the following outcomes: (1) fusion rates, (2) subsidence rates, or (3) PROs for Ti and PEEK. Initial screenings of abstracts were performed, followed by full-text reviews. Covidence Systematic Review Software (Veritas Health Innovation, Melbourne, VIC, Australia) [22] was used to organize the screening of abstracts, fulltext articles, and the selection of studies that meet the inclusion criteria.
The primary outcome was fusion rate and we tested the null hypothesis that Ti and PEEK have the same fusion rate in PLIF. Ti and Ti-coated interbody cages were grouped because they bring together the bio-compatible characteristics of Ti important for fusion. We compared patient baseline characteristics (age, sex, and comorbidities) in studies reporting on the primary outcomes to examine if patient characteristics can affect fusion and subsidence rates and could therefore inform the interpretation of nondifferential results. Secondary outcomes included the rate of cage subsidence and PROs that were assessed in the included studies: (1) Oswestry Disability Index; (2) visual analogue scale (VAS) for low back or leg pain; (3) Japanese Orthopedic Association (JOA) score for LBP, and radiologic outcomes when available.
Data were independently extracted by 2 of the authors (EM and NF) using a standardized protocol and reporting electronic sheet. Disagreements between the 2 authors were resolved by arbitration when consensus could not be reached after discussion. Two reviewers independently assessed the quality of the included studies using the Newcastle-Ottawa scale, which allocates each study a quality grade of maximum 9 points based on (1) selection of the study groups, (2) comparability of the groups, and (3) assessment of outcomes [23].
Continuous data were analyzed by calculating the pooled weighted mean difference with 95% confidence interval (CI). The association between the type of interbody cages and the primary and secondary outcomes were reported using the odds ratio (OR) with 95% CI. Between-study heterogeneity was evaluated using the I2 statistic. A fixed-effect model was used for I2 < 50%, while for I2 > 50% a random-effect model was employed. Statistical tests were 2-sided and p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. We inspected the symmetry of the funnel plots and performed the Egger test to assess publication bias. Also, we used a nonparametric trim-and-fill procedure to identify and correct for funnel plot asymmetry and re-estimate the aggregate results [24]. We used R ver. 3.5.3 (R Project for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria), with meta [25] and metafor packages for all analyses [26].
Eleven studies involving PLIF with Ti and PEEK cages were included in this meta-analysis. The results of our search strategy are summarized in the PRISMA chart (Fig. 1). Eight single-center studies were retrospective, observational, and 3 single-center studies were prospective studies of which, 1 study was a randomized clinical pilot study. Four studies were carried out in Germany [17,20,27,28], 4 studies in Japan [13,16,18,19], 1 study in Italy [12], 1 study in China [15], 1 study in the United Kingdom (Table 1) [14].
The data of 1,094 patients was analyzed in this meta-analysis, of which 673 (61.5%) had lumbar interbody fusion using a Ti or Ti-coated cage and 421 (38.5%) had lumbar interbody fusion using a PEEK cage. The mean follow-up time in the Ti and PEEK groups was 20.5 and 22.3 months respectively (range, 6–84 months). The Ottawa-Newcastle quality assessment tool showed that most studies carry a potential risk of bias (Supplementary Table 1).
Demographic characteristics of Ti and PEEK patients extracted from each study are summarized in Table 2. There was no difference between the mean age of the Ti (59.23±3.89 years) and PEEK groups (58.44±3.43 years) (p = 0.89). Overall 49.5% and 48.9% were men in the Ti and PEEK groups, respectively. Body mass index (BMI) for Ti and PEEK patients was reported in 3 studies only [15-17]. Mean BMI for Ti and PEEK groups were similar (25.76±0.64 kg/m2 vs. 26.37±1.08 kg/m2; p = 0.93). Comorbidities such as diabetes mellitus, Parkinson disease, treatment with hemodialysis, long-term steroid use for rheumatoid arthritis or systemic lupus erythematosus, were reported only in one study (p = 0.64) [19].
Lumbar fusion was performed for a total of 1,094 patients (Ti421, PEEK-673). PLIF was performed in 5 studies [13,15,18,27,28] for 390 patients (35.64%) (Ti-165, PEEK-225) and transforaminal interbody fusion (TLIF) in 6 studies [12,14,16,17,19,20,29] for 704 patients (64.36%) (Ti-256, PEEK-448). The different types of interbody cages used were summarized in Table 1, revealing 3 studies using Ti-coated PEEK cages [13,17,18]. Only 3 studies reported local autograft in their surgical protocol [16-18]. One of these studies used autograft mixed with bone graft substitute [17]. Estimated blood loss and operative time were only reported in 1 study [16]. Mean blood loss in the Ti group was 386.4±128.8 mL vs. 360.8±145.0 mL (p = 0.53). Average operative time was 183.8±29.4 minutes vs. 174.7±32.9 minutes (p = 0.32).
Early fusion status was assessed most commonly at 12 months and 24 months but as early as 3 months in 1 study by dynamic plain radiographs, computed tomography (CT) scan, and multiplanar reformation (MPR)-CT scan (Table 3). The assessment of fusion was not uniform across the studies, although it was most commonly determined based on bone bridges inside and outside the cage (summary in Table 3). None of the studies reported using bone morphogenic protein. The fusion rates were reported in all studies at the last follow-up. The range of the reported fusion rates was 53%–100% in the Ti group and 32%–100% in the PEEK group. Pooled analysis of fusion rates showed a statistically significant difference with PEEK interbody devices demonstrating 38% lower odds of fusion compared with Ti interbody devices (OR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.41–0.93; p =0.02; I2=25%) (Fig. 2).
Subsidence rates were successfully extracted from 6 studies [12,15-18,27] at a follow-up range (6–24 months). Four studies used CT scans [12,15,18,27], 1 study used MPR-CT scan [16], and 1 study used X-ray [17]. The definition of subsidence used in the studies is summarized in Table 3. Two studies reported no subsidence in either groups and were excluded from the meta-analysis because they do not provide any indication of either the direction or the magnitude of the effect. The range of subsidence rates in the Ti and PEEK groups was 0%–36% and 0%–31%, respectively. Overall, there was no difference in the rate of subsidence between Ti and PEEK interbody cages (OR, 0.91; 95% CI, 0.54–1.52; p =0.71; I2= 0%) (Fig. 3).
PROs were not reported in most the included studies. VAS-leg and VAS-LBP were reported in only 2 studies [16,17], and JOA scale for LBP was only reported in 2 studies [16,18]. There were no statistically significant differences in VAS-LBP (p = 0.14) and JOA scale (p = 0.86) between the Ti and PEEK groups. However, the PEEK group had 39% lower odds of leg pain after surgery compared to the Ti group (OR [VAS-leg], 0.61; 95% CI, 0.28–0.94; p = 0.0003; I2= 88%) (Fig. 4).
We found some evidence of publication bias, as suggested by slight asymmetry of the funnel plot (Egger test, z=-3.367; p = 0.009) and association between effect sizes and corresponding sampling variances (Begg test, z=-2.415; p = 0.01). According to the trim-and-fill method to correct for publication bias (Fig. 5), the association between type of cage and fusion rate was not significant after imputing 3 possible missing studies (adjusted OR, 0.90; 95% CI, 0.60–1.35; p = 0.61), suggesting a potential role for small-study effects or publication bias on the meta-analysis results.
This systematic review and meta-analysis of 11 studies involving 1,094 patients who underwent posterior lumbar fusion demonstrated increased odds of bony fusion with use of Ti and Ti-coated interbody cages in comparison to PEEK interbody cages for posterior lumbar fusion (p = 0.02). Demographic characteristics including age, sex, and BMI were similar between the 2 groups. However, important factors such as smoking status, osteoporosis and bone mineral density (BMD) were not reported in the included studies. Studies investigating posterior lumbar fusion identified low BMI, diabetes mellitus, osteoporosis, loosening of posterior instrumentation, and pear-shaped disc as potential risk factors for subsidence [14,30]. In addition to that, posterior screw fixation, the size and shape of the interbody cage, and the number of spinal levels fused, could impact the biomechanics of the lumbar spine following posterior fusion [31,32]. However, none of the studies included in this meta-analysis presented a comparative analysis of PEEK vs. Ti to study the effect of potential risk factors across the types of interbody cages.
Ti and PEEK are the most common materials used for interbody cages. In fact, PEEK implants are widely used for different applications because of their mechanical properties and good chemical resistance. In addition to that, their radiolucent property allows for better assessment of fusion by imaging [33]. However, the application of PEEK has been limited by the formation of a biofilm layer around its surface that potentially affects fusion to cortical bone [34]. This limitation of PEEK could be avoided by the application of Ti which has a microscopic rough surface that increases osteogenic cell differentiation factors. To further explore the properties of Ti, several studies investigated PEEK interbody cages with electron beam coating of Ti onto the surfaces showing some benefits compared to PEEK alone [35]. In fact, Ti promotes an inflammatory cellular response in its environment affecting bone remodeling [36]. In this instance, bioactive substances, in particular microstructured Ti, have been shown to improve the biocompatibility of PEEK interbody cages and to increase the rate of bone fusion [37].
Unlike PEEK that has an elastic modulus similar to bone, Ti material has an elastic mismatch that can lead to stress shielding and bone remodeling around the implant [38,39]. In this study, there was no difference in subsidence rates between Ti and PEEK cages. However, Seaman et al. [40], reviewed 4 cervical studies and 2 lumbar studies and showed that the rate subsidence for Ti was greater in the cervical and lumbar spine. This meta-analysis included exclusively 11 lumbar studies that give our results more power, but also included Ti-coated PEEK cages, a composite that overcomes the modulus of elasticity of Ti that leads to subsidence and provides effective osseointegration. Ti-coated PEEK cages may benefit from the properties of both materials to allow early osseointegration and fusion, at the same time, maintaining ideal disc heights and alignments for degenerative lumbar disease [41].
In addition to that, this meta-analysis included 5 PLIF studies and 6 TLIF studies. Previous comparative studies revealed that PLIF with bilateral cage placement was shown to be equivalent in fusion to TLIF with a unilateral interbody device. Intraoperative and postoperative complications were shown to be lower in TLIF compared to PLIF procedures [42,43]. So far, only 1 randomized control study reported radiological and clinical outcomes using Ti-coated and uncoated PEEK cages for TLIF but did not demonstrate a superiority for Ti-coated PEEK. Høy et al. [44], noted several problems in their study could affect fusion, such as endplate preparation, severity of osteopenia, osteoporosis, and fixation stability. Nevertheless, several experienced centers have reported improved clinical outcomes with minimal subsidence if the endplates are prepared appropriately [45,46], but these clinical studies have small sample sizes and factors associated with poor clinical and radiological outcomes for lumbar interbody fusion have not been extensively explored yet.
This meta-analysis is adherent to PRISMA guidelines and includes all relevant articles identified by an extensive literature search to assess the outcomes of interbody fusion in posterior lumbar surgery. According to the Ottawa-Newcastle quality assessment tool the quality of the included studies is low. A heterogeneity between the studies for subsidence rate and PROs was identified in the statistical analysis. The definition criteria, follow-up period and modalities used for assessment of fusion and subsidence were different across studies as shown in Table 3. The effect of important factors such as smoking, osteoporosis, and BMD were not reported in these studies. Many studies did not report the type and size of interbody cages used (Table 1). Also, a small-study effect was demonstrated in the setting of low-quality evidence, indicating that the results should be carefully interpreted. While Seaman et al. [40] published a meta-analysis including 4 anterior cervical discectomy and fusion studies and 2 additional TLIF studies using Ti and PEEK, this is the first study that evaluates the outcomes of Ti and PEEK in posterior lumbar fusion procedures. However, the results of this meta-analysis need to be investigated in a randomized controlled trial (RCT) that takes into account all the possible factors that could be associated with the clinical outcomes of interbody lumbar fusion.
As detailed in this review, the comparison of cage materials between PEEK and Ti revealed a competitive advantage of Ti and PEEK on high fusion and low subsidence respectively. In this meta-analysis, Ti interbody cages demonstrated a significantly higher fusion rate than that of PEEK in posterior spinal fusion. However, PEEK did not show significant superiority to subsidence in posterior spinal fusion. Although our understanding of indications and outcomes is steadily increasing, rigorous evaluation of indications and characterization of risks and outcomes is still required. So far, one pilot RCT compared Ti and PEEK interbody cages for posterior lumbar fusion. Future RCTs are needed to better investigate the implants and the associated factors that influence the outcomes of interbody fusion.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Elie Massaad, MD research work, and education at Harvard Medical School are supported by a scholarship from the Dubai-Harvard Foundation for Medical Research (DHFMR).
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
Supplementary Table 1 can be found via https://doi.org/10.14245/ns.2040058.029.
Supplementary Table 1.
Detailed Newcastle-Ottawa Scale of each included cohort study
Fig. 2.
Forest plot showing the effect sizes and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) of studies comparing the fusion rates of PEEK vs. Ti. PEEK shows less odds of fusion compared to titanium cage for lumbar interbody fusion (odds ratio, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.41–0.93; p=0.02). PEEK, polyetheretherketone; Ti, titanium; df, degrees of freedom.

Fig. 3.
Forest plot showing effect sizes and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) of studies comparing subsidence rates for titanium and PEEK interbody cages. Titanium and PEEK have similar odds of subsidence (odds ratio, 0.91; 95% CI, 0.54–1.52; p=0.71). PEEK, polyetheretherketone; Ti, titanium; df, degrees of freedom.

Fig. 4.
Forest plot showing effect sizes and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) of studies comparing visual analogue scale (VAS) scores for low back pain (A) and leg pain (B), and the Japanese Orthopedic Association (JOA) score for low back pain (C) for titanium and PEEK interbody cages. PEEK, polyetheretherketone; df, degrees of freedom.
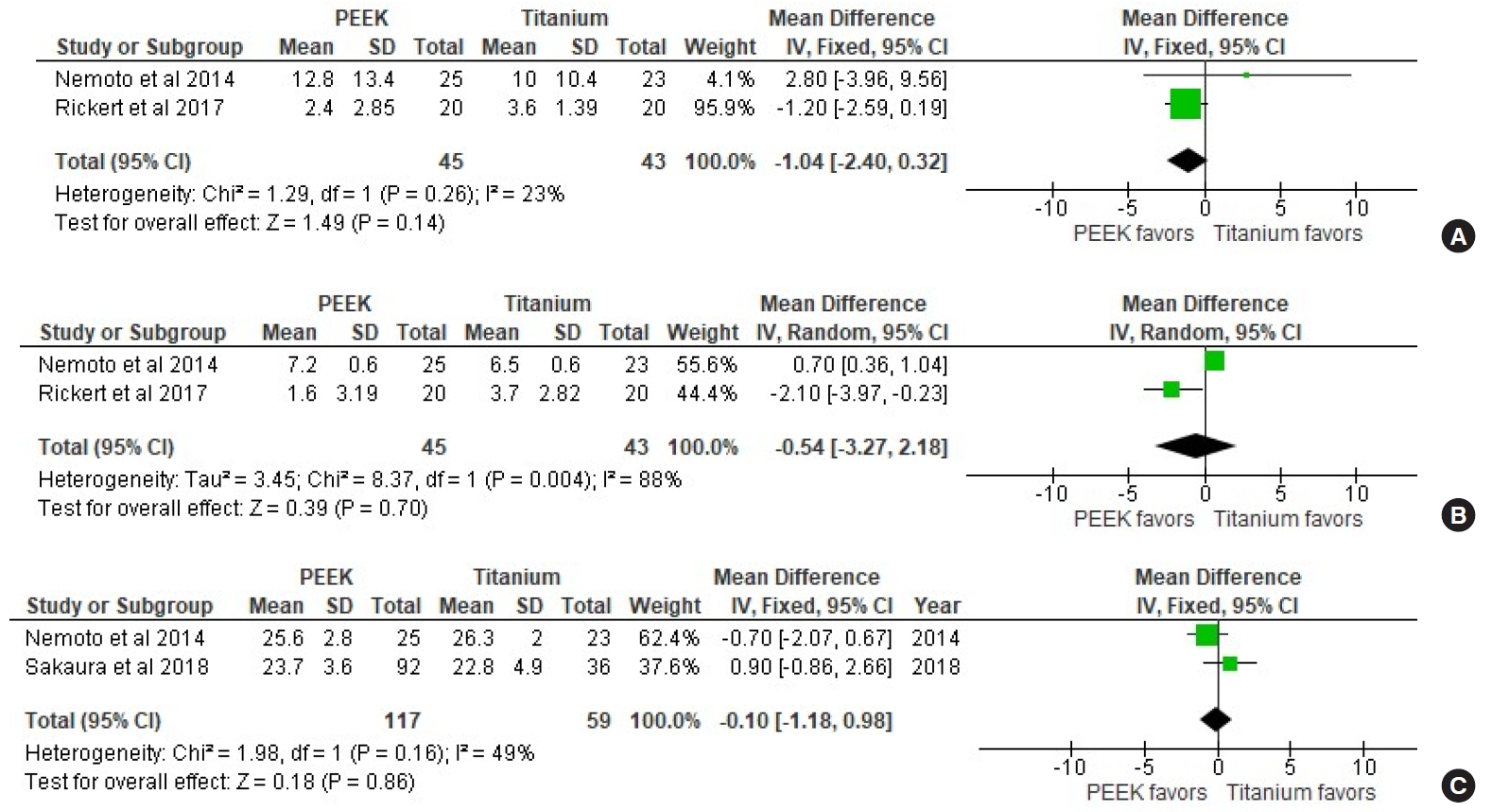
Table 1.
Summary of study design, cage type, total patients, and type of procedure done
| Study | Quality of evidence | Study design | Country |
No. of patients (%) |
Procedure |
Type of cage |
Bone graft used | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEEK | Titanium | Titanium | PEEK | ||||||
| Cuzzocrea et al. [12] 2019 | Very low | Retrospective | Italy | 20 (50) | 20 (50) | TLIF | - | - | - |
| Wrangel et al. [27] 2017 | Very low | Retrospective | Germany | 25 (62.5) | 15 (37.5) | PLIF | - | - | No grafting |
| Kashii et al. [13] 2019 | High | Prospective | Japan | 26 (50) | 26 (50) | PLIF | ProSpace Xp | ProSpace | Yes, local bone |
| Schnake et al. [11] 2015 | High | Prospective | Germany | 30 (50) | 30 (50) | PLIF | Titanium-coated PEEK cage | - | - |
| Tanida et al. [19] 2016 | Very low | Retrospective | Japan | 40 (31.2) | 77 (68.8) | TLIF | Crescent shaped: 8 Kidney Bean Mesh cages, 1 Devex cage, and 84 Boomerang II cages | Milestone cages, crescent shaped | Yes, local bone and iliac crest |
| Vazifehdan et al. [20] 2019 | Very low | Retrospective | Germany | 323 (77.1) | 96 (22.9) | TLIF | - | - | - |
| Sakaura et al. [18] 2019 | Very low | Retrospective | Japan | 92 (71.8) | 36 (28.2) | PLIF | - | - | Yes, local bone |
| Rickert et al. [17] 2017 | High | Prospective | Germany | 20 (50) | 20 (50) | TLIF | MectaLIF TiPEEK Oblique | MectaLIF PEEK | Autograft + bone graft substitute |
| Nemoto et al. [16] 2014 | Very low | Retrospective | Japan | 25 (52.1) | 23 (47.9) | TLIF | Bullet-shaped - Capstone | Bullet-shaped | Autograft |
| Liu et al. [15] 2015 | Very low | Retrospective | China | 52 (47.2) | 58 (52.8) | PLIF | - | - | - |
| Lee et al. [14] 2017 | Very low | Retrospective | UK | 20 (50) | 20 (50) | TLIF | 3D porous lamellar | - | - |
Eight of 11 were deemed to have very low quality of evidence. All studies included were from Europe or Asia. A transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion procedure was done in 6/11 studies.
PEEK, polyetheretherketone; PLIF, posterior lumbar interbody fusion; TLIF, transforaminal interbody fusion; 3D, 3 dimensional.
Table 2.
Patient demographic characteristics, surgical indication for lumbar interbody fusion and levels of operated lumbar spine
| Study |
Males, n (%) |
Age (yr), mean±SD |
BMI (kg/m2), mean±SD |
Surgical Indication |
Lumbar level |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium | PEEK | Titanium | PEEK | Titanium | PEEK | Titanium | PEEK | Titanium | PEEK | |
| Cuzzocrea et al. [12] 2019 | 8 (40) | 9 (45) | 55 (43–64) | 48 (39–57) | - | - | 8 Disc herniation, 5 spondylolisthesis, 7 lumbar stenosis | 12 Disc herniation, 3 spondylolisthesis, 5 lumbar stenosis | - | - |
| Wrangel et al. [27] 2017 | 10 (66.7) | 7 (28) | 63 ± 12 | 69 ± 10 | - | - | Degenerative instability | L2–3 (0%); L3–4 (29%); L4–5 (35%); L5–S1 (35%) | L2–3 (7%); L3–4 (29%); L4–5 (39%); L5–S1 (25%) | |
| Kashii et al. [13] 2019 | - | - | 67.6 ± 11.2 | 25.4 ± 4.2 | 1 Disc herniation, 14 spondylolisthesis, 11 lumbar stenosis | L2-3 to L4-5 | ||||
| Schnake et al. [11] 2015 | 19 (63.3) | 19 (63.3) | 51 (31-70) | - | - | Lumbar degenerative disease | L2/3 (3%), L3/4 (7%), L4/5 (45%) and L5/S1 (45%) | |||
| Tanida et al. [19] 2016 | 15 (19.4) | 36 (90) | 62.5 (20–86) | 65 (30–82) | - | - | - | - | T11–12 (1%); L2–L3 (9%); L3–L4 (14%); L4–L5 (70%); L5–S1 (22%) | L2–L3 (4%); L3–L4 (8%); L4–L5 (59%); L5–S1 (29%) |
| Vazifehdan et al. [20] 2019 | - | - | 70.9 ± 11.3 | - | - | Degenerative disc disease, recurrent disc herniation, facet joint arthritis, and spinal stenosis | - | - | ||
| Sakaura et al. [18] 2019 | 19 (52.7) | 44 (47.8) | 65.3 (37–83) | 68.5 (42–85) | - | - | Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis | L3–4 (11%), L4–5 (78%), L5–S1 (11%) | L1–2 (1%), L2–3 (1%), L3–4 (16.3%), L4–5 (77%), L5–6 (1%), L5–S1 (3%) | |
| Rickert et al. [17] 2017 | - | - | 67.7 ± 12.5 | 68.3 ± 10.5 | 27.7 ± 4.9 | 28.5 ± 3.6 | Degenerative disc disease n=9, spinal stenosis n=7, spondylolisthesis with stenosis n=3, and spondylolisthesis with degenerative disc n=1 | Degenerative disc disease n=10; spinal stenosis n=6; isthmic or low dysplastic spondylolisthesis n=2, degenerative spondylolisthesis with stenosis n=2 | L2–3 (4%); L3–4 (38%); L4–5 (58%) | L2–3 (4%); L3–4 (38%); L4–5 (58%) |
| Nemoto et al. [16] 2014 | 23 (100) | 22 (88) | 40.7 ± 10.2 | 42.9 ± 10.4 | 24.6 ± 2.8 | 25.3 ± 5.2 I | Isthmic spondylolisthesis n=6; foraminal stenosis n=3; Disc herniation n=6; degenerative disc disease n=7; canal stenosis n=1 | Isthmic spondylolisthesis n=4; foraminal stenosis n=2; Disc herniation n=7; degenerative disc disease n=9; canal stenosis n=3 | L4–5 (30%); L5–S1 (70%) | L4–5 (40%); L5–S1 (60%) |
| Liu et al. [15] 2015 | 29 (53) | 28 (56) | 40.8 ± 10.6 | 41.8 ± 10.4 | 25.8 ± 2.3 | 25.3 ± 4.2 | Lumbar spinal stenosis, lumbar disc herniation accompanied by lumbar spinal instability after 6 months of formal conservative treatment | L4–5 (63%); L5–S1 (37%) | L4–5 (56%); L5–S1 (44%) | |
| Lee et al. [14] 2017 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Table 3.
Summary of the definitions of fusion and subsidence rates used in the included studies, the follow-up period, and the modality used for assessment of fusion and subsidence
| Study | Fusion definition | Subsidence definition | Follow-up (mo) | Modality |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cuzzocrea et al. [12] 2019 | Fusion degrees described by Christensen et al. | - | 12 | CT |
| Wrangel et al. [27] 2017 | Bony bridging with at least 3 trabeculae was defined as a fused segment. Moreover, the fusion rate was additionally assessed by a fusion score that consisted of 3 parameters: bony bridging, in which at least 3 trabeculae are necessary for fusion (0 or 1 point); radiolucency of none, one, or both end plates (0–2 points); and finally transition in dynamic X-ray images (0–1 points). No fusion (0–1 points), semirigid pseudarthrosis (2 points), potential fusion (3 points), and fusion (4 points) were distinguished via this score | - | 33 | CT |
| Kashii et al. [13] 2019 | Achievement of fusion was determined to satisfy the 4 criteria as follows: (1) presence of continuous bone bridging across the disc space by CT, (2) absence of screw loosening assessed by CT, (3) absence of a radiolucent area around the cage assessed by functional radiograph and CT, and (4) angular change <3 degrees between the fused vertebrae on functional radiograph | - | 12 | Functional radiograph and CT |
| Schnake et al. [11] 2015 | - | - | 12 | X-ray and thin-sliced CT scans |
| Tanida et al. [19] 2016 | Bone union was defined according to the osseous continuity through and/or around the cage in both the sagittal and coronal CT-MPR images | - | 24 | CT-MPR |
| Vazifehdan et al. [20] 2019 | - | - | 50 | CT |
| Sakaura et al. [18] 2019 | Solid fusion was defined as the condition in which osseous continuity between the vertebrae and grafted bone was achieved on MPR-CT, with neither loosening of the PSs nor motion at the fused segments on lateral flex- ion-and-extension radiographs. Fusion status was graded as either union in situ (solid fusion without loss of graft height), collapsed union (solid fusion with ≥2-mm cage subsidence into the adjacent vertebral body), or nonunion according to the previously reported criteria | ≥2-mm cage subsidence into the adjacent vertebral body | 12 | CT, MPR-CT |
| Rickert et al. [17] 2017 | The presence of fusion was based on Bridwell et al.’s criteria which included presence or absence of bony bridging | Loss of disc space height of ≥1 mm with a visible fracture of the vertebral body endplate | 12 | Plain radiograph, CT |
| Nemoto et al. [16] 2014 | A solid fusion was defined as the presence of bridging bone within and around the cage both on the coronal and sagittal MPR CT images | If a cage was observed to sink into an adjacent vertebral body by ≥2 mm | 24 | MPR CT |
| Liu et al. [15] 2015 | - | - | 24 | CT |
| Lee et al. [14] 2017 | - | - | 12 | - |
REFERENCES
1. Ravindra VM, Senglaub SS, Rattani A, et al. Degenerative lumbar spine disease: estimating global incidence and worldwide volume. Global Spine J 2018 8:784-94.



2. Brox JI, Sørensen R, Friis A, et al. Randomized clinical trial of lumbar instrumented fusion and cognitive intervention and exercises in patients with chronic low back pain and disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2003 28:1913-21.


3. Fritzell P, Hägg O, Wessberg P. 2001 Volvo Award Winner in clinical studies: lumbar fusion versus nonsurgical treatment for chronic low back pain. Spine 2001 26:2521-4.


4. Hedlund R, Johansson C, Hägg O, et al. The long-term outcome of lumbar fusion in the Swedish lumbar spine study. Spine J 2016 16:579-87.


5. Yoshihara H, Yoneoka D. National trends in the surgical treatment for lumbar degenerative disc disease: United States, 2000 to 2009. Spine J 2015 15:265-71.


6. Norton RP, Bianco K, Klifto C, et al. Degenerative spondylolisthesis: an analysis of the nationwide inpatient sample database. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2015 40:1219-27.


7. Kuslich SD, Ulstrom CL, Griffith SL, et al. The Bagby and Kuslich method of lumbar interbody fusion. History, techniques, and 2-year follow-up results of a United States prospective, multicenter trial. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1998 23:1267-78.


8. Chou YC, Chen DC, Hsieh WA, et al. Efficacy of anterior cervical fusion: comparison of titanium cages, polyetheretherketone (PEEK) cages and autogenous bone grafts. J Clin Neurosci 2008 15:1240-5.


9. Chen Y, Wang X, Lu X, et al. Comparison of titanium and polyetheretherketone (PEEK) cages in the surgical treatment of multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy: a prospective, randomized, control study with over 7-year follow-up. Eur Spine J 2013 22:1539-46.




10. Kurtz SM, Devine JN. PEEK biomaterials in trauma, orthopedic, and spinal implants. Biomaterials 2007 28:4845-69.



12. Cuzzocrea F, Ivone A, Jannelli E, et al. PEEK versus metal cages in posterior lumbar interbody fusion: a clinical and radiological comparative study. Musculoskelet Surg 2019 103:237-41.



13. Kashii M, Kitaguchi K, Makino T, et al. Comparison in the same intervertebral space between titanium-coated and uncoated PEEK cages in lumbar interbody fusion surgery. J Orthop Sci 2019 Jul 30 [Epub]. pii: S0949-2658(19)30206-4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jos.2019.07.004.


14. Lee DY, Jeong ST, Hong CH, et al. Risk factors of cage subsidence after posterior lumbar interbody fusion. J Korean Soc Spine Surg 2016 23:100-7.

15. Liu R, Xiao R, Tang Z, et al. Titanium cage versus polyetheretherketone cage in posterior lumbar interbody fusion with pedicle screw fixation. Chin J Tissue Eng Res 2015 19:6953-7.
16. Nemoto O, Asazuma T, Yato Y, et al. Comparison of fusion rates following transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion using polyetheretherketone cages or titanium cages with transpedicular instrumentation. Eur Spine J 2014 23:2150-5.



17. Rickert M, Fleege C, Tarhan T, et al. Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion using polyetheretherketone oblique cages with and without a titanium coating: a randomised clinical pilot study. Bone Joint J 2017 99-B:1366-72.


18. Sakaura H, Ohnishi A, Yamagishi A, et al. Early fusion status after posterior lumbar interbody fusion with cortical bone trajectory screw fixation: a comparison of titanium-coated polyetheretherketone cages and carbon polyetheretherketone cages. Asian Spine J 2019 13:248-53.



19. Tanida S, Fujibayashi S, Otsuki B, et al. Vertebral endplate cyst as a predictor of nonunion after lumbar interbody fusion: comparison of titanium and polyetheretherketone cages. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2016 41:E1216-22.


20. Vazifehdan F, Karantzoulis VG, Igoumenou VG. Sagittal alignment assessment after short-segment lumbar fusion for degenerative disc disease. Int Orthop 2019 43:891-8.



21. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Int J Surg 2010 8:336-41.


22. Veritas Health Innovation. Covidence systematic review software. Melbourne (Australia): Veritas Health Innovation Melbourne; 2016.
23. Wells GA, Shea B, O’connell D, et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses [Internet] Ottawa (ON), Ottawa Hospital Research Institute. 2013 [cited 2020 Feb 5]. Available from: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp.
24. Duval S, Tweedie R. Trim and fill: a simple funnel-plot-based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics 2000 56:455-63.


25. Schwarzer G. meta: an R package for meta-analysis. R News 2007 7:40-5.
26. Viechtbauer W. Conducting meta-analyses in R with the metafor package. J Stat Softw 2010 36:1-48.
27. Wrangel CV, Karakoyun A, Buchholz KM, et al. Fusion rates of intervertebral polyetheretherketone and titanium cages without bone grafting in posterior interbody lumbar fusion surgery for degenerative lumbar instability. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg 2017 78:556-60.


28. EUROSPINE 2015 Copenhagen, Denmark, September 2-4: oral presentations. Eur Spine J 2015 24 Suppl 6:669-710.

29. Vilà Canet G, Isart Torruella A, Covaro A, et al. A comparative study to assess fusion rate differences between titanium and polyethereherketone (PEEK) cages in lumbar TLIF procedure. In: EUROSPINE 2014; 2014 Oct 1-3; Lyon, France. Uster-Zürich (Switzerland), EUROSPINE. 2014 Available from: http://eposterlyon.eurospine.org/cm_data/eposter/P14.PDF.
30. Lee DY, Park YJ, Song SY, et al. Risk factors for posterior cage migration after lumbar interbody fusion surgery. Asian Spine J 2018 12:59-68.




31. Aono H, Takenaka S, Nagamoto Y, et al. Fusion rate and clinical outcomes in two-level posterior lumbar interbody fusion. World Neurosurg 2018 112:e473-8.


32. McKissack HM, Levene HB. Does the cage position in transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion determine unilateral versus bilateral screw placement? A review of the literature. Asian Spine J 2019 13:325-33.



33. Han CM, Lee EJ, Kim HE, et al. The electron beam deposition of titanium on polyetheretherketone (PEEK) and the resulting enhanced biological properties. Biomaterials 2010 31:3465-70.


34. Yoon BJ, Xavier F, Walker BR, et al. Optimizing surface characteristics for cell adhesion and proliferation on titanium plasma spray coatings on polyetheretherketone. Spine J 2016 16:1238-43.


35. Rao PJ, Pelletier MH, Walsh WR, et al. Spine interbody implants: material selection and modification, functionalization and bioactivation of surfaces to improve osseointegration. Orthop Surg 2014 6:81-9.



36. Olivares-Navarrete R, Hyzy SL, Slosar PJ, et al. Implant materials generate different peri-implant inflammatory factors: poly-ether-ether-ketone promotes fibrosis and microtextured titanium promotes osteogenic factors. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2015 40:399-404.



37. McGilvray KC, Waldorff EI, Easley J, et al. Evaluation of a polyetheretherketone (PEEK) titanium composite interbody spacer in an ovine lumbar interbody fusion model: biomechanical, microcomputed tomographic, and histologic analyses. Spine J 2017 17:1907-16.


38. Niu CC, Liao JC, Chen WJ, et al. Outcomes of interbody fusion cages used in 1 and 2-levels anterior cervical discectomy and fusion: titanium cages versus polyetheretherketone (PEEK) cages. J Spinal Disord Tech 2010 23:310-6.


39. Peitgen DS, Innmann MM, Merle C, et al. Periprosthetic bone mineral density around uncemented titanium stems in the second and third decade after total hip arthroplasty: a DXA study after 12, 17 and 21 years. Calcif Tissue Int 2018 103:372-9.



40. Seaman S, Kerezoudis P, Bydon M, et al. Titanium vs. polyetheretherketone (PEEK) interbody fusion: meta-analysis and review of the literature. J Clin Neurosci 2017 44:23-9.


41. Chong E, Mobbs RJ, Pelletier MH, et al. Titanium/polyetheretherketone cages for cervical arthrodesis with degenerative and traumatic pathologies: early clinical outcomes and fusion rates. Orthop Surg 2016 8:19-26.



42. Yan DL, Pei FX, Li J, et al. Comparative study of PILF and TLIF treatment in adult degenerative spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J 2008 17:1311-6.




43. de Kunder SL, van Kuijk SMJ, Rijkers K, et al. Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) versus posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF) in lumbar spondylolisthesis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Spine J 2017 17:1712-21.


44. Høy K, Li H. Editorial on “Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion using polyetheretherketone oblique cages with and without a titanium coating: a randomised clinical pilot study”. J Spine Surg 2018 4:467-70.




- TOOLS
- Related articles in NS
-
Repeated Migration of a Fusion Cage after Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion2013 March;10(1)